Understanding Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide
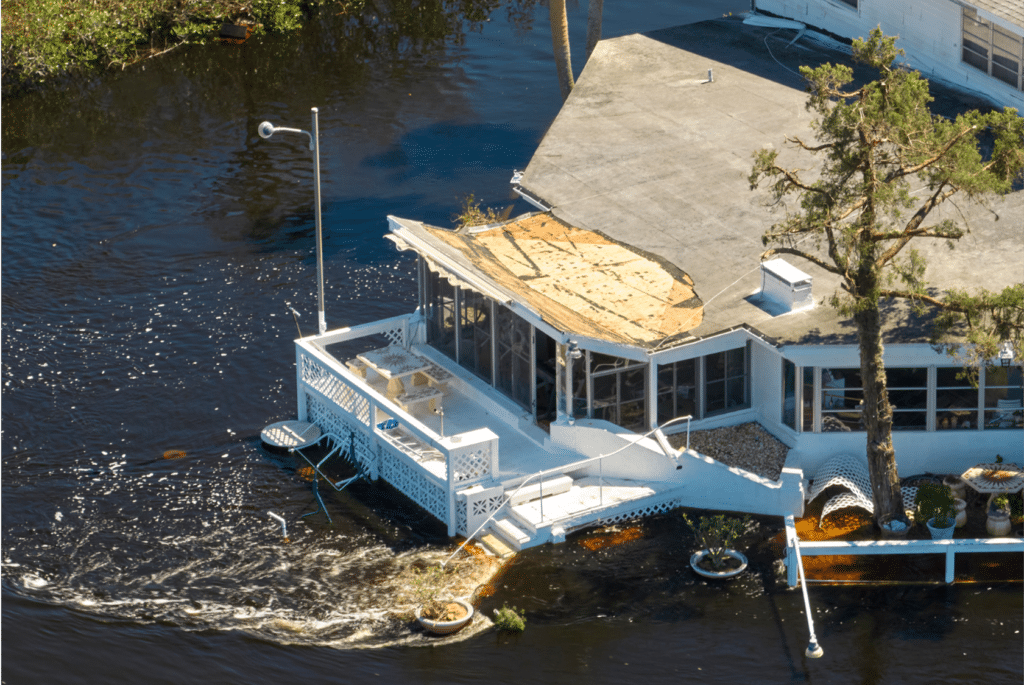

Hurricane season is a period of heightened risk for tropical cyclones, characterized by powerful storms that can cause widespread devastation. While the exact number and intensity of hurricanes vary annually, understanding the factors that contribute to their formation and the potential impacts they can have is crucial for preparedness and mitigation.
Understanding Hurricane Formation
Hurricanes, also known as typhoons or cyclones, are intense low-pressure systems that form over tropical waters. They require a specific set of conditions to develop and intensify, including:
- Warm Ocean Water: Hurricanes draw their energy from warm ocean waters, typically exceeding 80°F (26.5°C). The warmer the water, the more energy is available to fuel the storm.
- Low Wind Shear: Wind shear, the change in wind speed or direction with height, can disrupt the organization and development of a hurricane. Low wind shear allows the storm to grow vertically and intensify.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: Hurricanes often form from pre-existing weather disturbances like tropical waves or thunderstorms. These disturbances provide the initial organization and rotation necessary for development.
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation creates a force called the Coriolis effect, which deflects moving objects to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This effect contributes to the rotation of hurricanes.
Hurricane Stages and Classifications
As a hurricane develops, it progresses through various stages based on its wind speed, measured on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale:
- Tropical Depression: A tropical depression is a closed circulation of winds with maximum sustained winds of up to 38 mph (61 km/h).
- Tropical Storm: A tropical storm has maximum sustained winds of 39-73 mph (63-117 km/h).
- Hurricane: A hurricane is a tropical cyclone with maximum sustained winds of 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher.
