The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation
Related Articles: The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation
- 3.1 Understanding the Building Blocks of a Hurricane
- 3.2 Exploring the Stages of Hurricane Development
- 3.3 Understanding the Potential Impacts of a Hurricane
- 3.4 Related Searches: Another Hurricane Brewing
- 3.5 FAQs: Another Hurricane Brewing
- 3.6 Tips: Another Hurricane Brewing
- 3.7 Conclusion: Another Hurricane Brewing
- 4 Closure
The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation
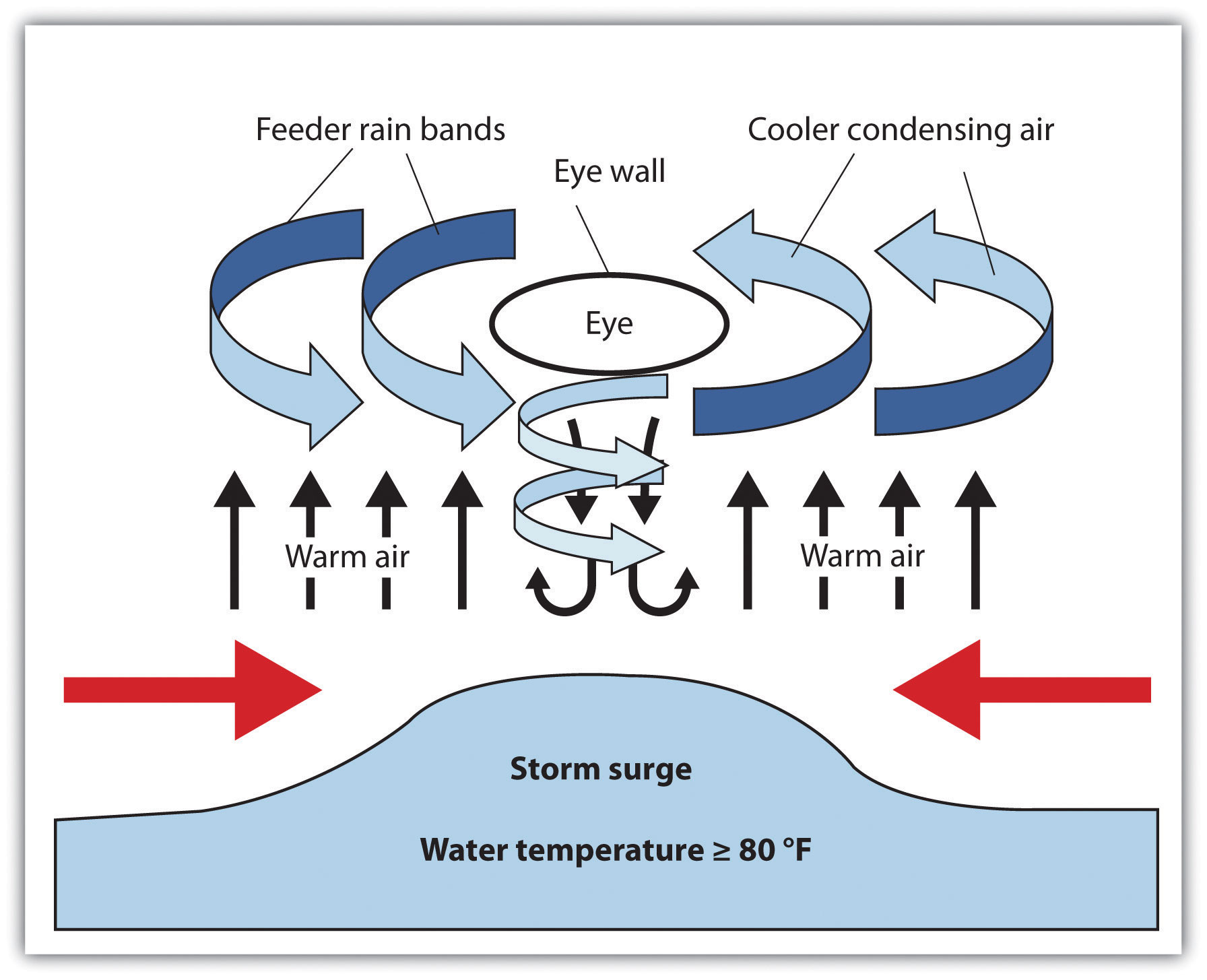
The term "another hurricane brewing" evokes a sense of impending danger, a natural phenomenon capable of wreaking havoc on coastal communities. While the phrase itself might sound ominous, it is crucial to understand the intricate processes that lead to the formation of these powerful storms.
