Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Delving Deeper into Doppler Radar
- 3.2 First Alert Weather Radar: Beyond the Basic Doppler Effect
- 3.3 First Alert Weather Radar Features and Benefits
- 3.4 First Alert Weather Radar: Applications and Importance
- 3.5 First Alert Weather Radar: Limitations and Challenges
- 3.6 Related Searches:
- 3.7 FAQs about First Alert Weather Radar
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide
/do0bihdskp9dy.cloudfront.net/05-09-2021/t_88e73f7540724d929bf5a772535050bb_name_t_0f071c07792d4de2bfb07607430d70a4_name_file_1280x720_2000_v3_1_.jpg)
The term "First Alert Weather Radar" is often used in the context of weather forecasting, signifying an advanced system that provides early warnings about impending weather events. While the term itself is a trademark used by various media outlets, the technology behind it is rooted in the principles of Doppler radar.
Doppler radar utilizes the Doppler effect, a phenomenon where the frequency of waves (in this case, electromagnetic waves) changes as the source of the waves moves relative to an observer. This change in frequency allows meteorologists to determine the speed and direction of precipitation, wind, and other atmospheric phenomena.
Delving Deeper into Doppler Radar
Doppler radar works by emitting pulses of electromagnetic radiation towards the atmosphere. These pulses interact with raindrops, snowflakes, hail, and other particles in the air. When these particles move towards the radar, the reflected waves are compressed, resulting in a higher frequency. Conversely, when the particles move away from the radar, the reflected waves are stretched, resulting in a lower frequency.
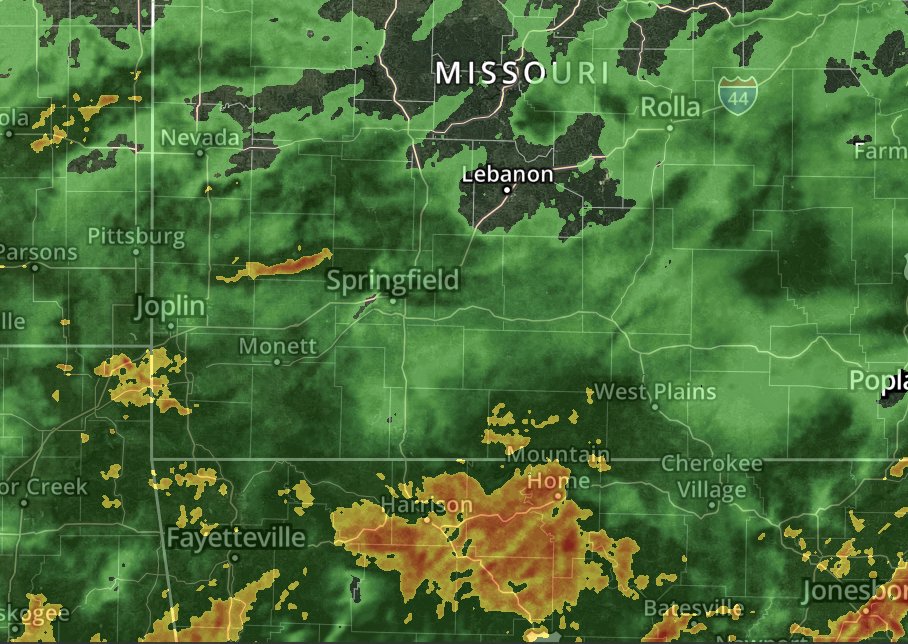
The difference between the emitted and received frequencies, known as the Doppler shift, is directly proportional to the speed of the target. This information is then processed and displayed on radar images, providing a visual representation of the movement and intensity of precipitation.
First Alert Weather Radar: Beyond the Basic Doppler Effect
While Doppler radar provides valuable insights into weather patterns, First Alert Weather Radar systems often incorporate additional technologies and data sources to enhance their capabilities. These advancements allow for more precise and detailed weather forecasts, ultimately contributing to better preparedness and safety.
First Alert Weather Radar Features and Benefits
Here are some of the key features and benefits commonly associated with First Alert Weather Radar systems:
- Enhanced Storm Tracking: These systems can track the movement of storms with greater accuracy, providing more precise information about their path, intensity, and potential impact.
- Early Warning Systems: By detecting the formation and movement of storms earlier, First Alert Weather Radar systems can trigger warnings and alerts, allowing people to prepare for potential dangers.
