Understanding Hurricane Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Hurricane Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Hurricane Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Hurricane Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide
![]()
Hurricane tracking is a crucial aspect of disaster preparedness, especially in regions prone to tropical storms and hurricanes. The ability to monitor and predict the path of these powerful weather systems allows for timely evacuation, mitigation of potential damage, and the safeguarding of lives. This article delves into the intricacies of hurricane tracking, providing a comprehensive understanding of the technology, processes, and information involved.
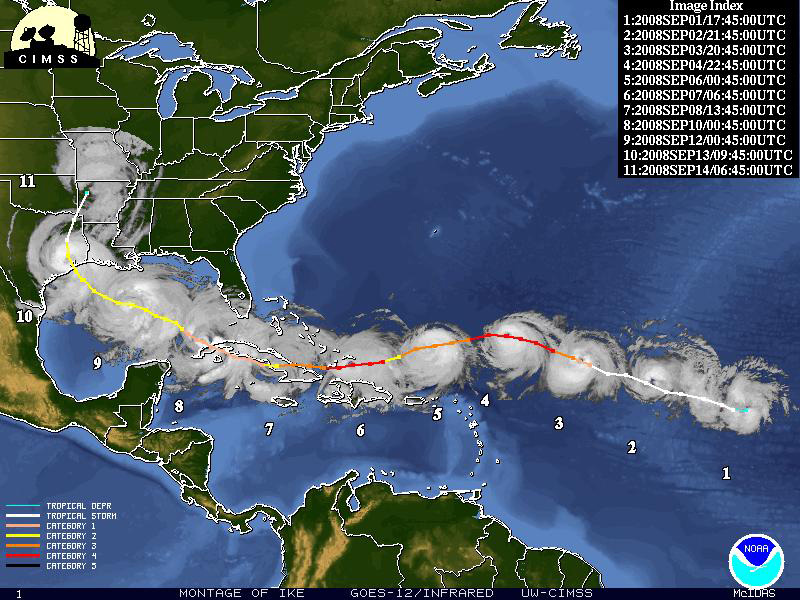
Hurricane Tracker 2024 Francine: A Case Study
While Hurricane Tracker 2024 Francine is a hypothetical example, it serves as a valuable tool to understand the principles of hurricane tracking and its practical applications. Let’s imagine a scenario where Hurricane Tracker 2024 Francine is active, and we are tasked with analyzing its potential impact.
Tracking the Storm’s Path:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide a bird’s-eye view of the storm’s development, offering insights into its size, intensity, and movement. Advanced sensors capture data on cloud formations, wind speed, and precipitation, providing a comprehensive picture of the storm’s structure.
- Weather Radar: Ground-based radar systems detect precipitation patterns, providing information about the storm’s intensity and rainfall distribution. This data is crucial for predicting potential flooding and determining the areas most likely to experience heavy rainfall.
- Aircraft Reconnaissance: Specialized aircraft equipped with sophisticated instruments fly directly into the storm, collecting data on wind speed, pressure, and temperature. This information provides a more detailed understanding of the storm’s internal dynamics and helps refine forecast models.
- Computer Models: Powerful computer models integrate data from various sources, including satellite imagery, radar data, and aircraft reconnaissance, to simulate the storm’s behavior and predict its future path. These models are constantly updated and refined as new data becomes available.
Disseminating Information:
- National Hurricane Center (NHC): The NHC, a branch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), serves as the primary source of information on hurricanes. The NHC issues advisories, forecasts, and warnings based on the latest data and computer model predictions.
- Local Media: Local news outlets and weather channels disseminate information from the NHC, providing updates on the storm’s progress and potential impacts for their specific regions.
- Emergency Management Agencies: Local, state, and federal emergency management agencies utilize hurricane tracking data to plan and execute emergency response measures, including evacuations, shelter operations, and resource allocation.
Understanding the Importance of Hurricane Tracking:
- Early Warning System: Hurricane tracking provides an early warning system, allowing residents in the storm’s path to prepare for potential impacts. This preparation can include securing property, stocking up on essential supplies, and evacuating if necessary.
- Disaster Mitigation: By understanding the potential path and intensity of a hurricane, authorities can take proactive measures to mitigate damage and minimize casualties. This may involve reinforcing critical infrastructure, clearing drainage systems, and implementing evacuation procedures.
- Resource Allocation: Hurricane tracking information helps emergency responders allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that personnel and equipment are deployed to the areas most in need.
- Research and Development: Data collected during hurricane tracking operations contributes to ongoing research efforts to improve hurricane forecasting models and develop more effective disaster preparedness strategies.
Related Searches
1. Hurricane Tracking Apps:
- Numerous mobile applications provide real-time hurricane tracking information, allowing users to monitor storms, receive alerts, and access crucial information on their smartphones. These apps often feature interactive maps, storm forecasts, and personalized alerts based on user location.
2. Hurricane Forecast Models:
- Several sophisticated computer models are used to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes. These models utilize data from various sources, including satellite imagery, radar, and aircraft reconnaissance, to simulate the storm’s behavior and generate forecasts. Understanding the different models and their strengths and weaknesses can provide a more comprehensive picture of the storm’s potential impacts.
3. Hurricane Safety Tips:
- Preparing for a hurricane involves taking proactive measures to ensure personal safety and minimize property damage. This includes securing windows and doors, stocking up on emergency supplies, developing an evacuation plan, and staying informed about the latest weather updates.
