Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Exploring the Spectrum of Storms
- 3.2 Delving Deeper: Factors Influencing Storm Development
- 3.3 Understanding the Impact of Storms
- 3.4 Related Searches: Expanding the Scope
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips: Enhancing Your Storm Preparedness
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Storms
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide

The term Nadine storm is not a recognized meteorological term. It appears you are referring to a specific event or phenomenon that might be associated with a particular storm or weather pattern. To provide you with a comprehensive and informative response, I will explore various aspects of storms and weather phenomena that could potentially be related to the term "Nadine."
Exploring the Spectrum of Storms
Storms are powerful weather events characterized by strong winds, heavy precipitation, and often accompanied by lightning, hail, or tornadoes. They are classified based on their formation mechanisms, geographic location, and associated intensity. Here’s a breakdown of some common storm types:
1. Tropical Cyclones: These are rotating storm systems that originate over tropical or subtropical waters. They are characterized by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and a distinct low-pressure center. Depending on their intensity, tropical cyclones are classified as tropical depressions, tropical storms, or hurricanes (in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific) or typhoons (in the Western Pacific).
2. Extratropical Cyclones: Unlike tropical cyclones, these storms form in mid-latitudes where warm and cold air masses meet. They are associated with fronts, which are boundaries between different air masses. Extratropical cyclones can produce a variety of weather phenomena, including rain, snow, sleet, and strong winds.
3. Thunderstorms: These are localized storms characterized by lightning and thunder. They form when warm, moist air rises rapidly, cools, and condenses into clouds. Thunderstorms can produce heavy rainfall, strong winds, hail, and tornadoes.
4. Derechos: These are widespread, straight-line windstorms that can extend for hundreds of miles. They are associated with powerful thunderstorms that produce strong downdrafts, which can cause significant damage to structures and trees.
5. Dust Storms: These are storms that occur in arid or semi-arid regions where strong winds pick up loose soil and sand, creating a dense cloud that reduces visibility. Dust storms can pose health risks to humans and animals and can damage crops and infrastructure.
6. Blizzards: These are severe winter storms characterized by heavy snowfall, strong winds, and low visibility. Blizzards can create dangerous conditions for travel and can lead to power outages and disruptions in daily life.
Delving Deeper: Factors Influencing Storm Development
Several factors contribute to the development and intensification of storms:
1. Atmospheric Instability: This refers to the tendency of air to rise, which is influenced by temperature differences between different layers of the atmosphere. Warm, moist air is more likely to rise and form clouds, leading to the development of storms.
2. Moisture: The presence of moisture in the atmosphere is crucial for storm formation. Moisture condenses into clouds and precipitation, providing the energy for storm development.
3. Lifting Mechanisms: These are processes that force air to rise, leading to the formation of clouds and storms. Lifting mechanisms can include fronts, mountains, and convection.
4. Wind Shear: This refers to changes in wind speed or direction with height. Wind shear can influence the rotation of storms and the formation of tornadoes.
5. Ocean Temperatures: Warm ocean waters provide a source of heat and moisture that fuel the development of tropical cyclones.
Understanding the Impact of Storms
Storms can have a wide range of impacts on human society and the natural environment:
1. Damage to Infrastructure: Strong winds and heavy precipitation can cause damage to buildings, roads, bridges, and power lines.
2. Flooding: Heavy rainfall can lead to flooding, which can displace residents, damage property, and disrupt transportation.
3. Landslides: Heavy rainfall can saturate soil, leading to landslides that can damage homes and infrastructure.
4. Coastal Erosion: Strong winds and storm surges can cause coastal erosion, which can threaten coastal communities and ecosystems.
5. Agricultural Losses: Storms can damage crops and livestock, leading to economic losses for farmers.
6. Health Impacts: Storms can pose health risks to humans, including injuries from flying debris, exposure to cold temperatures, and respiratory problems from air pollution.
Related Searches: Expanding the Scope
The term "Nadine" might be connected to a specific storm or weather event, but it’s important to consider broader related searches to gain a comprehensive understanding:
1. Hurricane Nadine: This could refer to a specific hurricane named Nadine. While hurricanes are named by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), there are many hurricanes with the name Nadine, and it’s crucial to specify the year or region to identify the specific event.
