Understanding Hurricane Paths: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Dynamics
Related Articles: Understanding Hurricane Paths: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Dynamics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Hurricane Paths: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Dynamics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Hurricane Paths: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Dynamics
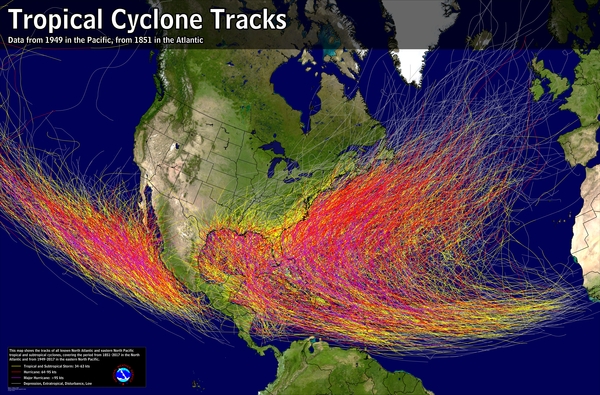
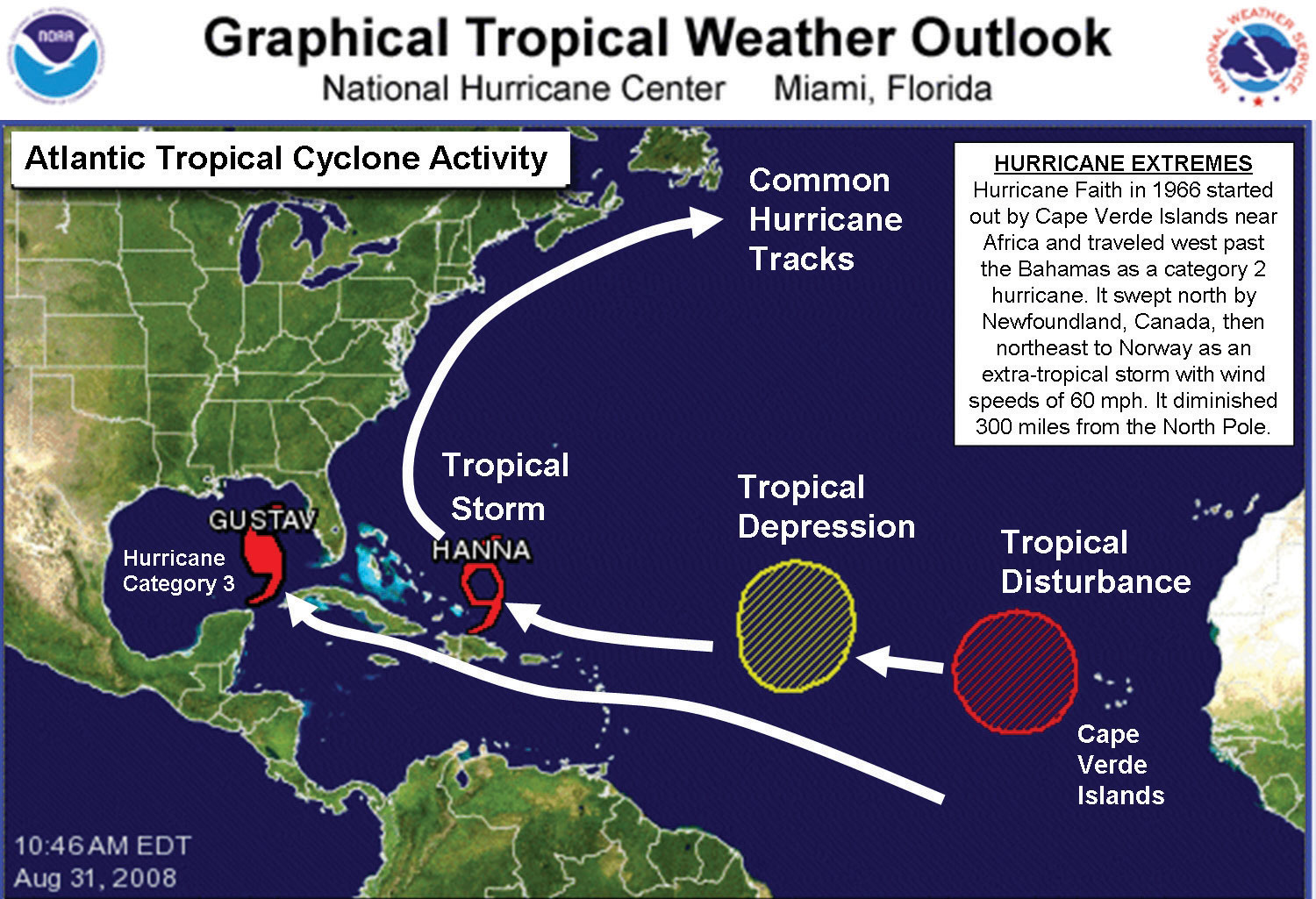
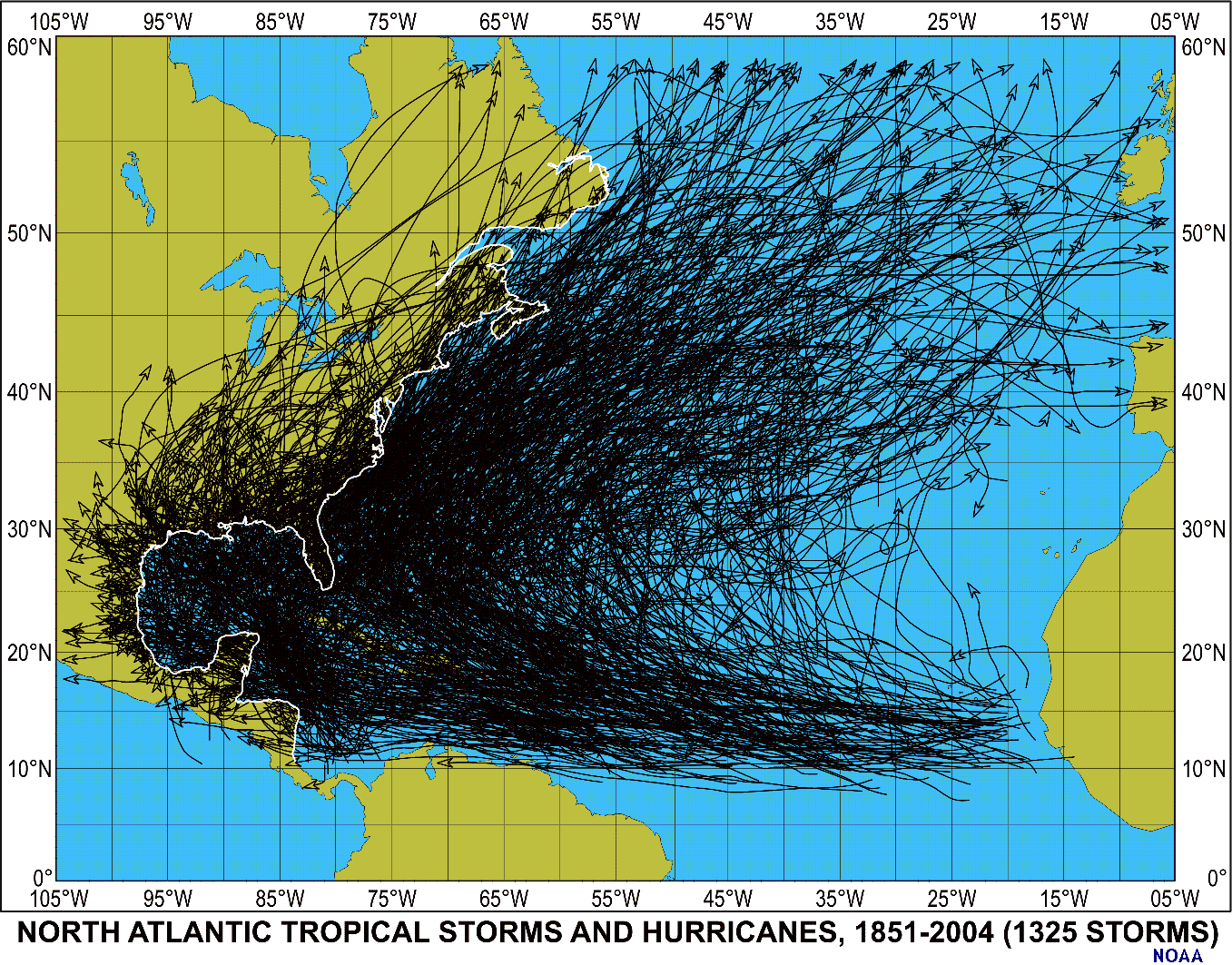
The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex system, constantly in motion. This movement manifests in various ways, from gentle breezes to powerful storms. Among these storms, hurricanes are some of the most destructive and unpredictable, capable of causing widespread devastation. One crucial element in understanding these storms is the path they take, known as their track.