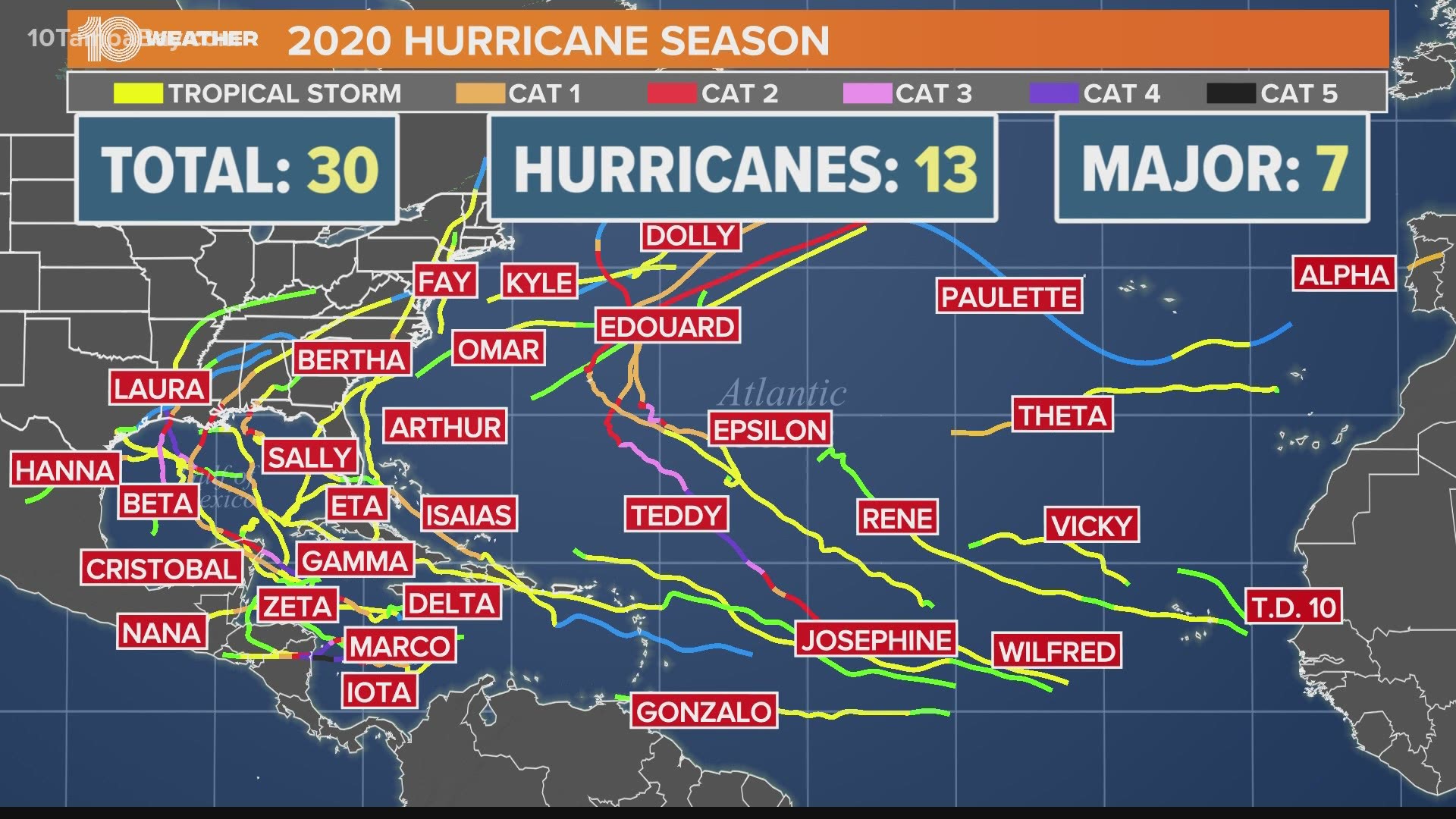
Hurricanes are further classified into categories 1-5 based on their wind speed, with Category 5 hurricanes being the most intense and destructive.
