Tropical Storm Ernesto: A Case Study in the Variability of Atlantic Hurricane Season
Related Articles: Tropical Storm Ernesto: A Case Study in the Variability of Atlantic Hurricane Season
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Tropical Storm Ernesto: A Case Study in the Variability of Atlantic Hurricane Season. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tropical Storm Ernesto: A Case Study in the Variability of Atlantic Hurricane Season
Tropical Storm Ernesto, a relatively minor storm in the grand scheme of Atlantic hurricane history, nonetheless offers valuable insights into the unpredictable nature of the hurricane season. While it did not cause widespread devastation, its formation and evolution highlight key aspects of tropical cyclone development and the complexities of weather forecasting.
Formation and Evolution:
Tropical Storm Ernesto formed on August 29, 2000, near the Cabo Verde Islands, a region known for spawning a significant number of Atlantic hurricanes. The storm developed from a tropical wave, a westward-moving trough of low pressure, that emerged from the African coast. As it moved across the Atlantic, it gradually intensified, fueled by warm ocean waters and favorable atmospheric conditions.
The storm reached peak intensity on September 1, 2000, with maximum sustained winds of 60 mph (95 km/h). However, it remained a tropical storm throughout its lifespan, never reaching hurricane status. This is a crucial point to emphasize, as it demonstrates that not all tropical waves develop into powerful hurricanes. Many dissipate before reaching significant strength or simply remain as tropical storms, highlighting the inherent variability of the hurricane season.
Impact and Significance:
Tropical Storm Ernesto ultimately made landfall in the Dominican Republic on September 4, 2000, bringing heavy rainfall and gusty winds. While the storm’s impact was relatively minor, it served as a reminder of the potential dangers posed by even relatively weak tropical cyclones. The heavy rainfall, for instance, caused localized flooding and landslides, highlighting the destructive power of water even in seemingly minor storms.
The storm’s significance extends beyond its immediate impact. Tropical Storm Ernesto served as a valuable case study for meteorologists and researchers, allowing them to refine their understanding of tropical cyclone formation and evolution. The storm’s path, intensity, and duration provided data that could be used to improve forecasting models and enhance preparedness for future events.
Related Searches:
1. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Path:
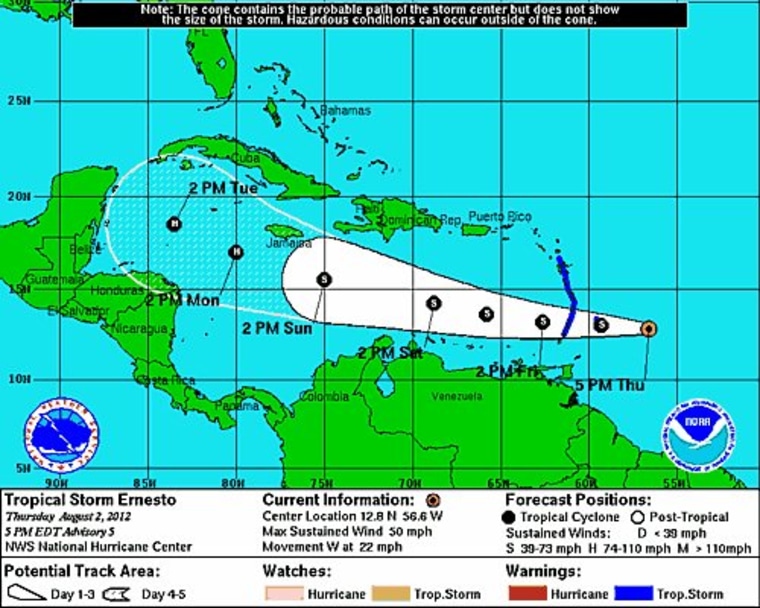
The path of Tropical Storm Ernesto is a key aspect of understanding its impact. The storm tracked westward across the Atlantic, passing north of the Lesser Antilles and then curving northward, making landfall in the Dominican Republic. This trajectory is characteristic of many Atlantic hurricanes, influenced by the prevailing winds and atmospheric conditions. Understanding the path of a storm allows for more accurate predictions of its impact on specific regions.
2. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Damage:
While Tropical Storm Ernesto did not cause significant damage, it is important to note that even relatively weak storms can have devastating consequences. The storm’s heavy rainfall caused localized flooding and landslides, particularly in mountainous regions. This underscores the importance of preparedness and the need to be aware of the potential dangers even from seemingly minor storms.
3. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Track:
The track of Tropical Storm Ernesto is another crucial element in its study. The storm’s movement across the Atlantic, its interaction with various weather systems, and its eventual landfall in the Dominican Republic all provide valuable insights into the dynamics of tropical cyclones. Tracking the movement of these storms allows for more accurate forecasts and enables authorities to issue timely warnings to affected populations.
4. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Rainfall:
The heavy rainfall associated with Tropical Storm Ernesto is a significant aspect of its impact. This rainfall led to localized flooding and landslides, demonstrating the destructive power of water even in seemingly minor storms. The storm’s rainfall pattern can be analyzed to understand the factors influencing its intensity and distribution, providing valuable data for future forecasting efforts.
5. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Wind Speed:
The wind speed of Tropical Storm Ernesto reached a maximum of 60 mph (95 km/h), categorized as a tropical storm. While not hurricane-force winds, these speeds were still significant enough to cause damage, particularly to vulnerable structures and vegetation. Analyzing the wind speed patterns of Tropical Storm Ernesto can help refine models for predicting the intensity of future storms.
6. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Forecast:
The forecasting of Tropical Storm Ernesto provides insights into the accuracy and limitations of current weather prediction models. While the storm’s trajectory and intensity were generally predicted with reasonable accuracy, it highlights the inherent uncertainties associated with forecasting tropical cyclones. This underscores the importance of continuous research and development of more sophisticated forecasting models.
7. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 Hurricane:
Tropical Storm Ernesto never reached hurricane status, despite its initial formation in a region known for spawning powerful hurricanes. This illustrates the complex factors influencing the development of tropical cyclones and highlights the variability of the hurricane season. Understanding the factors that prevent a storm from intensifying is crucial for accurate forecasting and preparation.
8. Tropical Storm Ernesto 2000 History:
The history of Tropical Storm Ernesto is an important aspect of understanding its significance. The storm’s formation, development, and eventual dissipation provide valuable data for analyzing the dynamics of tropical cyclones and improving forecasting models. Studying the history of past storms helps us better understand the potential risks posed by future events and develop more effective strategies for mitigation and preparedness.
FAQs:
1. What was the maximum wind speed of Tropical Storm Ernesto?
The maximum sustained wind speed of Tropical Storm Ernesto reached 60 mph (95 km/h).
2. Where did Tropical Storm Ernesto make landfall?
Tropical Storm Ernesto made landfall in the Dominican Republic on September 4, 2000.
3. Did Tropical Storm Ernesto cause any significant damage?
While Tropical Storm Ernesto did not cause widespread devastation, it did lead to localized flooding and landslides due to heavy rainfall.
4. What is the significance of Tropical Storm Ernesto?
Tropical Storm Ernesto serves as a valuable case study for understanding the dynamics of tropical cyclones and the variability of the hurricane season. It also highlights the importance of preparedness even for seemingly minor storms.
5. How was Tropical Storm Ernesto formed?
Tropical Storm Ernesto formed from a tropical wave that emerged from the African coast and gradually intensified as it moved across the Atlantic.
6. Did Tropical Storm Ernesto reach hurricane status?
No, Tropical Storm Ernesto remained a tropical storm throughout its lifespan, never reaching hurricane intensity.
7. What were the main impacts of Tropical Storm Ernesto?
The main impacts of Tropical Storm Ernesto included heavy rainfall, localized flooding, and landslides in the Dominican Republic.
