Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes
- 3.1 Storms: A Symphony of Wind, Water, and Weather
- 3.2 Earthquakes: The Earth’s Internal Tremors
- 3.3 Related Searches:
- 3.4 FAQs:
- 3.5 Tips:
- 3.6 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes
The Earth is a dynamic planet, constantly in motion and subject to powerful forces that shape its landscapes and influence life on its surface. Two of the most dramatic and potentially destructive of these forces are storms and earthquakes. While distinct in their origins and manifestations, both storms and earthquakes demonstrate the raw power of nature and highlight the importance of understanding and preparing for their impacts.
Storms: A Symphony of Wind, Water, and Weather
Storms are atmospheric disturbances characterized by strong winds, heavy precipitation, and often lightning. They can range in scale from localized thunderstorms to vast, destructive hurricanes. The formation of a storm is a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions, including:
- Temperature differences: Warm, moist air rises, creating instability in the atmosphere.
- Moisture: Abundant moisture in the air fuels the formation of clouds and precipitation.
- Wind patterns: Winds converge and lift air upward, intensifying the storm.
- Rotation: The Earth’s rotation influences the direction and intensity of storms, particularly in the case of hurricanes.
Storms can be classified based on their intensity and characteristics. Some common types include:
- Thunderstorms: These are localized storms with strong winds, heavy rainfall, and lightning. They form rapidly and can dissipate quickly.
- Hurricanes: These are powerful, rotating storms that form over warm ocean waters. They are characterized by sustained high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
- Tornadoes: These are violently rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm cloud to the ground. They are known for their destructive power and rapid movement.
- Blizzards: These are intense winter storms characterized by heavy snowfall, strong winds, and low visibility. They can lead to significant disruptions to travel and daily life.
Storms can have significant impacts on human society, including:
- Property damage: Strong winds, heavy rains, and flooding can damage buildings, infrastructure, and crops.
- Injuries and fatalities: High winds, flying debris, and flooding can cause injuries and loss of life.
- Disruptions to power and transportation: Storms can damage power lines and disrupt transportation networks, leading to widespread outages and delays.
- Economic losses: Storms can cause significant economic losses due to property damage, business closures, and disruptions to supply chains.