Hurricane Season and its Impacts
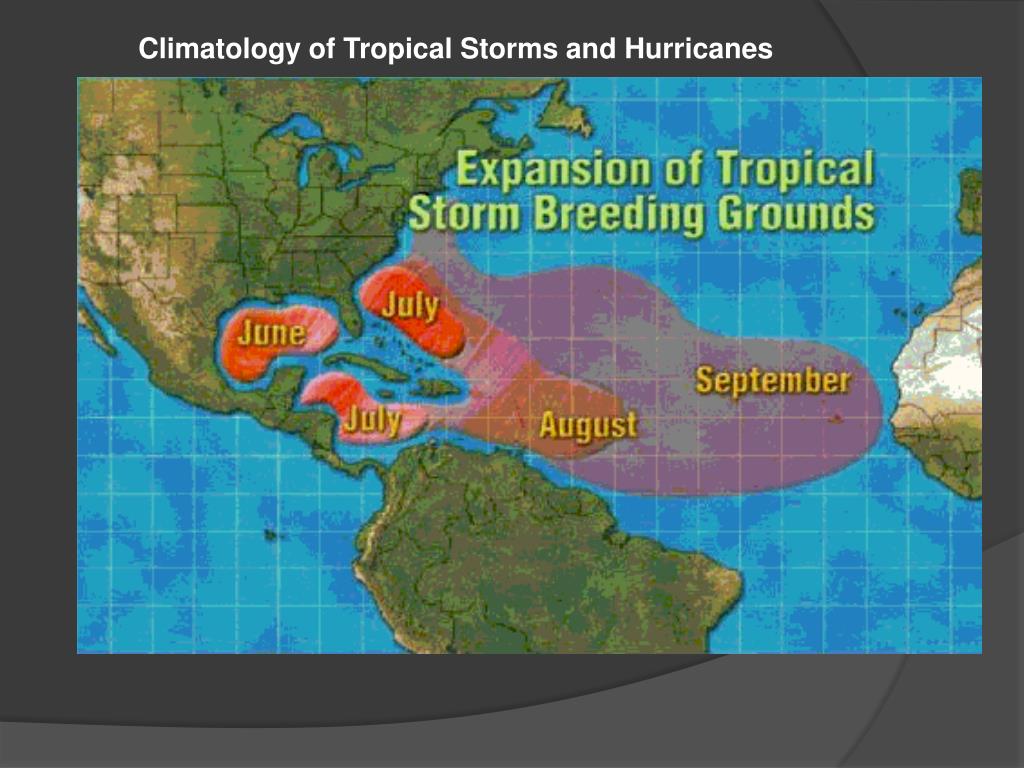
Hurricane season in the Atlantic basin runs from June 1st to November 30th, with the peak months typically being August and September. However, hurricanes can form outside of this designated period.
The potential impacts of hurricanes can be devastating, including:
- Strong Winds: Hurricane-force winds can cause widespread damage to buildings, infrastructure, and trees.
- Storm Surge: Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s winds pushing water towards the shore. It can cause severe flooding and erosion.
- Heavy Rainfall: Hurricanes can produce torrential rainfall, leading to flash floods, landslides, and riverine flooding.
- Tornadoes: Tornadoes can form in the outer bands of hurricanes, posing an additional threat.
Importance of Hurricane Preparedness
Being prepared for hurricane season is crucial for minimizing the potential impacts of these storms. This includes:
- Developing an Evacuation Plan: Having a plan for evacuating your home in case of a hurricane is essential.
- Securing Your Property: Protecting your home from hurricane damage involves securing windows, doors, and loose objects.
- Building an Emergency Kit: A well-stocked emergency kit should include food, water, first-aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Staying Informed: Monitoring weather forecasts and official advisories is crucial for staying informed about potential hurricane threats.
Related Searches and FAQs
Related Searches:
- Hurricane Tracking: Websites and apps provide real-time tracking of hurricanes, allowing individuals to monitor their paths and potential impacts.
- Hurricane Safety Tips: Numerous resources offer safety tips for preparing for and surviving a hurricane.