8. What lessons can be learned from Tropical Storm Ernesto?
Tropical Storm Ernesto reminds us of the unpredictable nature of the hurricane season and the importance of preparedness even for relatively weak storms. It also highlights the value of ongoing research and development of more accurate forecasting models.
Tips:
1. Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and advisories from reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
2. Prepare an emergency kit: Gather essential supplies like food, water, first-aid kit, batteries, and a weather radio.
3. Develop an evacuation plan: Identify safe evacuation routes and designated shelters in your area.
4. Secure your property: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and reinforce vulnerable structures.
5. Be aware of potential hazards: Understand the risks associated with flooding, landslides, and high winds.
6. Follow official instructions: Obey evacuation orders and heed warnings from authorities.
7. Check on your neighbors: Assist elderly, disabled, and vulnerable individuals in your community.
8. Stay calm and informed: Avoid spreading rumors and misinformation.
Conclusion:
Tropical Storm Ernesto, while not a major hurricane, serves as a valuable reminder of the potential dangers posed by even relatively weak storms. Its formation, evolution, and impact highlight the complexities of weather forecasting and the importance of preparedness. By understanding the dynamics of tropical cyclones and heeding the warnings of experts, we can better mitigate the risks and ensure the safety of our communities.



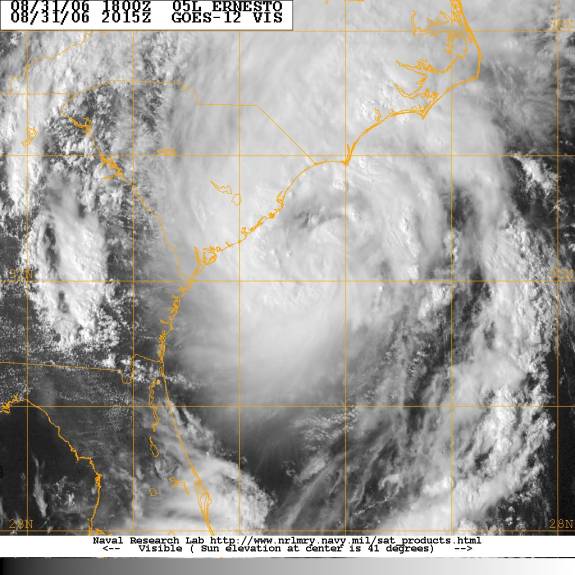
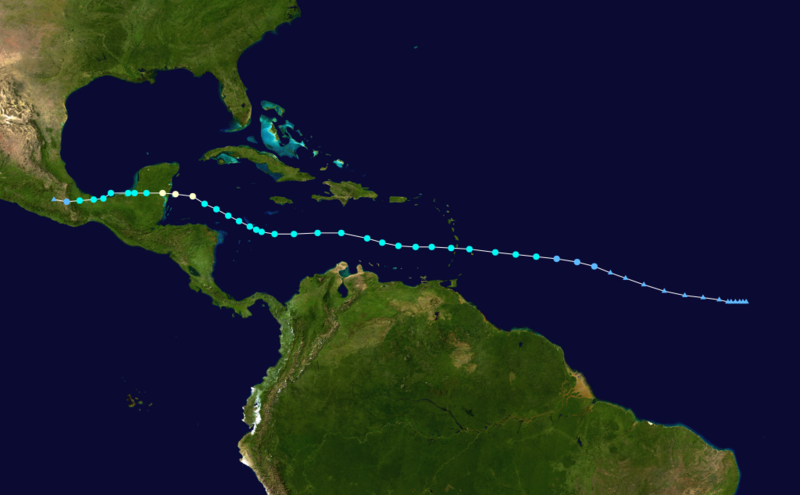

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tropical Storm Ernesto: A Case Study in the Variability of Atlantic Hurricane Season. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!