Earthquakes: The Earth’s Internal Tremors
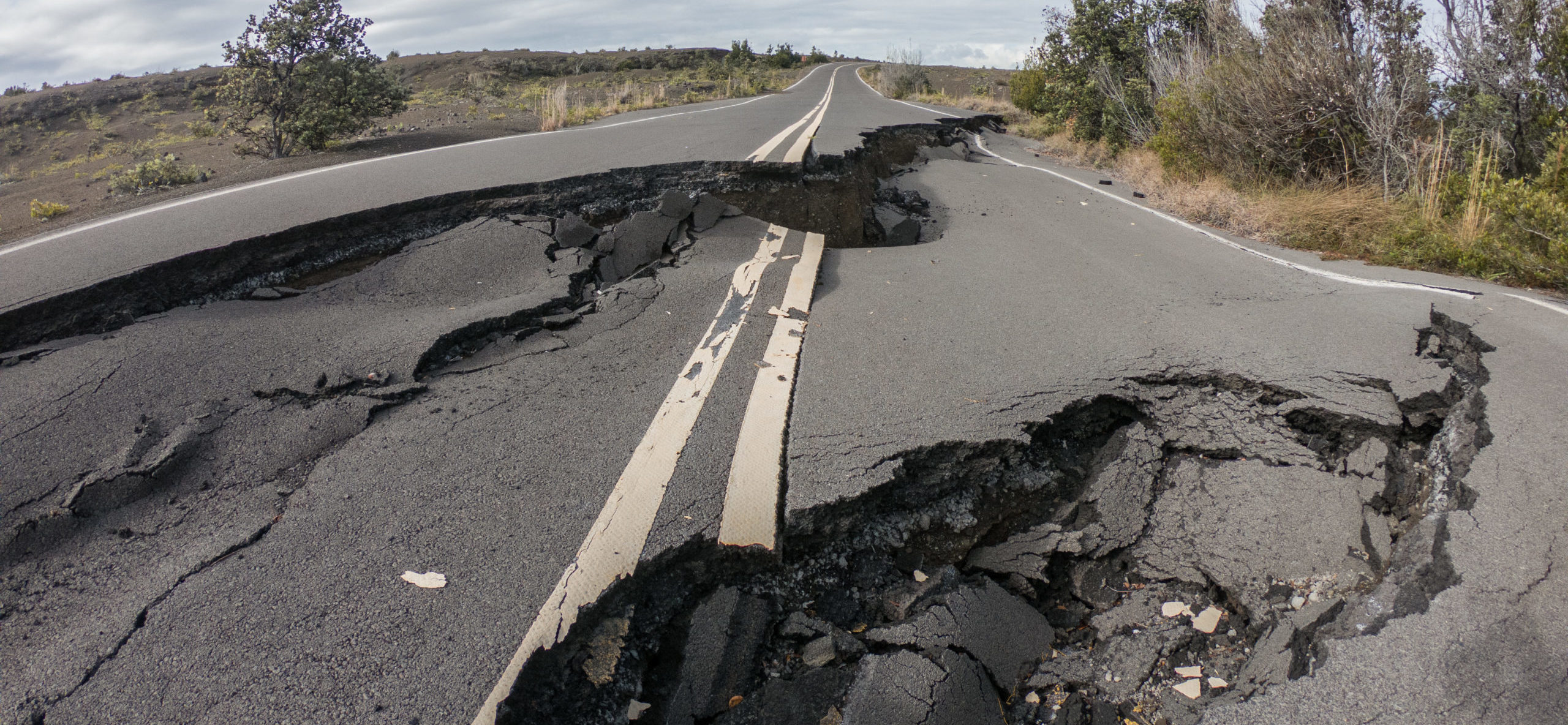
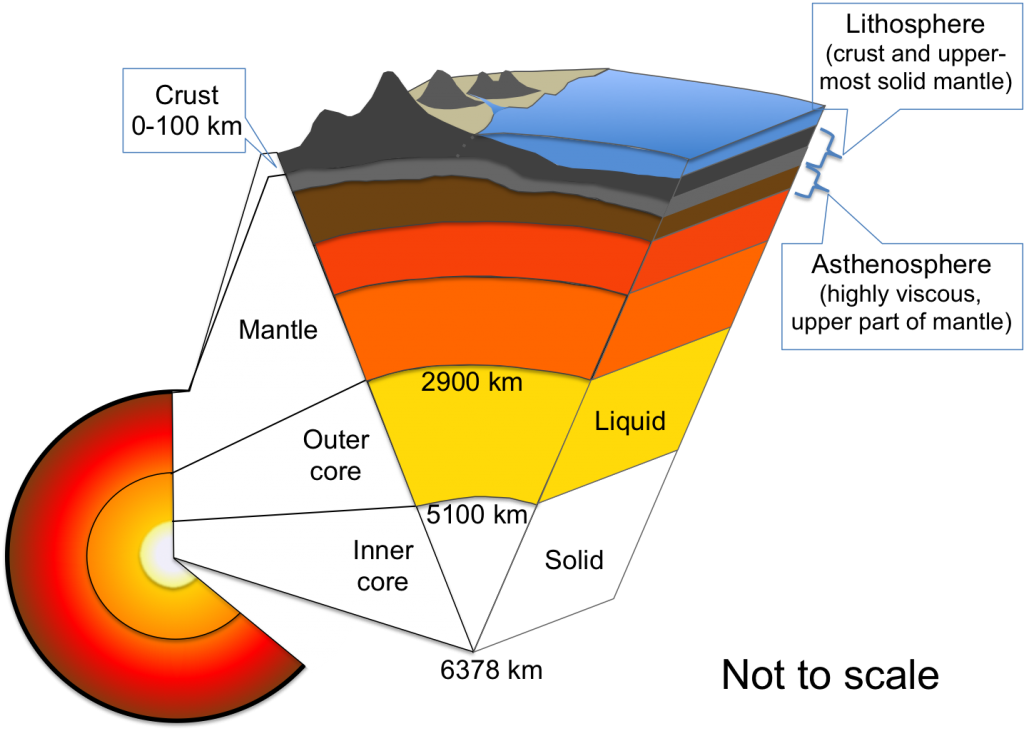
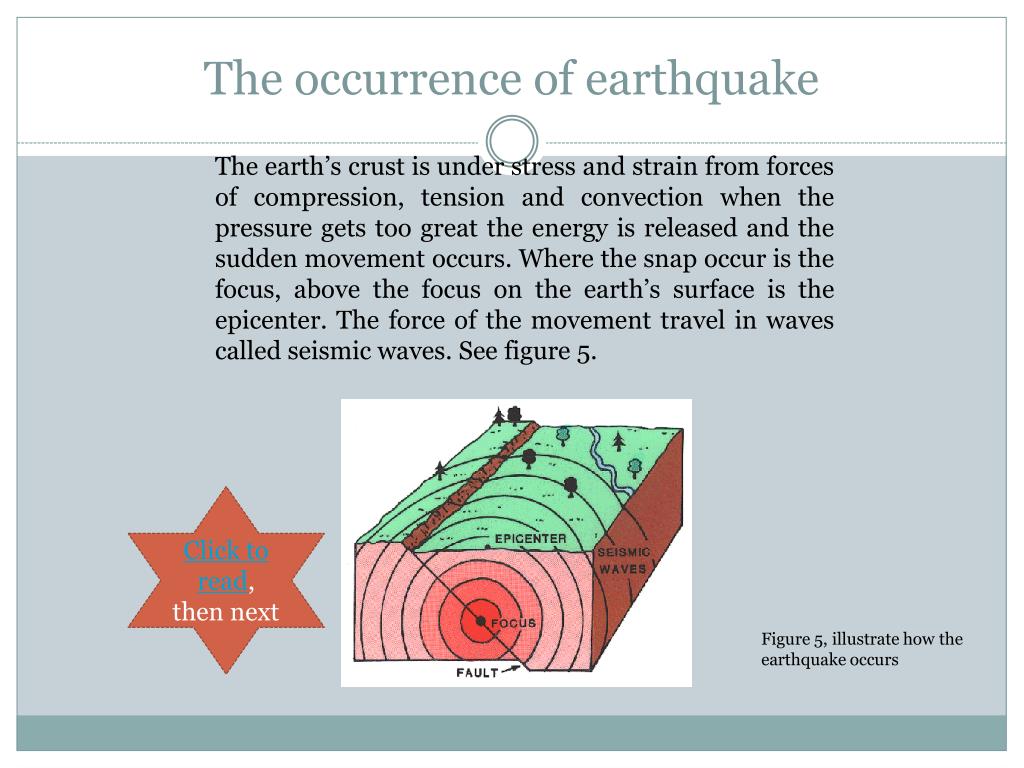
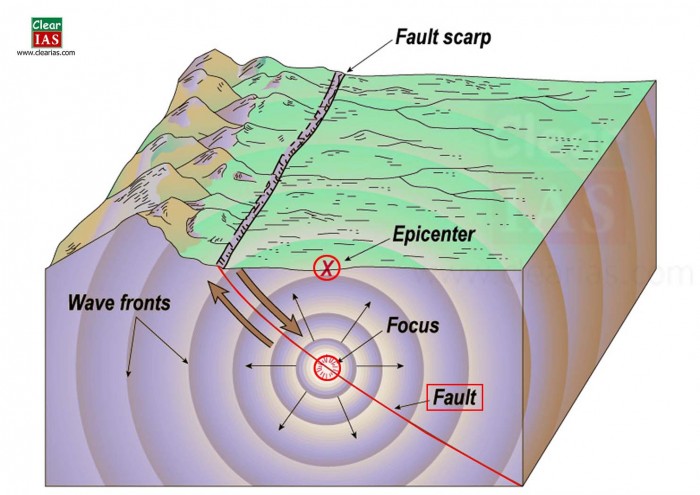
Earthquakes are sudden releases of energy in the Earth’s crust, caused by the movement of tectonic plates. These plates are constantly shifting and colliding, creating stress along fault lines. When the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, they rupture, releasing energy in the form of seismic waves.
Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale, which is a logarithmic scale that measures the magnitude of the earthquake. Each increase of one unit on the Richter scale represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of the seismic waves.
The location where the earthquake originates is called the epicenter, and the point beneath the Earth’s surface where the rupture begins is called the hypocenter or focus. Earthquakes can cause a range of effects, including:
- Ground shaking: This is the most common effect of an earthquake, and it can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Tsunamis: These are giant waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. They can travel thousands of miles and cause widespread destruction when they reach coastal areas.
