Understanding the Complexities of Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Complexities of Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complexities of Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complexities of Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
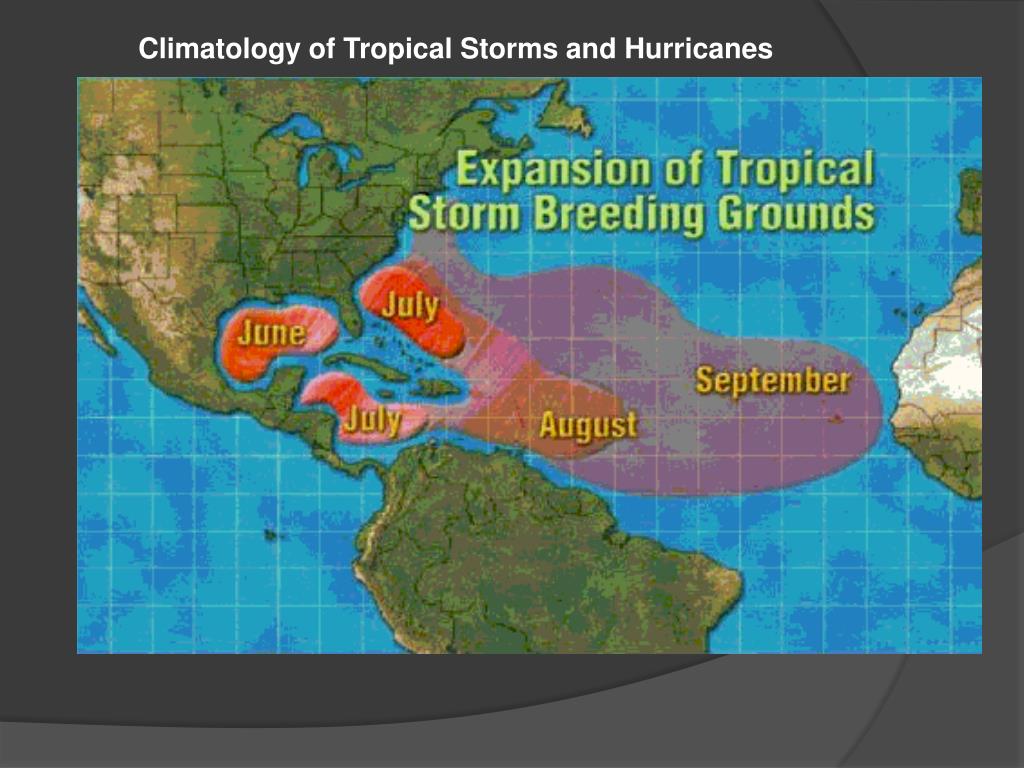
The Atlantic hurricane season, a period of heightened risk for devastating storms, officially runs from June 1st to November 30th each year. This timeframe, however, does not represent a rigid schedule. Hurricanes can and do form outside of these dates, though they are less frequent.
Understanding the "Hurricane Schedule"
The concept of a "hurricane schedule" is a misnomer. Hurricanes are not predictable like scheduled events. While the Atlantic hurricane season provides a framework for heightened awareness, the timing, intensity, and path of individual hurricanes are influenced by complex meteorological factors that are inherently unpredictable.
Key Factors Influencing Hurricane Formation and Activity
Several factors contribute to the development and movement of hurricanes:
- Sea Surface Temperature: Warmer waters provide the energy necessary for hurricanes to form and intensify. Temperatures above 80°F (26.5°C) are ideal for hurricane development.
- Wind Shear: Vertical wind shear, or the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, can inhibit hurricane formation or weaken existing storms. Low wind shear allows hurricanes to strengthen.
- Coriolis Effect: This force, caused by the Earth’s rotation, influences the direction of hurricane movement, causing them to curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Atmospheric Pressure: Low atmospheric pressure at the center of a hurricane creates an area of low pressure, drawing in surrounding air and fueling the storm.
- Location: The Atlantic hurricane season primarily affects the eastern coast of North America, Central America, and the Caribbean. However, hurricanes can also impact other regions, including the Gulf of Mexico and even the west coast of Africa.
