Understanding the Impact of Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Impact of Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Impact of Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Impact of Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide

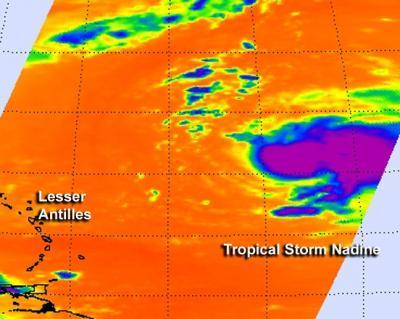
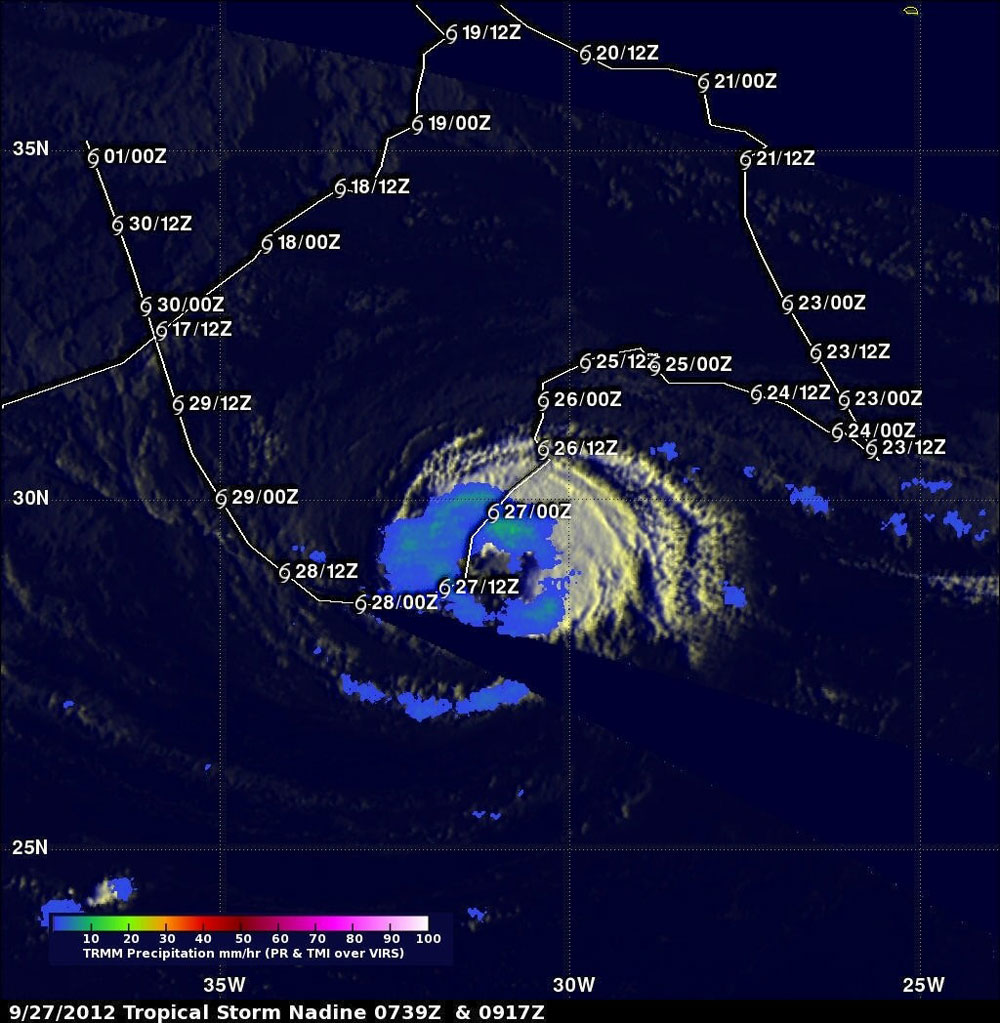
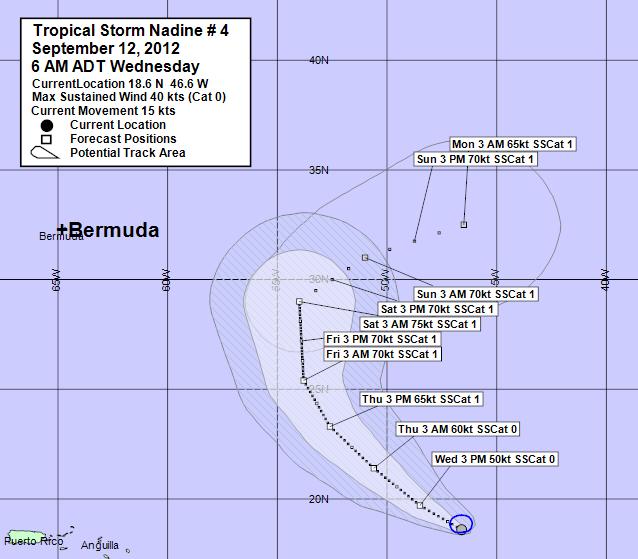
The Nadine storm, a significant meteorological event, has left an indelible mark on various aspects of life, from natural environments to human societies. Understanding the Nadine storm’s impact requires delving into its various facets, including its origins, characteristics, and consequences. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Nadine storm, exploring its impact on various domains, addressing frequently asked questions, and offering insightful tips for preparedness and mitigation.
