Understanding the Dynamics of a New Hurricane
Related Articles: Understanding the Dynamics of a New Hurricane
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Dynamics of a New Hurricane. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Dynamics of a New Hurricane
A new hurricane signifies the birth of a powerful and potentially destructive weather phenomenon. While the term "new" might imply a recent occurrence, it’s essential to understand that it refers to the formation and development of a tropical cyclone that has reached hurricane intensity. This process, from initial disturbance to a fully formed hurricane, is complex and driven by specific atmospheric conditions.
Formation of a New Hurricane:
Hurricanes are born in the tropical oceans, where warm, humid air fuels their growth. The genesis of a new hurricane begins with a tropical disturbance, a cluster of thunderstorms. These disturbances can develop from various sources, including:
- Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): This area of low pressure near the equator, where trade winds converge, is a common breeding ground for tropical disturbances.
- African Easterly Waves: These waves of low pressure, originating over Africa, travel westward across the Atlantic, often seeding tropical disturbances.
- Remnants of other weather systems: The remnants of tropical storms or even extratropical cyclones can sometimes provide the initial energy for a new hurricane.
Conditions for Hurricane Formation:
For a tropical disturbance to evolve into a new hurricane, specific atmospheric conditions are crucial:
- Warm Ocean Water: The ocean surface temperature must be at least 26.5°C (80°F) to provide the heat and moisture necessary for the storm’s development.
- Low Vertical Wind Shear: Wind shear, the change in wind speed and direction with altitude, can disrupt the storm’s structure. Low wind shear allows the thunderstorms to grow vertically and organize into a more cohesive system.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing area of low pressure or a tropical wave provides a foundation for the storm’s development.
Hurricane Development Stages:
As the disturbance gathers strength, it progresses through several stages:
- Tropical Depression: When the disturbance’s maximum sustained wind speed reaches 38 mph (61 km/h), it is classified as a tropical depression.
- Tropical Storm: As the storm intensifies further, with sustained winds reaching 39-73 mph (63-118 km/h), it is classified as a tropical storm and is given a name.
- Hurricane: When the sustained winds reach 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher, the storm is classified as a hurricane.
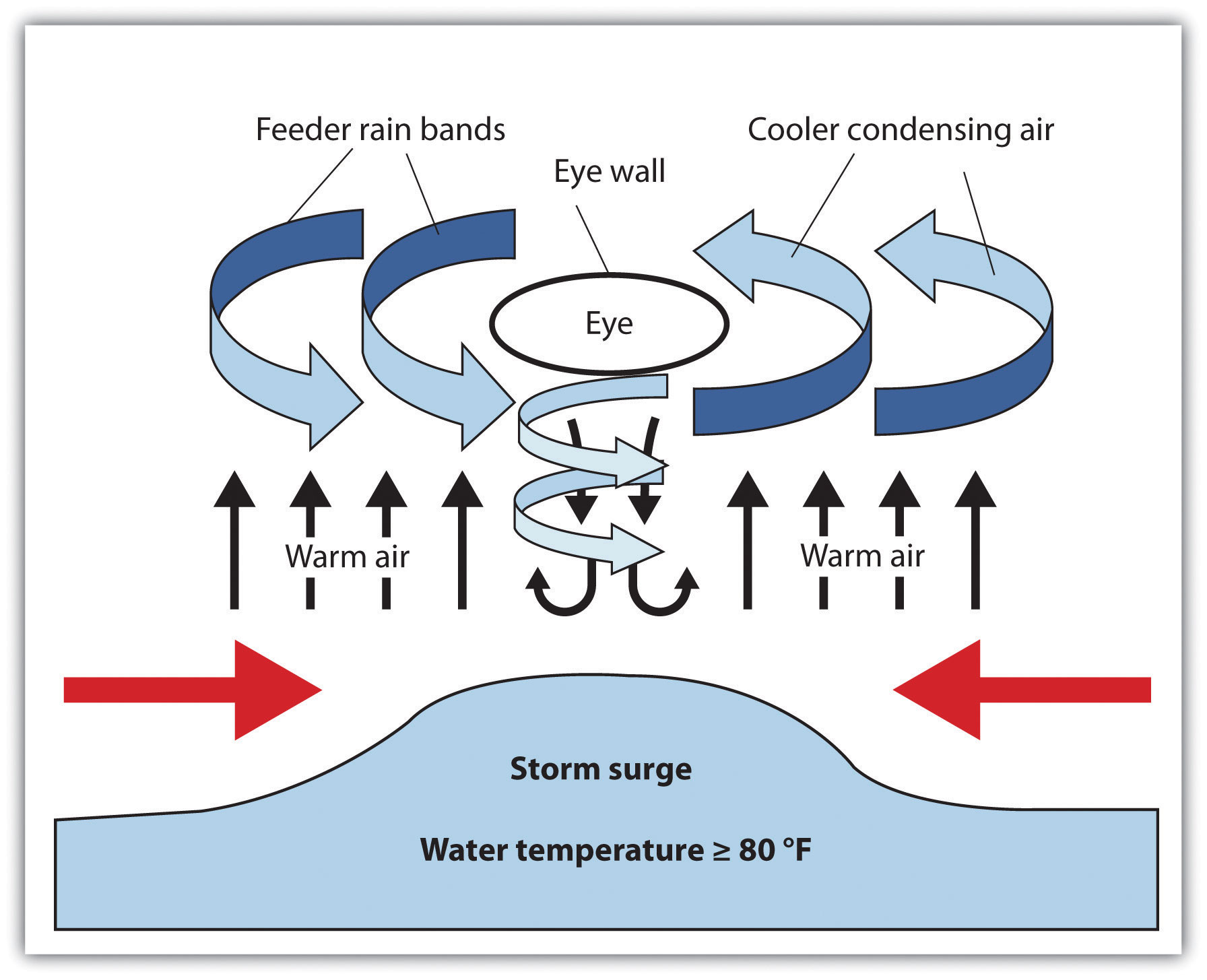
Hurricane Structure:
A fully formed hurricane features a distinct structure:
- Eye: The center of the hurricane, characterized by calm conditions and clear skies.