The Importance of Understanding Hurricane Season
While a precise "hurricane schedule" does not exist, understanding the Atlantic hurricane season is crucial for preparedness and safety. Recognizing the timeframe and the potential for hurricane formation allows individuals, communities, and governments to:
- Increase Awareness: Public awareness campaigns can educate the public about hurricane risks, preparedness measures, and evacuation procedures.
- Enhance Preparedness: Individuals, families, and communities can prepare for potential hurricane impacts by creating emergency plans, stocking supplies, and securing property.
- Improve Response Efforts: Emergency responders and disaster relief organizations can better prepare for potential hurricane events by pre-positioning resources and coordinating response strategies.
- Reduce Potential Damage: Early warning systems and timely evacuations can help minimize the impact of hurricanes on infrastructure, property, and human life.
Related Searches: Expanding on Key Aspects of Hurricane Season
1. Hurricane Season History:
Understanding the history of hurricane seasons provides valuable insight into long-term trends and potential future scenarios. Data analysis reveals:
- Peak Years: 1998, 2004, and 2005 saw record-breaking hurricane activity.
- Quiet Years: The 2010s were relatively quiet compared to the previous decade.
- Long-Term Trends: The overall frequency and intensity of hurricanes show no clear long-term trends, but the impact of climate change on hurricane activity is a growing concern.
2. Hurricane Forecasting and Prediction:
Modern technology and sophisticated models have significantly improved hurricane forecasting. However, predicting the exact path and intensity of a hurricane remains a challenge.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide real-time data on storm formation, movement, and intensity.
- Weather Models: Numerical weather prediction models use complex algorithms to simulate hurricane development and track their paths.
- Hurricane Hunter Aircraft: These aircraft fly directly into hurricanes to gather data on wind speed, pressure, and storm structure.
3. Hurricane Categories and Intensity:
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale categorizes hurricanes based on wind speed, providing a standardized system for understanding the potential severity of a storm.
- Category 1 (74-95 mph): Minimal damage to vegetation and some structural damage.
- Category 2 (96-110 mph): Significant tree damage, major roof damage, and coastal flooding.
- Category 3 (111-129 mph): Extensive structural damage, widespread power outages, and significant coastal erosion.
- Category 4 (130-156 mph): Catastrophic damage to buildings, severe flooding, and widespread power outages.
- Category 5 (157+ mph): Devastating damage to buildings and infrastructure, massive flooding, and potential loss of life.
4. Hurricane Impacts and Consequences:
Hurricanes can cause widespread damage and disruption, affecting various aspects of life:
- Property Damage: Hurricanes can destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, leading to significant economic losses.
- Coastal Erosion: Storm surge, the rise in sea level caused by hurricanes, can erode coastlines and damage coastal communities.
- Flooding: Heavy rainfall associated with hurricanes can cause widespread flooding, damaging property and infrastructure.
- Power Outages: Hurricane-force winds can damage power lines, leading to prolonged power outages.
- Human Health: Hurricanes can cause injuries, illnesses, and fatalities, particularly due to flooding, storm surge, and flying debris.
5. Hurricane Preparedness and Safety:
Preparing for hurricane season is crucial to minimizing the impact of these storms.
- Emergency Planning: Develop a plan for your family, including evacuation routes, communication strategies, and emergency supplies.
- Home Preparation: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and stock up on essential supplies like food, water, batteries, and first-aid kits.
- Staying Informed: Monitor weather forecasts, warnings, and advisories from reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
- Evacuation Orders: Follow evacuation orders promptly and seek safe shelter in designated evacuation zones.
6. Hurricane Recovery and Resilience:
Recovering from a hurricane can be a long and challenging process.
- Immediate Response: Emergency responders, disaster relief organizations, and government agencies provide immediate assistance with search and rescue, medical care, and shelter.
- Reconstruction and Repair: The process of rebuilding and repairing damaged infrastructure, homes, and businesses can take months or even years.
- Economic Recovery: Hurricanes can have significant economic impacts, affecting businesses, employment, and tourism.
