Understanding the Formation and Impact of Tropical Cyclones: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Formation and Impact of Tropical Cyclones: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Formation and Impact of Tropical Cyclones: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Formation and Impact of Tropical Cyclones: A Comprehensive Guide
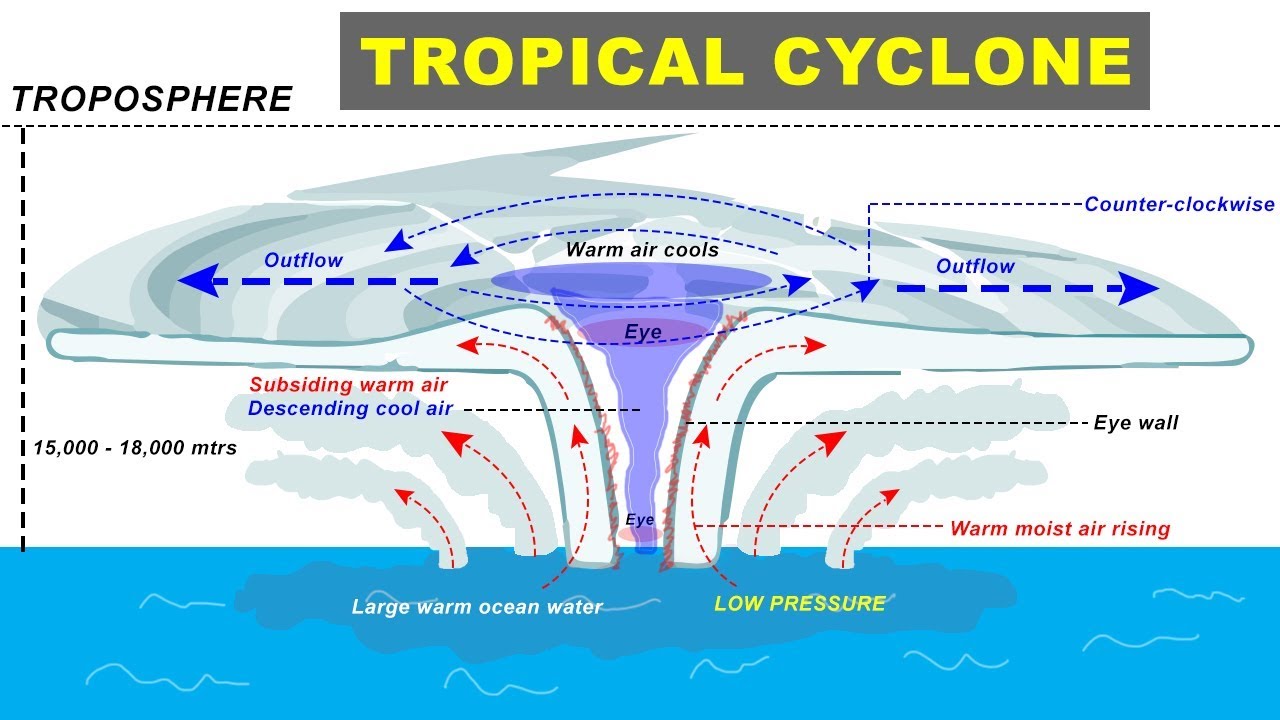
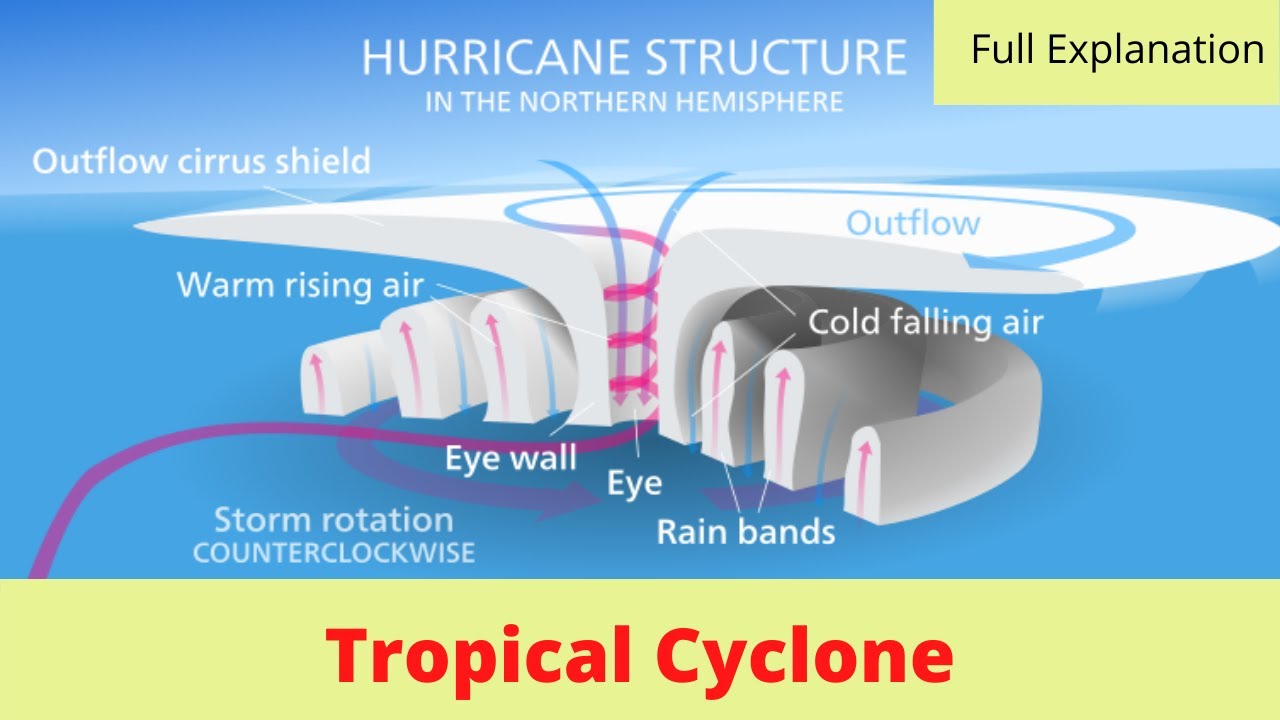
Tropical cyclones, often referred to as hurricanes, typhoons, or cyclones depending on their location, are powerful and destructive weather events that can have devastating impacts on coastal communities. These storms form over warm ocean waters and are characterized by their intense winds, heavy rainfall, and potential for storm surge.
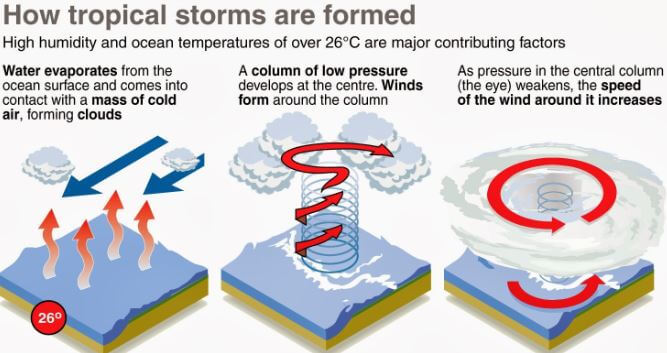
The Formation of a Tropical Cyclone
Tropical cyclones develop when certain atmospheric conditions are met. These include:
- Warm Ocean Waters: The ocean surface temperature must be at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (26.5 degrees Celsius) to provide the necessary heat and moisture for storm development.
- Low Wind Shear: Low wind shear, or the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, is crucial for the storm to organize and strengthen. High wind shear can disrupt the storm’s structure.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave or a low-pressure system, is needed to provide the initial spin and organization for the storm.
Stages of Development
Tropical cyclones progress through several stages of development:
- Tropical Depression: A tropical depression is a closed circulation with maximum sustained winds of less than 38 mph (62 km/h).
- Tropical Storm: A tropical storm is a stronger system with maximum sustained winds between 39 and 73 mph (63 and 118 km/h).
- Hurricane (Typhoon, Cyclone): A hurricane is the most intense stage of a tropical cyclone, with maximum sustained winds of 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher.