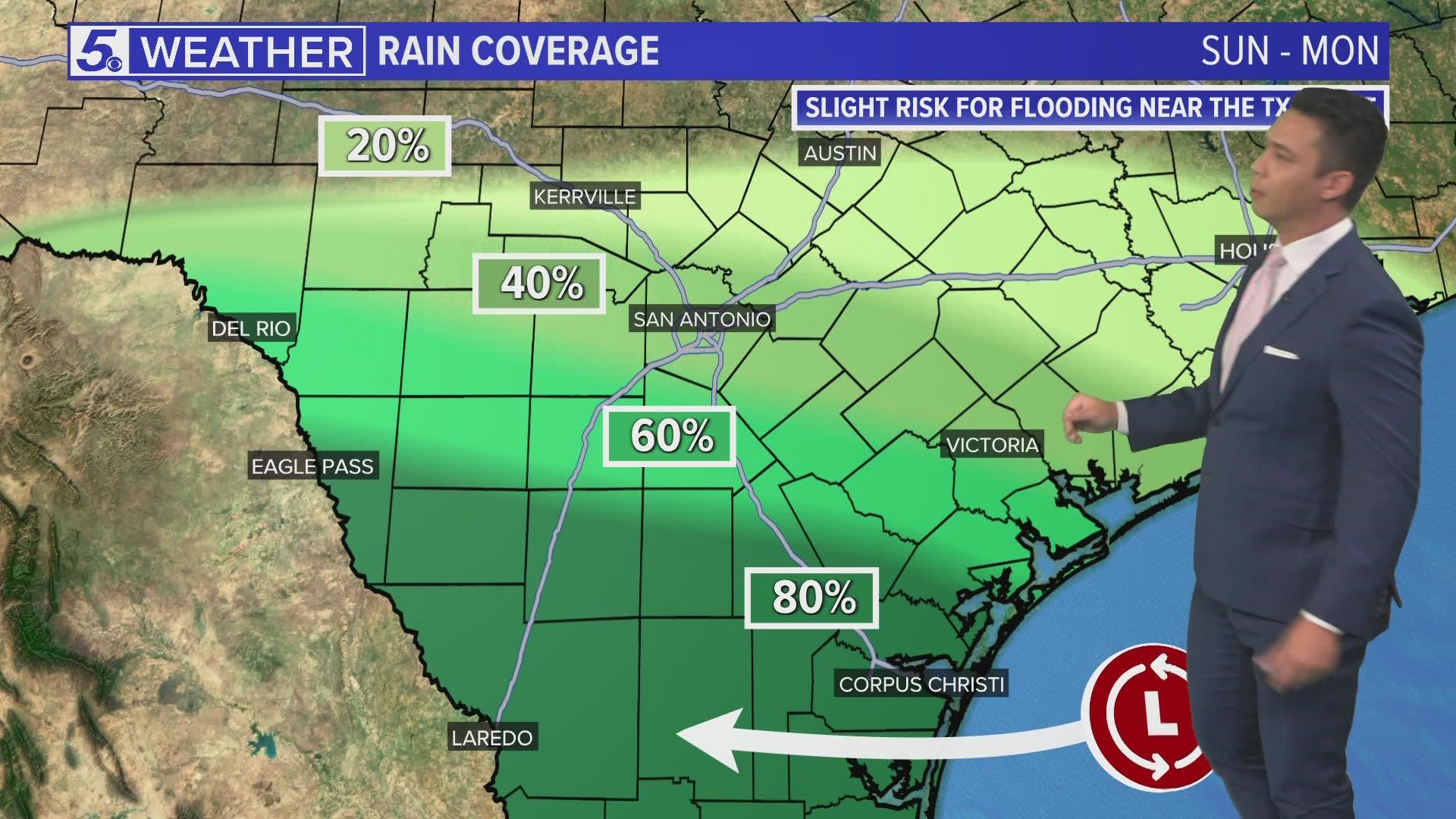
- Detailed Precipitation Information: These systems provide detailed information about the type, intensity, and location of precipitation, enabling more accurate rainfall forecasts and flood warnings.
- Wind Shear Detection: First Alert Weather Radar can detect changes in wind speed and direction, which is crucial for aviation safety and warning about potential hazards like tornadoes.
- Integration with Other Data Sources: These systems can integrate data from other sources, such as weather satellites, surface observations, and numerical weather models, to provide a comprehensive view of the weather situation.
First Alert Weather Radar: Applications and Importance
First Alert Weather Radar systems play a crucial role in various sectors:
- Public Safety: By providing timely and accurate weather information, these systems help emergency responders prepare for and manage weather-related emergencies, minimizing risks and potential damage.
- Transportation: First Alert Weather Radar information is essential for aviation, maritime, and road transportation, ensuring safe travel and minimizing disruptions caused by severe weather.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on First Alert Weather Radar data to make informed decisions about irrigation, planting, and harvesting, optimizing crop yields and minimizing weather-related losses.
- Energy: Power companies use First Alert Weather Radar data to anticipate and prepare for weather events that could impact power grids and distribution systems.
- Media and Public Awareness: News organizations and weather websites utilize First Alert Weather Radar data to provide timely and accurate weather updates to the public, fostering awareness and preparedness.
First Alert Weather Radar: Limitations and Challenges
Despite its numerous benefits, First Alert Weather Radar systems have limitations and challenges:
- Limited Coverage: The range of weather radar is limited by the curvature of the Earth and the strength of the radar signal. This can lead to gaps in coverage, especially in mountainous or remote areas.
- Interference: Weather radar signals can be interfered with by various sources, including buildings, trees, and other weather phenomena. This can lead to inaccuracies in the data.
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting weather radar data requires specialized skills and knowledge. Misinterpretation can lead to inaccurate forecasts and inappropriate warnings.