The Genesis of the Nadine Storm
Nadine, a tropical cyclone, originated in the vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean, where warm ocean waters and favorable atmospheric conditions coalesce to create the perfect breeding ground for such storms. The storm’s formation can be attributed to a complex interplay of meteorological factors, including:
- Warm Ocean Waters: Tropical cyclones thrive on warm ocean waters, typically exceeding 26.5°C (80°F). These warm waters provide the necessary heat and moisture for the storm to intensify.
- Low-Level Wind Shear: Low wind shear, a condition where winds at different altitudes vary minimally, allows the storm to organize and strengthen.
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation deflects moving air masses, influencing the storm’s path and direction.
Characteristics of the Nadine Storm
The Nadine storm, like all tropical cyclones, exhibited distinct characteristics:
- Strong Winds: The storm’s most prominent feature was its high wind speeds, capable of causing significant damage to infrastructure and vegetation.
- Heavy Rainfall: Nadine unleashed torrential rainfall, resulting in widespread flooding and landslides.
- Storm Surge: The storm’s powerful winds pushed seawater towards coastlines, causing destructive storm surges that inundated coastal areas.
Impact of the Nadine Storm
The Nadine storm’s impact extended far beyond its immediate path, affecting various aspects of life:
- Environmental Impact: The storm’s strong winds and heavy rainfall significantly impacted ecosystems, causing damage to forests, coastal habitats, and agricultural lands.
- Economic Impact: The storm’s destructive force led to extensive infrastructure damage, disrupting transportation, power supply, and businesses, causing significant economic losses.
- Social Impact: The storm’s aftermath resulted in widespread displacement of communities, disruption of essential services, and loss of life, leaving lasting social and psychological scars.
Related Searches and FAQs
1. What are the Different Stages of a Tropical Cyclone?
Tropical cyclones progress through various stages, each characterized by specific wind speeds and organizational structures. The stages typically include:
- Tropical Depression: Characterized by winds below 38 mph (61 km/h).
- Tropical Storm: Winds range from 39 mph (63 km/h) to 73 mph (118 km/h).
- Hurricane (or Typhoon): Winds reach or exceed 74 mph (119 km/h).
2. How are Tropical Cyclones Named?
Tropical cyclones are named according to established lists maintained by regional meteorological organizations. These lists rotate annually, and the names are chosen to facilitate communication and awareness.
3. What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale categorizes hurricanes based on their wind speeds, providing a measure of their potential for damage. The scale ranges from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (over 157 mph), with increasing severity and potential for destruction.
4. What are the Warning Signals for Tropical Cyclones?
Tropical cyclone warnings are issued by meteorological agencies to alert communities of potential hazards. These warnings include:
- Tropical Storm Warning: Issued when sustained winds of 39-73 mph (63-118 km/h) are expected within 24 hours.
- Hurricane Warning: Issued when sustained winds of 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher are expected within 24 hours.
5. What are the Best Practices for Preparing for a Tropical Cyclone?
Preparing for a tropical cyclone involves taking proactive measures to minimize potential risks:
- Developing an Emergency Plan: Establishing a plan that includes evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies.
- Securing Property: Boarding up windows, securing loose objects, and moving valuable belongings to higher ground.
- Preparing Emergency Supplies: Assembling a kit containing food, water, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
6. How can Communities Recover from the Impact of a Tropical Cyclone?
Recovery from a tropical cyclone requires a coordinated effort involving government agencies, humanitarian organizations, and local communities. This includes:
- Providing Emergency Aid: Delivering food, water, shelter, and medical assistance to affected populations.
- Restoring Infrastructure: Repairing damaged roads, bridges, power lines, and communication networks.
- Supporting Economic Recovery: Providing financial assistance to businesses and individuals impacted by the storm.
7. What are the Long-Term Impacts of Tropical Cyclones?
Tropical cyclones can leave lasting impacts on communities and ecosystems:
- Environmental Degradation: Damage to forests, coastal habitats, and agricultural lands can lead to erosion, biodiversity loss, and habitat fragmentation.
- Economic Disruption: The storm’s impact on infrastructure and businesses can lead to long-term economic hardship and unemployment.
- Social Disruption: Displacement of communities, loss of livelihoods, and psychological trauma can have lasting social consequences.
8. How can Climate Change Influence the Intensity and Frequency of Tropical Cyclones?
Climate change is expected to influence the intensity and frequency of tropical cyclones, with potential for:
- Increased Intensity: Warmer ocean temperatures can fuel stronger storms with higher wind speeds and heavier rainfall.
- Increased Frequency: Climate change may alter atmospheric circulation patterns, potentially leading to more frequent storms.
Tips for Preparedness and Mitigation
1. Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and warnings issued by meteorological agencies.
2. Prepare a Family Emergency Plan: Discuss potential hazards, evacuation routes, and communication strategies.
3. Assemble an Emergency Kit: Stock up on essential supplies, including food, water, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
4. Secure Your Home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and move valuable belongings to higher ground.
5. Know Your Evacuation Routes: Be familiar with evacuation routes and designated shelters.
6. Practice Safety Measures: Avoid floodwaters, stay away from damaged areas, and follow official instructions.
7. Stay Connected: Maintain communication with family and friends, and be aware of emergency updates.
Conclusion
The Nadine storm serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of nature and the importance of preparedness and mitigation. Understanding the origins, characteristics, and impacts of such storms empowers individuals and communities to take proactive measures to minimize risks and ensure resilience in the face of future events. By embracing a culture of preparedness, fostering community resilience, and advocating for sustainable practices, we can collectively mitigate the devastating consequences of natural disasters like the Nadine storm.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Impact of Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!