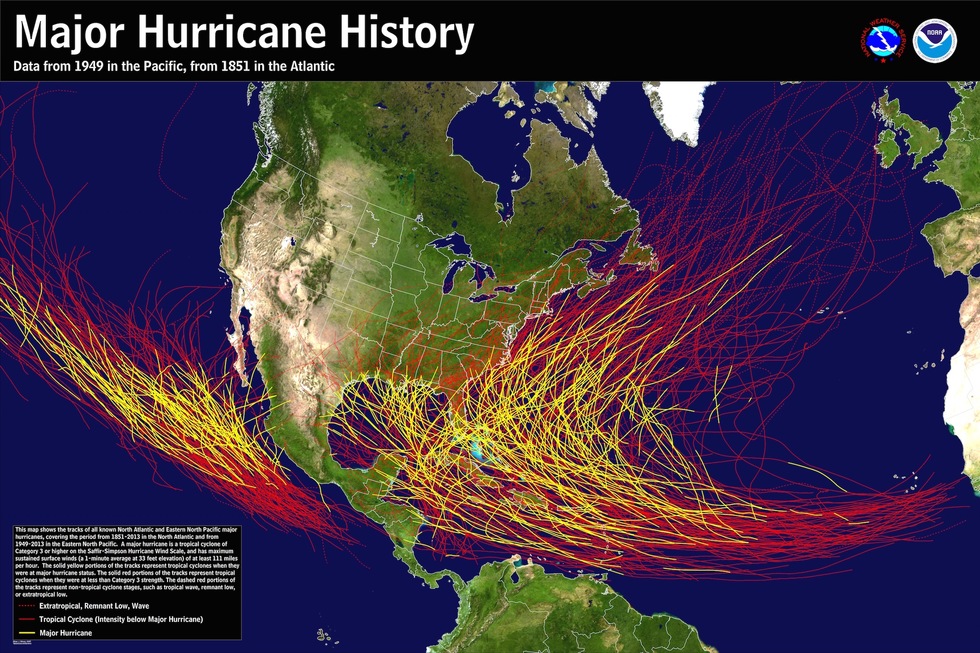
- Hurricane History: Understanding past hurricane events helps to provide context for future preparedness.
- Hurricane Insurance: Having adequate insurance coverage can help mitigate financial losses from hurricane damage.
- Hurricane Recovery: The process of recovering from a hurricane involves rebuilding homes and communities, and addressing the long-term impacts.
- Hurricane Mitigation: Efforts to mitigate hurricane risks involve building codes, infrastructure improvements, and coastal protection measures.
- Hurricane Research: Ongoing research is conducted to improve hurricane forecasting, understand their formation, and develop mitigation strategies.
- Hurricane Impacts on Climate Change: Climate change is expected to influence hurricane intensity and frequency, raising concerns about future risks.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane, a typhoon, and a cyclone?
A: These terms all refer to the same type of storm, but they are used in different regions. Hurricane is used in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific, typhoon is used in the Western Pacific, and cyclone is used in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific.
Q: How are hurricanes predicted?
A: Hurricanes are predicted using sophisticated computer models that take into account various factors, including wind speed, atmospheric pressure, and ocean temperature.
Q: How do I prepare for a hurricane?
A: Preparation involves developing an evacuation plan, securing your property, building an emergency kit, and staying informed about weather forecasts.
Q: What should I do during a hurricane?
A: During a hurricane, it is essential to seek shelter, stay informed, and follow official instructions.
Q: What should I do after a hurricane?
A: After a hurricane, prioritize safety, assess damage, and follow instructions from authorities.
Tips for Hurricane Preparedness
- Develop a Communication Plan: Establish a plan for communicating with family and friends in case of a hurricane.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Ensure your emergency kit includes essential items such as food, water, first-aid supplies, a weather radio, and a flashlight.
- Secure Your Property: Protect your home by securing windows, doors, and loose objects that could be blown away by strong winds.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and official advisories from reliable sources.
- Be Prepared to Evacuate: If an evacuation order is issued, follow instructions and evacuate promptly.
Conclusion
Hurricane season is a period of heightened risk for tropical cyclones, which can cause significant damage and disruption. Understanding hurricane formation, classification, and potential impacts is crucial for preparedness and mitigation. By developing a comprehensive plan, securing your property, and staying informed, individuals and communities can reduce the risks associated with hurricanes and enhance their resilience in the face of these powerful storms.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Hurricane Season: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!