Understanding Voice Disorders: A Comprehensive Look at Kerry Kennedy’s Condition
Related Articles: Understanding Voice Disorders: A Comprehensive Look at Kerry Kennedy’s Condition
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Voice Disorders: A Comprehensive Look at Kerry Kennedy’s Condition. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Voice Disorders: A Comprehensive Look at Kerry Kennedy’s Condition

The public spotlight often shines on the personal lives of prominent individuals, and in the case of Kerry Kennedy, a prominent figure in the Kennedy family, a medical condition has drawn attention. While specifics about her diagnosis remain private, discussions surrounding her condition have sparked interest in voice disorders. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of voice disorders, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, without referring to any specific individual.
Voice Disorders: A Complex Spectrum
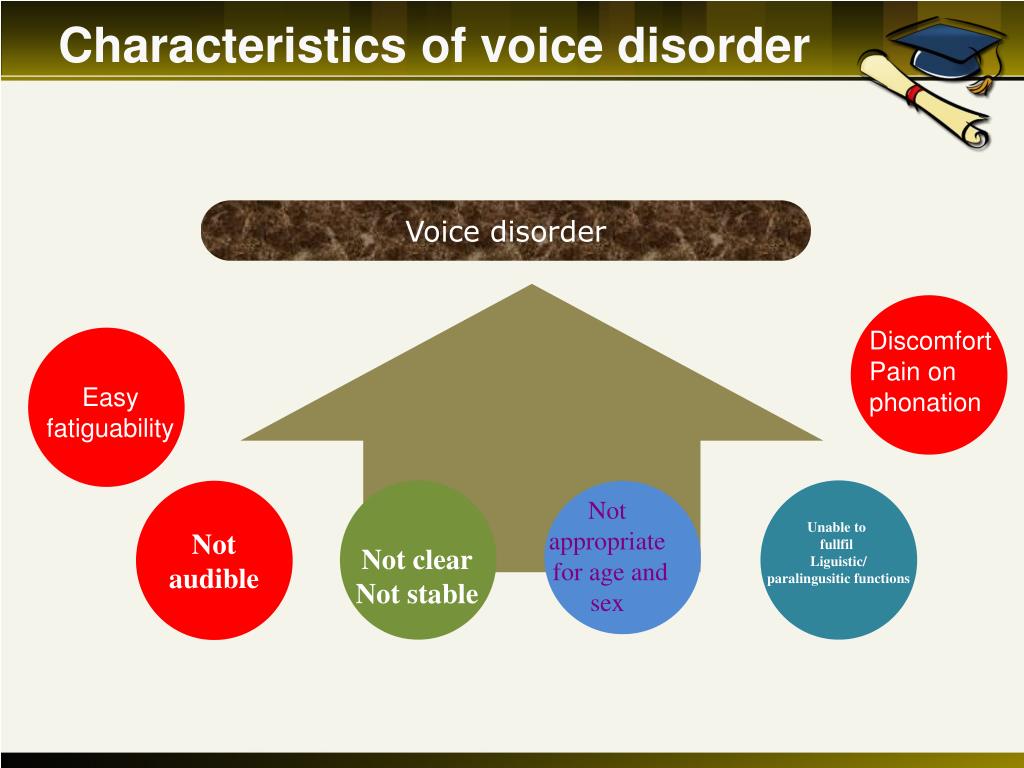
A voice disorder is a condition that affects the quality, pitch, loudness, or overall functionality of the voice. These disorders can range from mild, temporary issues to severe, debilitating conditions that significantly impact an individual’s ability to communicate effectively.
Causes of Voice Disorders
The underlying causes of voice disorders are diverse and can be categorized into several groups:
- Vocal Abuse and Misuse: This is the most common cause of voice disorders. Excessive yelling, singing, or talking, particularly without proper technique, can strain the vocal cords, leading to inflammation, nodules, or polyps.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as allergies, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), thyroid disorders, and neurological disorders, can affect the voice.
- Structural Abnormalities: Physical abnormalities in the vocal cords, larynx, or surrounding structures, such as vocal cord paralysis, tumors, or cysts, can disrupt vocal function.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and emotional distress can contribute to voice disorders, often manifesting as vocal cord tension or spasms.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to irritants such as smoke, dust, or chemicals can damage the vocal cords, leading to voice problems.
Symptoms of Voice Disorders
The symptoms of voice disorders vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Hoarseness or raspy voice: This is the most common symptom, often described as a rough or scratchy voice.
- Loss of vocal range: Difficulty reaching high or low notes, resulting in a limited vocal range.
- Vocal fatigue: Experiencing tiredness or strain in the voice after minimal talking.
- Pain or discomfort: Discomfort or pain in the throat or neck when speaking.
- Breathy voice: A soft, airy voice that lacks projection.
- Strained or effortful voice: Speaking with noticeable tension or effort.