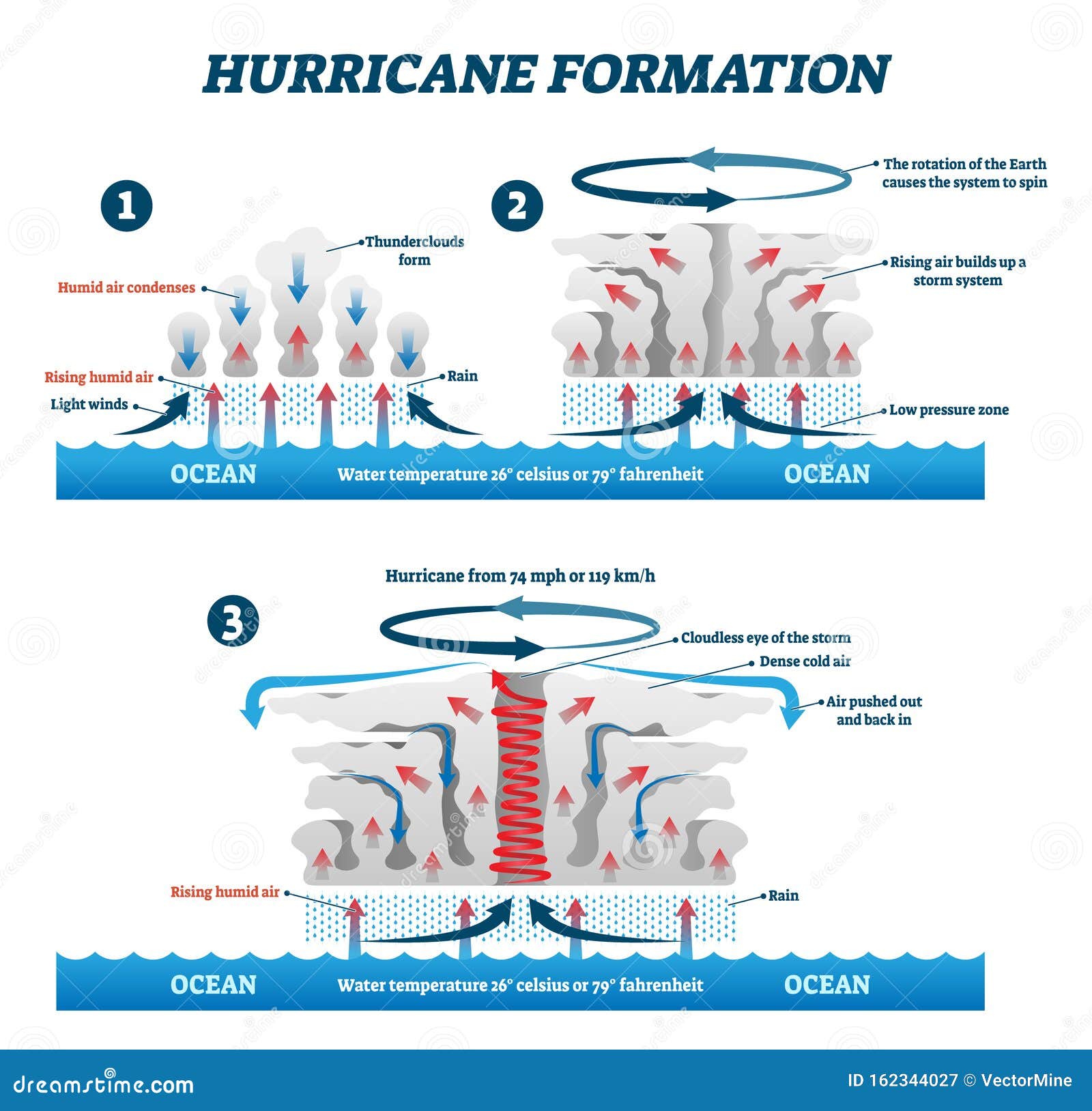
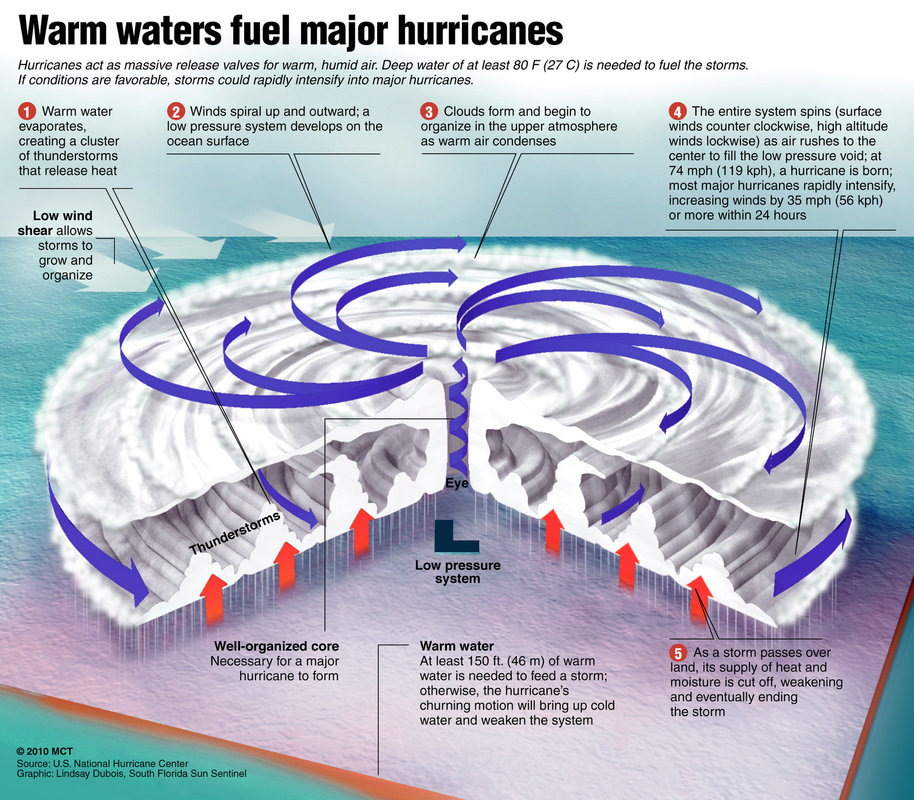
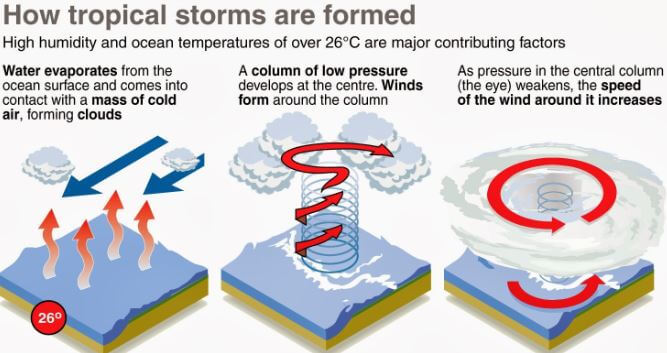
The development of a hurricane, often referred to as a tropical cyclone or typhoon, is a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions. It is not simply a matter of "another hurricane brewing," but rather a culmination of specific factors that create the perfect environment for these storms to form and intensify.
Understanding the Building Blocks of a Hurricane
1. Warm Ocean Waters: Hurricanes draw their energy from the heat stored in the upper layers of the ocean. Water temperatures exceeding 80°F (26.5°C) provide the necessary fuel for the storm to develop and intensify. The warmer the water, the more energy the hurricane can extract, leading to stronger winds and heavier rainfall.