- Eyewall: A ring of intense thunderstorms surrounding the eye, where the strongest winds and heaviest rainfall occur.
- Spiral Bands: Bands of thunderstorms that extend outward from the eyewall, bringing rain and wind to a wider area.
Hurricane Intensity:
Hurricane intensity is measured using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, which classifies hurricanes into five categories based on wind speed. Category 5 hurricanes, with sustained winds of 157 mph (252 km/h) or higher, represent the most intense storms.
Hurricane Impacts:
New hurricanes can have devastating impacts, including:
- Storm Surge: A rise in sea level caused by the hurricane’s powerful winds pushing water towards the shore.
- High Winds: Hurricanes can produce winds strong enough to cause widespread damage to buildings, trees, and infrastructure.
- Heavy Rainfall: Torrential rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and mudslides.
- Tornadoes: Hurricanes can spawn tornadoes, which can cause significant damage.
Hurricane Forecasting and Warning Systems:
Advanced meteorological technology plays a crucial role in forecasting new hurricanes and issuing timely warnings. Sophisticated weather models, satellite imagery, and reconnaissance aircraft provide valuable data that help predict the storm’s track, intensity, and potential impacts.
Importance of Hurricane Awareness:
Understanding the formation, development, and impacts of new hurricanes is crucial for preparedness and mitigation. Awareness of hurricane risks, evacuation procedures, and safety measures can significantly reduce the potential for loss of life and property damage.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Tracking:
Hurricane tracking involves monitoring the movement and intensity of hurricanes using various tools, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide a wide-angle view of the storm’s structure and movement.
- Doppler Radar: Radar systems detect the storm’s precipitation and wind patterns.
- Reconnaissance Aircraft: Aircraft fly directly into the storm to collect data on wind speed, pressure, and other parameters.
2. Hurricane Preparation:
Preparing for a hurricane involves taking proactive steps to mitigate potential risks:
- Developing a Family Emergency Plan: This plan should outline communication strategies, evacuation routes, and designated meeting points.
- Securing Your Home: This includes securing windows, doors, and loose objects that could be blown away by strong winds.
- Building a Hurricane Kit: This kit should contain essential supplies like water, food, first aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
3. Hurricane Safety Tips:
During a hurricane, it’s crucial to prioritize safety:
- Evacuate if Ordered: Follow evacuation orders from local authorities.
- Stay Indoors: If you cannot evacuate, find a safe, interior room away from windows.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and news updates for the latest information.
- Avoid Driving: Flooded roads can be extremely dangerous.
4. Hurricane Impact Assessment:
After a hurricane passes, assessing the damage and providing relief is crucial:
- Damage Assessment: Teams assess the extent of damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
- Search and Rescue: Emergency responders search for survivors and provide medical assistance.
- Relief Efforts: Government agencies and non-profit organizations provide food, water, shelter, and other essential aid to affected communities.
5. Hurricane History:
Studying hurricane history helps us understand the frequency, intensity, and tracks of past storms, providing valuable insights for future preparedness:
- Historical Data: Records of past hurricanes, including their tracks, intensity, and impacts, are valuable for understanding hurricane patterns.
- Hurricane Archives: Organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) maintain extensive archives of hurricane data.
6. Hurricane Research:
Ongoing research into hurricanes aims to improve our understanding of their dynamics, forecasting, and mitigation strategies:
- Climate Change and Hurricanes: Scientists are investigating the potential impact of climate change on hurricane frequency, intensity, and track.
- Hurricane Modeling: Advanced computer models are being developed to improve hurricane forecasts and predictions.
- Hurricane Mitigation Technologies: Researchers are exploring new technologies and strategies to mitigate hurricane impacts.
7. Hurricane Naming Conventions:
Hurricanes are given names to help distinguish them and facilitate communication:
- Named Storms: Tropical storms and hurricanes are assigned names from pre-determined lists.
- Alternating Male and Female Names: The lists alternate between male and female names, with names rotating every six years.
- Retirement of Names: Names of particularly destructive hurricanes are retired to avoid confusion and to honor the victims.