- Landslides: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, which can bury homes, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Liquefaction: This occurs when the ground becomes saturated with water, causing it to behave like a liquid. Liquefaction can cause buildings to collapse and roads to buckle.
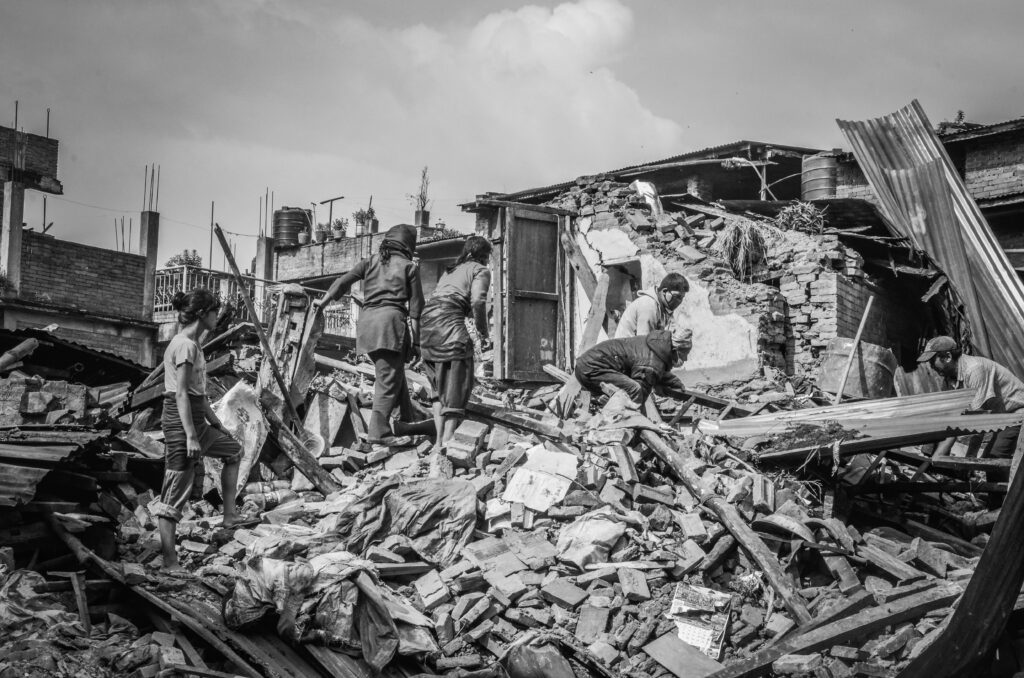
Earthquakes can have devastating consequences for human society, including:
- Loss of life: Earthquakes are often responsible for thousands of deaths, particularly in densely populated areas.
- Property damage: Ground shaking, tsunamis, and landslides can cause widespread damage to buildings, infrastructure, and property.
- Economic losses: Earthquakes can cause significant economic losses due to property damage, business closures, and disruptions to supply chains.
- Psychological trauma: Earthquakes can have a profound psychological impact on survivors, leading to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Related Searches:
Storms:
- Hurricane preparedness: This search focuses on preparing for the potential impact of hurricanes, including creating emergency plans, securing homes, and stocking up on supplies.
- Tornado warning systems: This search explores the various warning systems in place to alert people about approaching tornadoes, including weather radars, sirens, and mobile alerts.
- Storm surge forecasting: This search delves into the science behind storm surge prediction, which is crucial for understanding the potential flooding risks associated with hurricanes and other storms.
- Climate change and storms: This search investigates the potential impact of climate change on storm frequency and intensity, highlighting the growing threat of extreme weather events.
- Storm damage insurance: This search focuses on the various insurance options available to protect against storm damage, including homeowner’s insurance, flood insurance, and wind insurance.
- Storm recovery efforts: This search explores the various efforts undertaken to rebuild and recover from storm damage, including government assistance, community support, and infrastructure restoration.
- Storm safety tips: This search provides practical advice on staying safe during storms, including seeking shelter, avoiding flooded areas, and being aware of potential hazards.
- Storm tracking websites: This search directs users to reliable websites that provide real-time storm tracking information, including weather maps, satellite imagery, and radar data.