4. Hurricane History and Statistics:
- Studying historical hurricane data provides valuable insights into the frequency, intensity, and impact of hurricanes over time. Analyzing trends and patterns can help improve forecasting models and develop more effective disaster preparedness strategies.
5. Hurricane Watch vs. Hurricane Warning:
- A hurricane watch is issued when hurricane conditions are possible within a specified area within 48 hours. A hurricane warning is issued when hurricane conditions are expected within a specified area within 36 hours. Understanding the difference between these advisories is crucial for taking appropriate action.
6. Hurricane Terminology:
- Familiarity with hurricane terminology is essential for interpreting weather reports and understanding the severity of the storm. Terms such as "eye," "wind shear," "storm surge," and "Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale" provide a common language for discussing hurricanes and their potential impacts.
7. Hurricane Impact Assessment:
- After a hurricane makes landfall, assessing the damage and impact is crucial for initiating recovery efforts. This assessment involves evaluating infrastructure damage, assessing the extent of flooding, and determining the number of people affected.
8. Hurricane Preparedness Resources:
- Numerous resources are available to help individuals and communities prepare for hurricanes. These resources include government websites, emergency management agency websites, and non-profit organizations dedicated to disaster preparedness.
FAQs
1. How accurate are hurricane forecasts?
Hurricane forecasting has significantly improved in recent decades, with models becoming more sophisticated and data collection methods advancing. However, predicting the exact path and intensity of a hurricane remains a complex task. Forecasts are generally more accurate in the short term (1-3 days) and become less precise as the forecast window extends.
2. What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale categorizes hurricanes based on their sustained wind speed, providing a standardized measure of their intensity. The scale ranges from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (157 mph or higher), with higher categories indicating greater potential for damage and destruction.
3. What is a storm surge?
A storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s winds pushing water towards the shore. Storm surge is often the most destructive aspect of a hurricane, causing widespread flooding and erosion.
4. How do I prepare for a hurricane?
Preparing for a hurricane involves taking proactive measures to protect yourself, your family, and your property. This includes securing windows and doors, stocking up on emergency supplies, developing an evacuation plan, and staying informed about the latest weather updates.
5. What should I do during a hurricane?
During a hurricane, it is essential to stay safe and avoid unnecessary risks. This includes staying indoors, avoiding flooded areas, and following the instructions of local authorities.
6. What should I do after a hurricane?
After a hurricane, it is important to assess the damage, seek assistance if needed, and follow safety precautions. This may involve checking for gas leaks, avoiding downed power lines, and staying informed about the latest updates from local authorities.
Tips
1. Stay informed: Monitor weather reports from reputable sources such as the National Hurricane Center (NHC), local news outlets, and weather channels.
2. Develop an evacuation plan: Plan your evacuation route in advance and know where you will go if you need to evacuate.
3. Prepare an emergency kit: Stock up on essential supplies such as water, food, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
4. Secure your property: Reinforce windows and doors, bring in loose objects, and clear your yard of debris.
5. Stay calm and follow instructions: During a hurricane, stay calm and follow the instructions of local authorities.
Conclusion
Hurricane tracking is a vital tool for safeguarding lives and mitigating the impacts of these powerful weather systems. By understanding the technology, processes, and information involved in hurricane tracking, we can make informed decisions, prepare effectively, and minimize the risks associated with hurricanes. As technology continues to advance, hurricane tracking is expected to become even more accurate and reliable, further enhancing our ability to protect ourselves and our communities from these natural hazards.


![]()


/atlantictrackmap2010-56a9e13e3df78cf772ab33d0-5b882329c9e77c002ccda027.jpg)
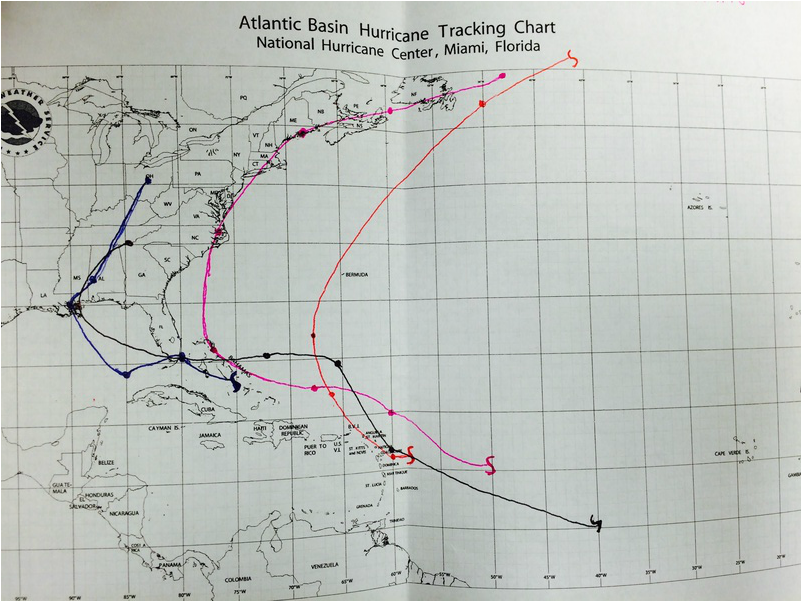
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Hurricane Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!