8. Hurricane Myths and Misconceptions:
There are several common myths and misconceptions about hurricanes:
- Myth: Hurricanes are always strong: While some hurricanes can be extremely powerful, others can be relatively weak.
- Myth: Hurricanes always hit the same areas: Hurricanes can track in various directions and can impact different regions.
- Myth: Hurricanes are predictable: While forecasting has improved, hurricanes are still complex and unpredictable weather events.
FAQs About New Hurricanes
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane, a tropical storm, and a tropical depression?
A: The classification of a tropical cyclone depends on its wind speed:
- Tropical Depression: Maximum sustained winds of 38 mph (61 km/h) or less.
- Tropical Storm: Maximum sustained winds of 39-73 mph (63-118 km/h).
- Hurricane: Maximum sustained winds of 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher.
Q: How often do hurricanes form?
A: The frequency of hurricanes varies by region and year. The Atlantic hurricane season typically runs from June 1st to November 30th, with an average of 12 named storms, six hurricanes, and three major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher).
Q: How long does a hurricane last?
A: The duration of a hurricane can range from a few hours to several days or even weeks. The storm’s lifespan depends on various factors, including the availability of warm ocean water and the strength of the steering winds.
Q: How do hurricanes impact the environment?
A: Hurricanes can have significant environmental impacts:
- Coastal Erosion: Strong waves and storm surge can erode coastlines, leading to beach loss and habitat destruction.
- Water Pollution: Heavy rainfall can wash pollutants into waterways, affecting water quality and marine life.
- Forest Damage: High winds can damage and uproot trees, affecting forest ecosystems.
Q: What are the most common hurricane myths?
A: Some common hurricane myths include:
- Myth: Hurricanes always hit the same areas: Hurricanes can track in various directions and can impact different regions.
- Myth: Hurricanes are always strong: While some hurricanes can be extremely powerful, others can be relatively weak.
- Myth: Hurricanes are predictable: While forecasting has improved, hurricanes are still complex and unpredictable weather events.
Q: What can I do to prepare for a hurricane?
A: Preparing for a hurricane involves taking proactive steps:
- Developing a Family Emergency Plan: This plan should outline communication strategies, evacuation routes, and designated meeting points.
- Securing Your Home: This includes securing windows, doors, and loose objects that could be blown away by strong winds.
- Building a Hurricane Kit: This kit should contain essential supplies like water, food, first aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
Tips for Staying Safe During a New Hurricane
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and news updates for the latest information.
- Evacuate if Ordered: Follow evacuation orders from local authorities.
- Stay Indoors: If you cannot evacuate, find a safe, interior room away from windows.
- Avoid Driving: Flooded roads can be extremely dangerous.
- Secure Loose Objects: Secure any outdoor objects that could be blown away by strong winds.
- Have a Communication Plan: Establish a plan for how you will communicate with family and friends during the storm.
- Be Prepared for Power Outages: Have a backup power source, such as a generator, and ensure you have enough batteries for essential devices.
- Protect Your Property: Take steps to protect your home and property from storm surge and flooding.
- Be Patient and Understanding: Remember that hurricane recovery can take time, and there may be disruptions to services.
- Check on Your Neighbors: Check on elderly or disabled neighbors to ensure their safety.
Conclusion: The Importance of Hurricane Awareness
New hurricanes are a reminder of the power and unpredictability of nature. Understanding the dynamics of these storms, their potential impacts, and the importance of preparedness is essential for ensuring the safety of individuals and communities. By staying informed, following safety guidelines, and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks, we can minimize the potential for loss of life and property damage. Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to enhance our understanding of hurricanes and improve our ability to forecast and prepare for these powerful weather events.

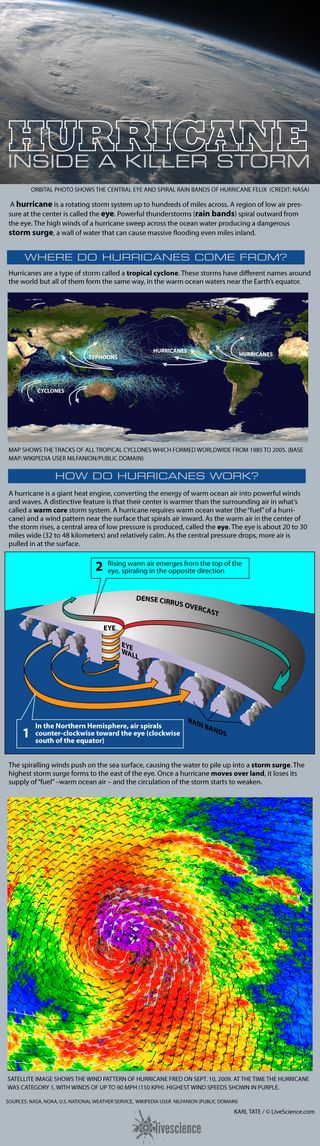

![Dynamics of air flow in hurricane [16] Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/P_Jain4/publication/281612751/figure/fig5/AS:670546983415823@1536882267338/Dynamics-of-air-flow-in-hurricane-16.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Dynamics of a New Hurricane. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!