Impact of Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones can cause significant damage and disruption, including:
- High Winds: Strong winds can cause widespread damage to buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation.
- Heavy Rainfall: Torrential rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and erosion.
- Storm Surge: Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds pushing water towards the coast. This can inundate coastal areas, causing significant damage and loss of life.
- Tornadoes: Tropical cyclones can spawn tornadoes, which can cause localized damage and injuries.
Monitoring and Prediction
Modern technology plays a crucial role in monitoring and predicting the path and intensity of tropical cyclones. Satellites, radar systems, and weather buoys provide real-time data on storm development, movement, and strength. Sophisticated computer models are used to forecast the storm’s track and intensity, allowing for timely warnings and evacuation procedures.
Preparing for a Tropical Cyclone
Preparation is essential for minimizing the impact of a tropical cyclone. Individuals and communities should:
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Know your evacuation route and designated shelter location.
- Secure Your Property: Board up windows, trim trees, and secure loose objects.
- Gather Emergency Supplies: Stock up on food, water, batteries, first-aid kit, and other essential items.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and heed warnings from local authorities.
Related Searches
1. Hurricane Season: The period of the year when tropical cyclones are most likely to occur.
2. Hurricane Tracking: The process of monitoring the path and intensity of a tropical cyclone using satellite imagery, radar data, and other tools.
3. Hurricane Warning: An official announcement issued by a weather agency indicating that hurricane conditions are expected in a specific area.
4. Hurricane Watch: An official announcement indicating that hurricane conditions are possible in a specific area within a specified timeframe.
5. Hurricane Damage Assessment: The process of evaluating the damage caused by a hurricane, including infrastructure damage, economic losses, and potential environmental impacts.
6. Hurricane Recovery: The process of restoring infrastructure, rebuilding homes and businesses, and providing assistance to affected communities following a hurricane.
7. Hurricane Preparedness: The steps individuals and communities can take to prepare for a hurricane, including developing evacuation plans, securing property, and gathering emergency supplies.
8. Hurricane History: The study of past hurricanes, including their tracks, intensities, and impacts, to understand the patterns and trends of these storms.
FAQs about Tropical Cyclones
1. What is the difference between a hurricane, typhoon, and cyclone?
The terms hurricane, typhoon, and cyclone refer to the same type of weather event, but they are used in different regions of the world. Hurricanes are typically used in the North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific, typhoons in the Northwest Pacific, and cyclones in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
2. How are tropical cyclones named?
Tropical cyclones are named by regional weather agencies using pre-determined lists of names. The names alternate between male and female and are chosen to be easily recognizable and memorable.
3. What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a five-category scale that classifies hurricanes based on their maximum sustained wind speeds. Category 1 hurricanes have the weakest winds, while Category 5 hurricanes have the strongest winds.
4. What are some of the long-term effects of a tropical cyclone?
The long-term effects of a tropical cyclone can include damage to infrastructure, loss of life, economic disruption, and environmental impacts, such as soil erosion, coastal damage, and water pollution.
5. How can I stay safe during a hurricane?
During a hurricane, it is essential to follow the instructions of local authorities. Stay indoors, avoid driving, and be aware of potential hazards such as downed power lines, flooding, and debris.
Tips for Staying Safe During a Tropical Cyclone
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and heed warnings from local authorities.
- Have a Plan: Develop an evacuation plan and know your designated shelter location.
- Prepare Your Home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and trim trees.
- Gather Supplies: Stock up on food, water, batteries, first-aid kit, and other essential items.
- Stay Indoors: During the storm, stay indoors and avoid driving or going outside.
- Be Aware of Hazards: Watch out for downed power lines, flooding, and debris.
Conclusion
Tropical cyclones are powerful and destructive weather events that can have devastating impacts on coastal communities. Understanding the formation, impact, and prediction of these storms is crucial for minimizing their effects. By staying informed, preparing for potential threats, and following safety guidelines, individuals and communities can mitigate the risks associated with tropical cyclones.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Formation and Impact of Tropical Cyclones: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!