Hurricane Tracks are not random events; they are guided by several factors, including:
- Steering Currents: The Earth’s rotation and atmospheric pressure differences create large-scale wind patterns known as steering currents. Hurricanes are embedded within these currents, and their movement is influenced by the direction and speed of these currents.
- Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation causes a deflection of moving objects, including hurricanes. This deflection, known as the Coriolis effect, causes hurricanes in the Northern Hemisphere to curve to the right and those in the Southern Hemisphere to curve to the left.
- Sea Surface Temperatures: Hurricanes derive their energy from warm ocean waters. As they move over colder waters or land, they weaken. Therefore, the location of warm ocean currents can significantly influence a hurricane’s path.
- Upper-Level Winds: Winds in the upper atmosphere can also influence a hurricane’s track. Strong winds can push a hurricane in a particular direction, while weak winds can allow the storm to meander.
Forecasting Hurricane Paths:
Predicting the path of a hurricane is a complex process that relies on sophisticated computer models and the expertise of meteorologists. These models incorporate various factors, including current weather conditions, historical data, and satellite imagery.
Importance of Understanding Hurricane Tracks:
Understanding hurricane tracks is crucial for:
- Effective Disaster Preparedness: Knowing the potential path of a hurricane allows for timely evacuation plans, preparation of emergency supplies, and the deployment of resources.
- Accurate Storm Surge Predictions: Storm surge, the abnormal rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s winds, is one of the most destructive aspects of these storms. Understanding the hurricane’s track allows for better predictions of storm surge intensity and location.
- Economic Impact Mitigation: Hurricane tracks influence the areas that will be affected, allowing businesses and governments to prepare for potential economic losses and implement mitigation strategies.
- Scientific Research: Studying hurricane tracks provides valuable data for understanding the dynamics of the atmosphere, improving forecasting models, and developing strategies for climate change adaptation.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Path Prediction:
- Hurricane Forecasting Models: Sophisticated computer models like the Global Forecast System (GFS) and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) are used to predict hurricane paths. These models incorporate various factors, including current weather conditions, historical data, and satellite imagery.
- Ensemble Forecasting: This technique involves running multiple simulations with slightly different initial conditions to account for uncertainties. The resulting ensemble of forecasts provides a range of potential hurricane tracks, highlighting areas of higher risk.
- Hurricane Track Cone: The cone of uncertainty, often depicted on weather maps, represents the area where a hurricane is most likely to make landfall. It is not a prediction of the exact path but rather a probabilistic estimate of the storm’s potential track.
2. Hurricane Intensity Forecasting:
- Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale: This scale categorizes hurricanes based on their sustained wind speeds, ranging from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (over 157 mph). Understanding a hurricane’s intensity is crucial for assessing potential damage and implementing appropriate safety measures.
- Hurricane Intensity Forecasting Models: Models like the Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF) model are used to predict a hurricane’s intensity. They consider factors like sea surface temperatures, wind shear, and the presence of dry air.
- Hurricane Intensity Change: Hurricanes can intensify or weaken over time, depending on the conditions they encounter. Factors like warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and favorable atmospheric conditions can lead to intensification, while cold waters, high wind shear, and dry air can cause weakening.
3. Hurricane Landfall:
- Hurricane Landfall Predictions: Predicting where a hurricane will make landfall is a critical aspect of forecasting. This information is crucial for issuing evacuation orders, deploying emergency resources, and preparing for potential damage.
- Hurricane Landfall Impacts: Hurricanes can cause significant damage upon landfall, including flooding, wind damage, power outages, and landslides. Understanding the potential impacts of a hurricane is crucial for planning mitigation measures and ensuring public safety.
- Hurricane Landfall History: Analyzing historical hurricane landfall data helps to understand the frequency and intensity of hurricanes in different regions. This data is valuable for developing building codes, planning infrastructure, and assessing future risks.