Earthquakes:
- Earthquake prediction: This search explores the ongoing research and efforts to predict earthquakes, highlighting the challenges and limitations of current technology.
- Earthquake-resistant buildings: This search examines the design and construction techniques used to build structures that can withstand the forces of an earthquake, including reinforced concrete, seismic isolation, and flexible framing.
- Earthquake early warning systems: This search focuses on the development and implementation of early warning systems that can detect earthquakes and provide seconds to minutes of warning before the shaking begins.
- Earthquake preparedness kits: This search provides guidance on assembling emergency kits that can help people survive and cope with the aftermath of an earthquake, including food, water, first aid supplies, and communication tools.
- Earthquake history: This search explores the historical record of earthquakes, including significant events, their impact on human civilizations, and the scientific understanding of earthquake patterns.
- Earthquake safety tips: This search provides practical advice on staying safe during an earthquake, including drop, cover, and hold on, avoiding windows and heavy objects, and being prepared to evacuate.
- Earthquake fault lines: This search investigates the location and characteristics of major fault lines around the world, highlighting the areas most vulnerable to earthquakes.
- Earthquake research organizations: This search identifies key organizations involved in earthquake research, monitoring, and preparedness, including government agencies, academic institutions, and non-profit organizations.
FAQs:
Storms:
- What is the difference between a hurricane and a typhoon? Hurricanes and typhoons are essentially the same type of storm, but the term "hurricane" is used in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific, while "typhoon" is used in the western Pacific.
- How can I stay safe during a thunderstorm? During a thunderstorm, seek shelter indoors or in a hard-top vehicle. Avoid open fields, water, and tall trees.
- What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale? The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale classifies hurricanes based on their sustained wind speed, ranging from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (157 mph or higher).
- What is a storm surge? A storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the strong winds of a hurricane or other storms. It can cause significant flooding in coastal areas.
- How can I prepare for a hurricane? Hurricane preparedness involves creating an emergency plan, securing your home, stocking up on supplies, and staying informed about weather forecasts and warnings.
Earthquakes:
- What is the difference between an earthquake’s magnitude and intensity? Magnitude refers to the amount of energy released by an earthquake, while intensity measures the effects of the earthquake at a particular location.
- How do earthquakes cause tsunamis? Tsunamis are generated by underwater earthquakes that displace large volumes of water, creating giant waves.
- What is the difference between a fault and an epicenter? A fault is a fracture in the Earth’s crust where rocks move past each other, while the epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake.
- What is the difference between a foreshock and an aftershock? A foreshock is an earthquake that precedes a larger earthquake, while an aftershock is an earthquake that follows a larger earthquake.
- How can I prepare for an earthquake? Earthquake preparedness involves creating an emergency plan, securing your home, stocking up on supplies, and knowing how to stay safe during an earthquake.
Tips:
Storms:
- Stay informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources, such as the National Weather Service.
- Create an emergency plan: Develop a plan for your family that includes evacuation routes, communication procedures, and meeting points.
- Secure your home: Trim trees, secure loose objects, and board up windows to minimize damage from strong winds.
- Stock up on supplies: Keep a supply of food, water, first aid supplies, batteries, and other essentials on hand.
- Stay safe during a storm: Seek shelter indoors or in a hard-top vehicle, avoid flooded areas, and be aware of potential hazards like downed power lines.
Earthquakes:
- Secure your home: Secure heavy objects, install earthquake-resistant bolts, and make sure your water heater is properly secured.
- Create an emergency plan: Develop a plan for your family that includes evacuation routes, communication procedures, and meeting points.
- Stock up on supplies: Keep a supply of food, water, first aid supplies, batteries, and other essentials on hand.
- Learn earthquake safety tips: Practice drop, cover, and hold on, and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
- Stay informed: Learn about the earthquake risks in your area and stay informed about potential threats.
Conclusion:
Storms and earthquakes are natural phenomena that can have devastating consequences for human society. Understanding the science behind these events, preparing for their potential impacts, and learning how to stay safe during these events is crucial for minimizing their risks. By taking proactive steps to prepare and respond to storms and earthquakes, we can reduce the damage they cause and protect ourselves and our communities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Nature: Storms and Earthquakes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