- Community Resilience: Building community resilience through disaster preparedness, infrastructure improvements, and social support systems is crucial for mitigating future hurricane impacts.
7. Hurricane Climate Change Impacts:
Climate change is expected to influence hurricane activity in various ways:
- Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels exacerbate storm surge, increasing the risk of coastal flooding and erosion.
- Warmer Ocean Temperatures: Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for hurricanes, potentially increasing their intensity.
- Changes in Hurricane Tracks: Climate change may alter the paths of hurricanes, potentially affecting regions not historically impacted by these storms.
8. Hurricane Research and Innovation:
Ongoing research and technological advancements are improving hurricane prediction and mitigation efforts.
- Advanced Modeling: Sophisticated weather models are constantly being refined to improve hurricane forecasting accuracy.
- Satellite Technology: New satellite sensors provide more detailed information about hurricane structure and intensity.
- Hurricane Mitigation Strategies: Research is exploring innovative methods to reduce hurricane impacts, such as storm surge barriers and hurricane-resistant building codes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hurricane Season
Q: When is hurricane season?
A: The Atlantic hurricane season officially runs from June 1st to November 30th each year. However, hurricanes can form outside of this timeframe.
Q: What is the peak of hurricane season?
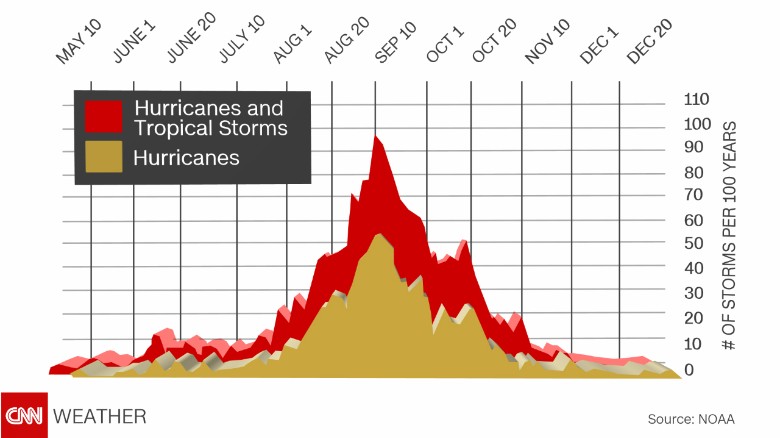
A: The peak of hurricane season is typically from mid-August to late October.
Q: How often do hurricanes occur?
A: The number of hurricanes in a given year varies. Some years are very active, while others are relatively quiet.
Q: What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A: A tropical storm has sustained wind speeds of 39-73 mph, while a hurricane has sustained wind speeds of 74 mph or higher.
Q: How are hurricanes named?
A: Hurricanes are named using a pre-determined list of names that rotate each year. The list alternates between male and female names, and names are retired if a hurricane causes significant damage or loss of life.
Q: What should I do if a hurricane is approaching?
A: Monitor weather forecasts, follow evacuation orders, secure your property, and prepare an emergency kit.
Q: What are the most common hurricane impacts?
A: Hurricanes can cause property damage, flooding, power outages, coastal erosion, and loss of life.
Tips for Staying Safe During Hurricane Season
- Prepare an emergency kit: Stock up on essential supplies like food, water, batteries, first-aid supplies, and a weather radio.
- Develop an evacuation plan: Identify safe evacuation routes and designated evacuation zones.
- Secure your property: Trim trees, secure loose objects, and bring in outdoor furniture.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources.
- Follow evacuation orders: If ordered to evacuate, do so promptly and safely.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Watch out for flooding, downed power lines, and debris.
- Stay calm and follow instructions: During a hurricane, listen to emergency officials and follow their instructions.
Conclusion
While a precise "hurricane schedule" does not exist, understanding the Atlantic hurricane season is vital for preparedness and safety. By recognizing the timeframe, key influencing factors, and potential impacts of hurricanes, individuals, communities, and governments can work together to mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and minimize the devastating consequences of these powerful storms. Continued research, technological advancements, and public awareness campaigns are crucial for effectively managing hurricane risks and protecting lives and property.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complexities of Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!