2. Low Wind Shear: Wind shear refers to the change in wind speed and direction with height. Low wind shear allows the hurricane’s thunderstorms to develop vertically, creating a strong, well-defined central core. Conversely, high wind shear can disrupt the storm’s structure, preventing it from intensifying.
3. Pre-existing Disturbance: Hurricanes often form from pre-existing weather disturbances, such as tropical waves or low-pressure systems. These disturbances create areas of rising air and converging winds, providing a foundation for the hurricane’s development.
4. The Coriolis Effect: The Earth’s rotation influences the direction of the hurricane’s movement. The Coriolis effect causes the storm to rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
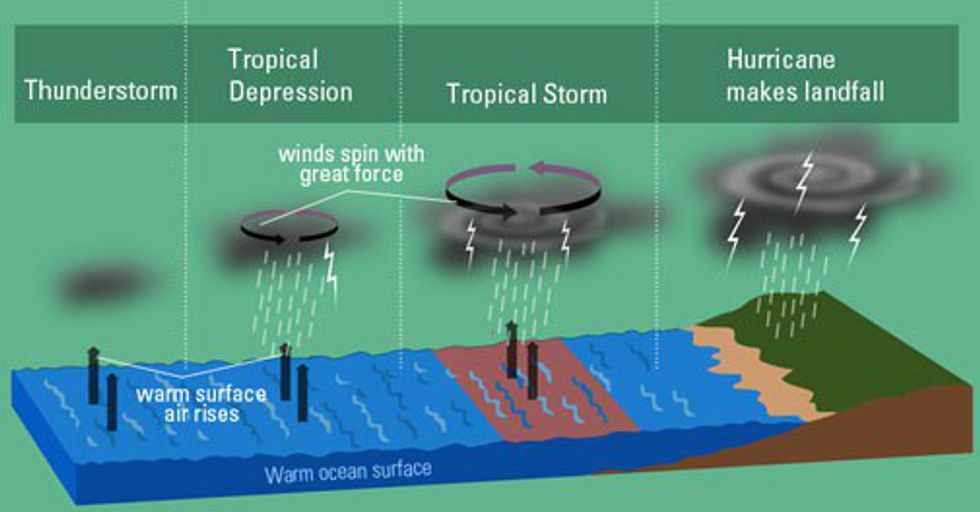
Exploring the Stages of Hurricane Development
The life cycle of a hurricane can be broadly divided into four stages:
1. Tropical Depression: This is the initial stage where the storm is characterized by organized thunderstorms with maximum sustained winds of less than 38 mph (62 km/h).