4. Hurricane Season:
- Hurricane Season Timeline: Hurricane seasons vary by region, with the Atlantic hurricane season typically running from June 1st to November 30th. Understanding the timing of hurricane season allows for better preparedness and timely response.
- Hurricane Season Activity: The number and intensity of hurricanes can vary significantly from year to year. Factors like El Niño and La Niña patterns, sea surface temperatures, and atmospheric conditions can influence hurricane activity.
- Hurricane Season Forecasting: Scientists use various techniques to forecast the potential activity of a hurricane season, including analyzing historical data, monitoring atmospheric conditions, and studying climate patterns.
5. Hurricane Hazards:
- Storm Surge: The abnormal rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s winds is one of the most destructive aspects of these storms. Storm surge can cause widespread flooding, erosion, and damage to coastal infrastructure.
- High Winds: Hurricane winds can cause significant damage to buildings, trees, and power lines. Strong winds can also generate tornadoes, further exacerbating the risks associated with hurricanes.
- Heavy Rainfall: Hurricanes can produce torrential rainfall, leading to flash floods, riverine flooding, and landslides. This rainfall can also cause widespread damage to infrastructure and disrupt transportation.
6. Hurricane Safety:
- Hurricane Evacuation: Evacuating from the path of a hurricane is one of the most effective ways to stay safe. Evacuation orders should be followed promptly, and individuals should have a plan in place for where to go and how to get there.
- Hurricane Preparedness: Having a hurricane preparedness plan is essential for minimizing risks and ensuring safety. This plan should include securing your home, preparing emergency supplies, and knowing how to stay informed during a hurricane.
- Hurricane Safety Tips: During a hurricane, it is important to stay indoors, avoid flooded areas, and follow instructions from local authorities. It is also essential to stay informed about the latest weather updates and be prepared for potential power outages and communication disruptions.
7. Hurricane Impacts on Ecosystems:
- Coastal Erosion: Hurricane winds and storm surge can cause significant coastal erosion, damaging beaches, dunes, and coastal ecosystems. This erosion can disrupt wildlife habitats and impact the livelihoods of coastal communities.
- Water Quality: Hurricane rainfall can contaminate water sources with pollutants and debris, posing health risks to humans and wildlife. The storm surge can also cause saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers, affecting water quality and availability.
- Ecosystem Recovery: Hurricanes can cause significant damage to ecosystems, but they also play a role in natural regeneration. After a hurricane, new plant growth can occur, and wildlife populations can rebound.
8. Hurricane Climate Change:
- Hurricane Intensity and Frequency: Climate change is expected to increase the intensity and frequency of hurricanes. Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for hurricanes, leading to stronger storms.
- Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels exacerbate the impacts of storm surge, increasing the risk of flooding and damage to coastal areas.
- Hurricane Adaptation: Understanding the impacts of climate change on hurricanes is crucial for developing adaptation strategies to mitigate the risks and build resilience in vulnerable communities.
FAQs About Hurricane Paths:
1. How are hurricane paths predicted?
Hurricane paths are predicted using a combination of sophisticated computer models and the expertise of meteorologists. These models incorporate various factors, including current weather conditions, historical data, and satellite imagery.
2. Why do hurricanes curve?
Hurricanes curve due to the Coriolis effect, which is caused by the Earth’s rotation. This effect deflects moving objects, including hurricanes, to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
3. How accurate are hurricane path predictions?
Hurricane path predictions are becoming increasingly accurate due to advancements in forecasting models and data collection. However, there is always a degree of uncertainty, and the cone of uncertainty reflects the potential range of a hurricane’s track.
4. What factors influence a hurricane’s path?
A hurricane’s path is influenced by several factors, including steering currents, the Coriolis effect, sea surface temperatures, and upper-level winds.
5. How can I stay safe during a hurricane?
Staying safe during a hurricane requires following evacuation orders, having a preparedness plan, and staying informed about the latest weather updates. It is also important to stay indoors, avoid flooded areas, and follow instructions from local authorities.
Tips for Understanding Hurricane Paths:
- Stay Informed: Follow reputable weather sources like the National Hurricane Center and local news outlets for updates on hurricane activity and forecasts.
- Know Your Risk: Understand the potential hurricane risks in your area and familiarize yourself with evacuation routes and shelter locations.