2. Storm Nadine: This might be a general term for a storm associated with the name Nadine, possibly a local storm or weather event with a particular significance in a specific region.
3. Weather Patterns in [Region]: If Nadine refers to a specific location, searching for weather patterns in that region can provide insights into typical storm activity and potential connections to the term.
4. Historical Weather Events: Examining historical weather records for the region associated with Nadine might reveal significant storms or weather patterns that could be linked to the term.
5. Climate Change and Storms: Investigating the potential impact of climate change on storm frequency, intensity, and patterns can offer valuable context for understanding the significance of Nadine.
6. Storm Surge: If Nadine is related to a coastal storm, understanding the concept of storm surge, which is the abnormal rise in sea level caused by a storm, is crucial for assessing potential risks.
7. Forecasting and Warning Systems: Exploring how weather forecasting and warning systems are used to predict and prepare for storms can provide valuable insights into the importance of understanding and responding to weather events.
8. Disaster Preparedness: Understanding how communities prepare for and respond to storms, including evacuation plans, emergency shelters, and disaster relief efforts, is essential for mitigating the impact of these events.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How are storms named?
A: In the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific, tropical cyclones are named using a pre-determined list of names that rotate every six years. The names are chosen by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and alternate between male and female names.
Q: How are storm intensities measured?
A: Tropical cyclones are classified based on their wind speeds using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. This scale ranges from Category 1 (the weakest) to Category 5 (the strongest).
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane and a typhoon?
