Understanding the Power of Weather Forecasting: A Deep Dive into Hurricane Beryl (2000)
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Weather Forecasting: A Deep Dive into Hurricane Beryl (2000)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Weather Forecasting: A Deep Dive into Hurricane Beryl (2000). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Weather Forecasting: A Deep Dive into Hurricane Beryl (2000)

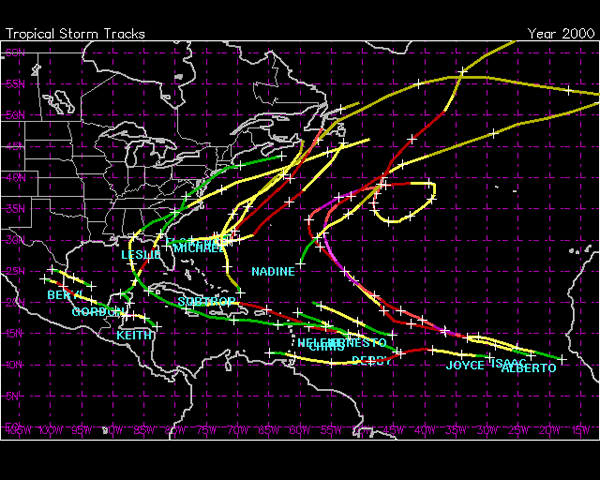
The Atlantic hurricane season of 2000 saw its fair share of storms, with a total of 12 named storms, 8 of which reached hurricane strength. Among these, Hurricane Beryl stands out as a significant event, showcasing the complexities and potential dangers of tropical cyclones. Understanding Beryl’s trajectory and impact provides valuable insights into the science of weather forecasting and the importance of preparedness in the face of such natural disasters.
A Comprehensive Look at Hurricane Beryl:
Beryl’s Formation and Development:
Beryl formed on June 28, 2000, as a tropical depression over the eastern Atlantic. The system quickly intensified, becoming a tropical storm later that day. Favorable conditions, including warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear, fueled its rapid development. By June 29, Beryl reached hurricane status, marking the first hurricane of the 2000 season.
Beryl’s Path and Intensity:
Beryl initially moved westward, but its path became more erratic as it encountered a complex interplay of atmospheric forces. It weakened slightly as it moved over cooler waters but regained intensity as it re-entered warmer areas. Beryl reached its peak intensity on July 2, 2000, with maximum sustained winds of 100 miles per hour (mph), making it a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Beryl’s Impact:
While Beryl did not make landfall, it caused significant impacts on the Lesser Antilles and the Caribbean Sea. Its strong winds and heavy rains generated rough seas and coastal flooding, leading to property damage and disruption of life.
The Importance of Storm Tracking:
Beryl’s journey highlights the crucial role of accurate storm tracking and forecasting. Meteorological agencies, using advanced weather models and satellite imagery, monitor the development and movement of tropical cyclones. This information is vital for issuing timely warnings to vulnerable populations, allowing for preparedness and minimizing the potential for loss of life and property damage.
Related Searches & Expanding Insights:
1. Hurricane Beryl Path:
Beryl’s path was initially westward but became increasingly complex as it encountered various atmospheric conditions. Tracking its meandering trajectory allows for a better understanding of the factors that influence hurricane movement, including the steering currents and high-altitude winds.
2. Hurricane Beryl Wind Speed:
Beryl reached a maximum sustained wind speed of 100 mph, making it a Category 2 hurricane. This information is critical for understanding the potential destructive power of the storm and for issuing appropriate warnings to coastal communities.
3. Hurricane Beryl Rainfall:
Beryl’s heavy rainfall caused significant flooding in the Lesser Antilles and the Caribbean Sea. Studying the rainfall patterns associated with Beryl helps meteorologists better predict the potential for flooding and develop more effective flood mitigation strategies.
4. Hurricane Beryl Damage:
Beryl’s strong winds and heavy rains resulted in property damage and disruption of life in the Caribbean. Analyzing the extent of damage caused by Beryl provides valuable data for assessing the economic and social impacts of hurricanes and informing future disaster preparedness plans.
5. Hurricane Beryl Formation:
Beryl’s formation was influenced by favorable conditions, including warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear. Understanding the factors that contribute to hurricane formation is crucial for developing accurate forecasts and issuing timely warnings.
6. Hurricane Beryl Track:
Tracking Beryl’s path allows for a better understanding of the forces that influence hurricane movement and helps predict future hurricane tracks. This information is essential for preparing vulnerable populations and minimizing the potential for loss of life and property damage.
7. Hurricane Beryl Forecast:
Forecasting Beryl’s intensity and track is a complex process involving advanced weather models and satellite imagery. Studying the accuracy of Beryl’s forecast helps refine forecasting techniques and improve the reliability of future hurricane predictions.
8. Hurricane Beryl History:
Examining Beryl’s history provides valuable insights into the historical patterns of hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin. This information is essential for understanding long-term trends in hurricane frequency and intensity, informing climate change research and disaster preparedness efforts.
FAQs About Hurricane Beryl:
1. What was the strongest intensity reached by Hurricane Beryl?
Beryl reached its peak intensity on July 2, 2000, as a Category 2 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 100 mph.
2. Did Hurricane Beryl make landfall?
No, Beryl did not make landfall. It primarily impacted the Lesser Antilles and the Caribbean Sea.
3. What were the main impacts of Hurricane Beryl?
Beryl’s strong winds and heavy rains caused rough seas, coastal flooding, property damage, and disruption of life in the Caribbean.
4. How was Hurricane Beryl tracked?
Meteorological agencies used advanced weather models, satellite imagery, and reconnaissance aircraft to track Beryl’s development and movement.
5. What lessons can be learned from Hurricane Beryl?
Beryl highlights the importance of accurate storm tracking, timely warnings, and preparedness in the face of hurricane threats. It also underscores the need for continued research and improvements in hurricane forecasting.
Tips for Preparing for Hurricanes:
1. Develop a Hurricane Plan:
Create a plan for your family, including evacuation routes, communication methods, and emergency supplies.
2. Stay Informed:
Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reputable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
3. Secure Your Home:
Board up windows, trim trees, and secure loose objects to minimize damage from high winds.
4. Prepare an Emergency Kit:
Gather essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid kit, batteries, and a battery-powered radio.
5. Know Your Evacuation Zone:
Familiarize yourself with your local evacuation zones and routes to ensure a safe evacuation if necessary.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Beryl serves as a reminder of the unpredictable nature of tropical cyclones and the vital role of weather forecasting in protecting lives and property. By studying Beryl’s trajectory, impact, and the lessons learned, we can enhance our understanding of hurricane dynamics, improve forecasting accuracy, and strengthen preparedness efforts to mitigate the risks associated with these powerful storms. The continuous advancement of meteorological technology and the commitment to research and preparedness remain crucial for ensuring the safety and resilience of communities facing the threat of hurricanes.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Weather Forecasting: A Deep Dive into Hurricane Beryl (2000). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!