- Develop a Preparedness Plan: Have a plan in place for how you will prepare for a hurricane, including securing your home, gathering emergency supplies, and communicating with loved ones.
- Stay Vigilant: Monitor hurricane forecasts closely and be prepared to take action if a hurricane threatens your area.
Conclusion:
Understanding hurricane paths is crucial for effective disaster preparedness, accurate storm surge predictions, economic impact mitigation, and scientific research. By studying the factors that influence hurricane tracks and leveraging advanced forecasting models, we can better prepare for these powerful storms and minimize their impacts. As climate change continues to influence hurricane intensity and frequency, understanding hurricane paths becomes even more critical for ensuring public safety and resilience.


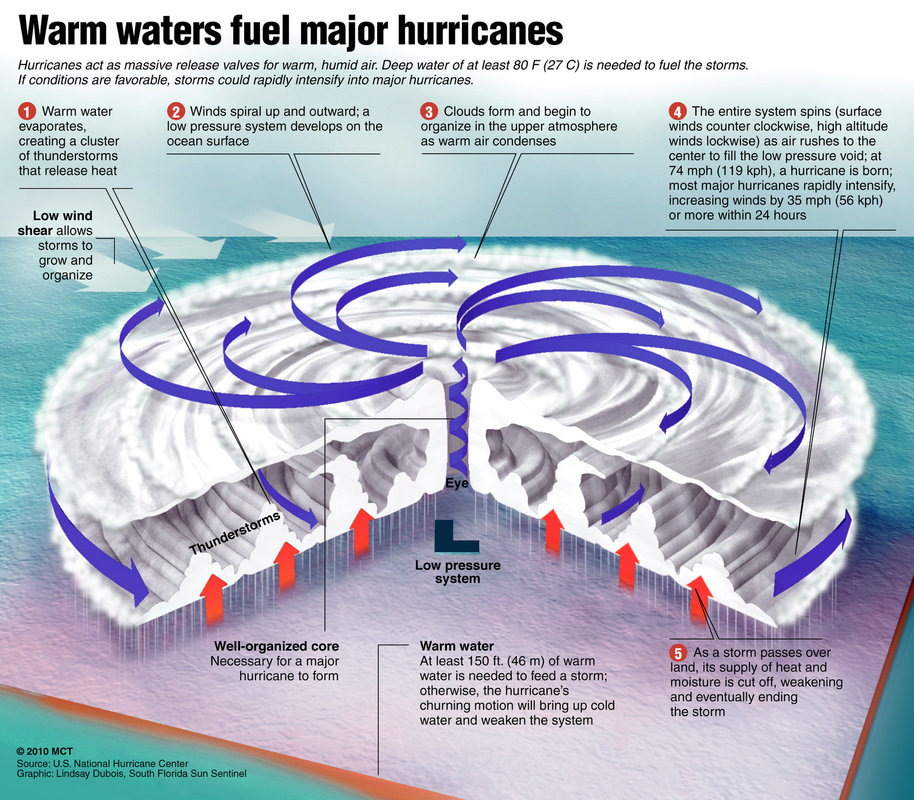
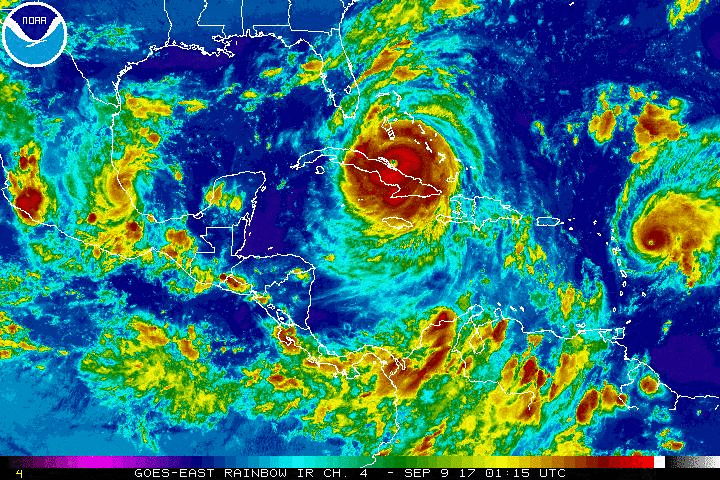

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Hurricane Paths: A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Dynamics. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!