A: Hurricanes and typhoons are essentially the same type of storm, but they are named differently based on their location. Hurricanes are found in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific, while typhoons occur in the Western Pacific.
Q: How can I stay safe during a storm?
A: It’s important to stay informed about weather forecasts and warnings. During a storm, seek shelter indoors, avoid areas prone to flooding, and stay away from windows.
Tips: Enhancing Your Storm Preparedness
1. Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a plan for your household that includes evacuation routes, communication procedures, and a designated meeting place.
2. Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit that includes essential supplies such as food, water, first aid supplies, medication, and a flashlight.
3. Secure Your Property: Before a storm, secure loose objects that could be blown around by strong winds.
4. Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources, such as the National Weather Service.
5. Be Aware of Your Surroundings: During a storm, be aware of your surroundings and avoid areas that could be dangerous.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Storms
Understanding the nature, dynamics, and impacts of storms is crucial for mitigating their risks and ensuring the safety and well-being of communities. By staying informed, taking precautions, and preparing for potential events, individuals and communities can better respond to these powerful forces of nature.
While the term "Nadine" storm might not have a specific meteorological definition, exploring related searches and understanding broader weather phenomena can provide valuable insights into the complexities of storms and their impact on our world.

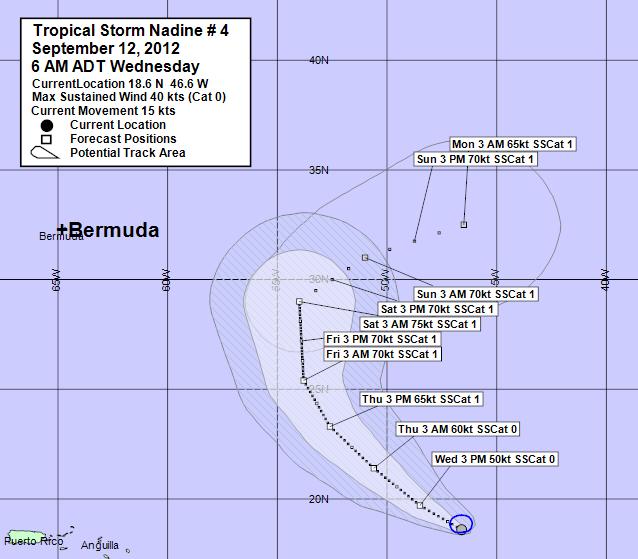
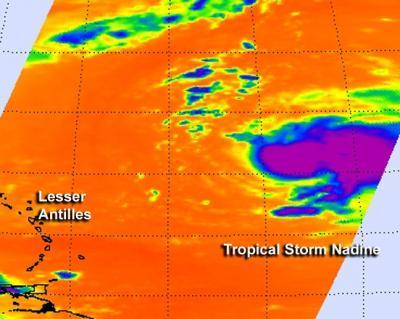

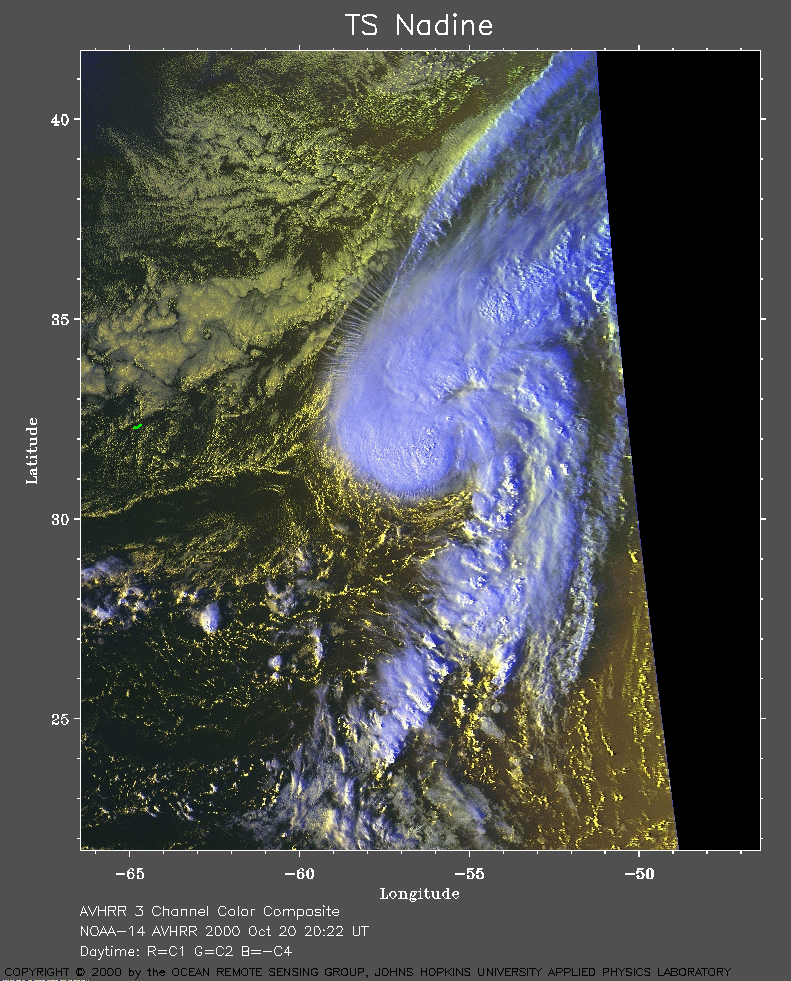
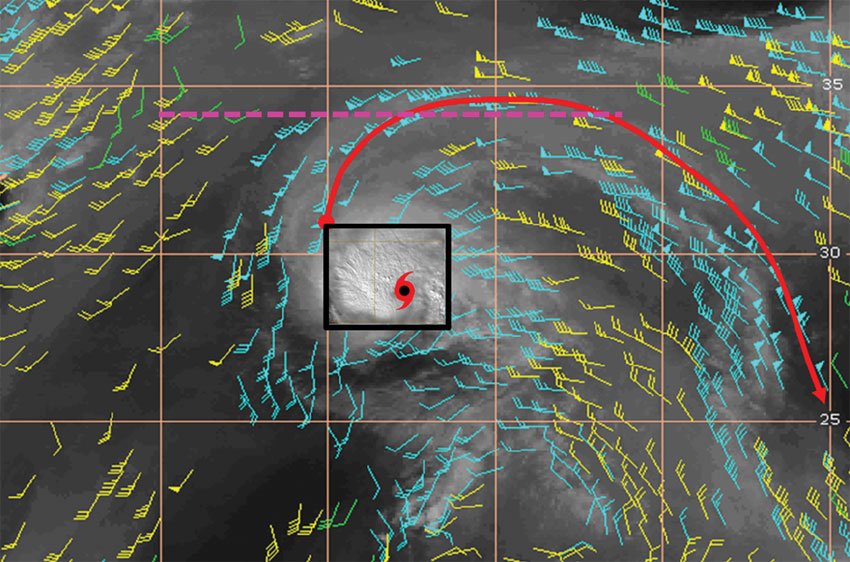

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Dynamics of a Nadine Storm: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!