- Cost and Maintenance: First Alert Weather Radar systems are expensive to install and maintain, limiting their accessibility to smaller communities or developing countries.
Related Searches:
1. Doppler Radar Basics:
This search explores the fundamental principles of Doppler radar, including the Doppler effect, radar frequencies, and the technology behind radar signal processing. It delves into the history of Doppler radar development and its role in weather forecasting.
2. Weather Radar Interpretation:
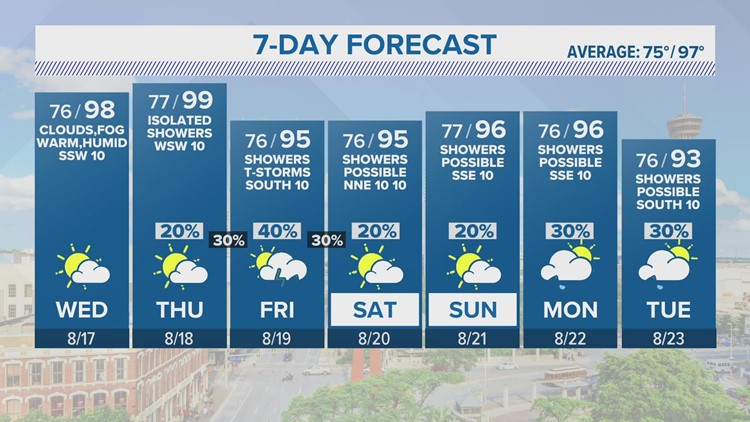
This search focuses on understanding and interpreting weather radar images. It covers topics like radar reflectivity, Doppler velocity, and the various patterns observed on radar screens. It also explores the use of radar data in weather forecasting and the challenges associated with data interpretation.
3. Weather Radar Networks:
This search delves into the structure and operation of national and regional weather radar networks. It examines the distribution of radar stations, data sharing protocols, and the role of these networks in providing comprehensive weather coverage.
4. Radar Meteorology:
This search explores the broader field of radar meteorology, covering the application of radar technology in various weather phenomena studies. It examines topics like precipitation measurement, wind profiling, and the use of radar data in climate research.
5. Weather Radar Applications:
This search explores the diverse applications of weather radar beyond traditional forecasting. It examines its use in aviation safety, flood monitoring, air quality assessment, and even wildlife tracking.
6. Future of Weather Radar:
This search delves into the latest advancements in weather radar technology, including the development of dual-polarization radar, phased array radar, and the integration of radar data with other atmospheric observations.
7. Weather Radar Safety:
This search explores the potential hazards associated with weather radar technology, including the impact on wildlife and the need for responsible radar operation. It also discusses the importance of radar safety protocols and regulations.
8. Weather Radar and Climate Change:
This search examines the role of weather radar in understanding and monitoring the impact of climate change on weather patterns. It explores the use of radar data in studying extreme weather events, precipitation trends, and the evolution of atmospheric processes.
FAQs about First Alert Weather Radar
1. What is the difference between Doppler radar and First Alert Weather Radar?
While the term "First Alert Weather Radar" is a marketing term, it generally refers to Doppler radar systems that incorporate advanced features and data sources. These systems can provide more detailed and accurate information about weather patterns, allowing for earlier warnings and better preparedness.
2. How does First Alert Weather Radar help predict tornadoes?
First Alert Weather Radar can detect the formation of mesocyclones, rotating columns of air that are often associated with tornadoes. By tracking the movement and intensity of these mesocyclones, meteorologists can issue warnings about potential tornado threats.
3. Is First Alert Weather Radar accurate?
While First Alert Weather Radar provides valuable information about weather patterns, it’s important to remember that all weather forecasts are subject to a degree of uncertainty. The accuracy of First Alert Weather Radar depends on various factors, including the quality of the radar data, the complexity of the weather system, and the skill of the meteorologists interpreting the data.
4. How often is First Alert Weather Radar updated?
First Alert Weather Radar data is typically updated every few minutes, allowing for real-time tracking of weather conditions. This frequent updating is essential for providing timely warnings and alerts about changing weather patterns.
5. What are some tips for using First Alert Weather Radar information?
- Pay attention to warnings and alerts: When you see a severe weather warning on your weather app or local news, take it seriously and take appropriate precautions.
- Understand the different types of weather alerts: Know the difference between a watch, a warning, and an advisory, and respond accordingly.
- Check the radar frequently: Keep an eye on the radar to track the movement of storms and stay informed about changing conditions.
- Have a plan in place: Develop a plan for what you will do if severe weather threatens your area, including where you will go and what you will do to stay safe.
Conclusion
First Alert Weather Radar systems, built upon the principles of Doppler radar, play a vital role in modern weather forecasting and public safety. By providing detailed and timely information about weather patterns, these systems empower individuals, communities, and organizations to prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with severe weather events. While limitations and challenges exist, continuous advancements in radar technology and data analysis techniques are constantly improving the accuracy and effectiveness of these systems, ensuring a safer and more informed future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Science Behind First Alert Weather Radar: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