- Loss of voice: Complete or partial loss of the ability to speak.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing a voice disorder requires a thorough evaluation by a qualified medical professional, typically an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat doctor) or a speech-language pathologist. The evaluation usually involves:
- Medical history: The doctor will inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any relevant conditions or medications.
- Physical examination: The doctor will examine the head, neck, and vocal cords using a laryngeal mirror or flexible laryngoscope.
- Voice assessment: The patient will be asked to perform various vocal tasks, such as reading aloud, counting, and sustained phonation, to assess the quality, pitch, and loudness of their voice.
- Imaging studies: In some cases, imaging studies, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be ordered to visualize the vocal cords and surrounding structures.
Treatment Options for Voice Disorders
Treatment for voice disorders depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Voice therapy: Speech-language pathologists provide voice therapy to teach proper vocal techniques, improve vocal hygiene, and address voice misuse or abuse.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to address underlying medical conditions or to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural abnormalities or remove growths on the vocal cords.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding vocal strain, managing stress, and quitting smoking can help prevent further damage to the vocal cords.
Related Searches
The information provided above is a starting point for understanding voice disorders. Let’s explore some related searches that delve deeper into specific aspects of voice disorders:
1. Vocal Cord Paralysis
Vocal cord paralysis occurs when one or both vocal cords become paralyzed due to nerve damage. This can result in a variety of voice problems, including hoarseness, breathiness, and difficulty speaking. Treatment options may include voice therapy, surgery, or injection of a substance into the paralyzed vocal cord to improve its position.
2. Vocal Cord Nodules
Vocal cord nodules are small, benign growths that develop on the vocal cords due to vocal abuse or misuse. They can cause hoarseness, vocal fatigue, and difficulty reaching high notes. Treatment often involves voice therapy to modify vocal habits and reduce strain on the vocal cords. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the nodules.
3. Vocal Cord Polyps
Vocal cord polyps are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the vocal cords, similar to nodules. They can cause hoarseness, breathiness, and vocal fatigue. Treatment typically involves voice therapy and, in some cases, surgery to remove the polyp.
4. Laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx, or voice box. It can cause hoarseness, a sore throat, and difficulty speaking. Laryngitis is often caused by a viral infection, but it can also be caused by allergies, smoking, or vocal abuse. Treatment usually involves rest, hydration, and avoiding irritants.
5. Spasmodic Dysphonia
Spasmodic dysphonia is a neurological disorder that causes involuntary spasms of the vocal cords, resulting in a strained, choked, or breathy voice. Treatment options include voice therapy, medications, and, in some cases, Botox injections into the vocal cords to reduce muscle spasms.
6. Voice Disorders in Children
Voice disorders can also occur in children, often due to vocal abuse, misuse, or underlying medical conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term voice problems.
7. Voice Disorders in Singers
Singers are particularly susceptible to voice disorders due to the demands of their profession. Proper vocal technique, vocal hygiene, and regular vocal rest are essential for preventing voice problems.
8. Voice Disorders in Teachers
Teachers also face a high risk of developing voice disorders due to the amount of time they spend speaking. Strategies for reducing vocal strain, such as using a microphone and taking regular breaks, can help prevent voice problems.
FAQs About Voice Disorders
1. Are voice disorders contagious?
Voice disorders are not contagious, except in cases of laryngitis, which can be caused by a viral infection.
2. Can voice disorders be prevented?
While not all voice disorders can be prevented, taking steps to reduce vocal abuse and misuse, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding environmental irritants can significantly lower the risk.
3. How long does it take to recover from a voice disorder?
Recovery time for voice disorders varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some disorders may resolve quickly with treatment, while others may require ongoing management.
4. Can voice disorders be cured?
The ability to cure a voice disorder depends on the underlying cause. Some disorders, such as vocal cord nodules, can be cured with treatment, while others, such as vocal cord paralysis, may require ongoing management.
5. What should I do if I suspect I have a voice disorder?
If you experience any persistent voice problems, it is essential to consult a qualified medical professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Tips for Managing Voice Disorders
- Avoid vocal abuse: Limit yelling, screaming, and excessive talking.
- Use proper vocal technique: Learn and practice proper breathing and voice production techniques.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your vocal cords lubricated.
- Avoid irritants: Avoid smoking, secondhand smoke, and exposure to dust, fumes, and other irritants.
- Manage stress: Stress can contribute to vocal tension, so find healthy ways to manage stress.
- Get regular vocal rest: Take breaks from talking, especially when your voice is tired.
- Seek professional help: Consult a speech-language pathologist or otolaryngologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Voice disorders can significantly impact an individual’s ability to communicate effectively. Understanding the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. By taking preventive measures, seeking early intervention, and adhering to treatment recommendations, individuals can improve their vocal health and maintain clear communication. Remember, while the specifics of a public figure’s medical condition may remain private, the information provided here offers valuable insights into the complex world of voice disorders and the importance of seeking professional help when needed.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Voice Disorders: A Comprehensive Look at Kerry Kennedy’s Condition. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!