2. Tropical Storm: As the storm intensifies, it becomes a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds between 39 mph (63 km/h) and 73 mph (117 km/h). At this stage, the storm is given a name.
3. Hurricane: When the maximum sustained winds reach 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher, the storm is classified as a hurricane.
4. Post-Tropical Cyclone: As the hurricane moves over land or colder waters, it loses its source of energy and weakens. It may transition into a post-tropical cyclone, which retains some characteristics of a hurricane but lacks the warm core.
Understanding the Potential Impacts of a Hurricane
1. High Winds: Hurricanes are known for their powerful winds, capable of causing significant damage to buildings, trees, and infrastructure. The wind speed determines the hurricane’s category on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, ranging from Category 1 (74-95 mph) to Category 5 (over 157 mph).
2. Heavy Rainfall: Hurricanes produce torrential rainfall, leading to widespread flooding, landslides, and erosion. The amount of rainfall can vary greatly depending on the storm’s intensity and track.
3. Storm Surge: The most devastating effect of a hurricane is often the storm surge, a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds pushing water towards the coast. Storm surge can cause significant flooding and damage, particularly in low-lying coastal areas.
4. Coastal Erosion: The powerful waves and currents associated with hurricanes can cause significant erosion of beaches and coastlines.
5. Power Outages: Hurricanes can disrupt power grids, leaving communities without electricity for extended periods.
Related Searches: Another Hurricane Brewing
Understanding the dynamics of hurricane formation and their potential impacts is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts. Here are some related searches that provide further insights:
- Hurricane Season: Understanding the timing and duration of hurricane season for different regions is essential for preparedness.
- Hurricane Tracking: Real-time tracking of hurricanes allows for timely warnings and evacuations.
- Hurricane Forecasting: Advanced forecasting models help predict the intensity, track, and potential impacts of hurricanes.
- Hurricane Preparedness: Planning for hurricanes includes securing your home, creating an emergency kit, and knowing evacuation routes.
- Hurricane Recovery: Recovery efforts after a hurricane focus on restoring infrastructure, providing aid to affected communities, and rebuilding damaged areas.
- Hurricane History: Studying historical hurricane records helps understand the frequency, intensity, and potential impacts of future storms.
- Hurricane Mitigation: Implementing mitigation strategies such as coastal protection measures and building codes can reduce hurricane damage.
- Hurricane Research: Ongoing research aims to improve hurricane forecasting, understanding, and mitigation efforts.
FAQs: Another Hurricane Brewing
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane, a typhoon, and a cyclone?
A: These terms refer to the same phenomenon, a tropical cyclone, but they are used in different parts of the world. Hurricane is used in the North Atlantic, Central North Pacific, and Eastern North Pacific. Typhoon is used in the Northwest Pacific, while Cyclone is used in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
Q: How often do hurricanes occur?
A: The frequency of hurricanes varies depending on the region. In the North Atlantic, an average of 12 named storms form each year, with about 6 becoming hurricanes.
Q: How are hurricanes named?
A: Hurricanes are named by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) using a pre-determined list of names that rotate every six years. The names are chosen to be distinct and easy to remember.
Q: Can hurricanes be controlled or prevented?
A: Currently, there is no way to control or prevent hurricanes. However, research is ongoing to develop technologies that might influence their intensity or track.
Q: What should I do if a hurricane is approaching my area?
A: It is crucial to stay informed about the storm’s track and potential impacts. Follow the instructions of local authorities, secure your home, prepare an emergency kit, and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
Tips: Another Hurricane Brewing
- Stay informed: Follow weather reports and official advisories from local authorities.
- Prepare your home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and bring in outdoor furniture.
- Create an emergency kit: Include essential supplies like food, water, medication, flashlights, and batteries.
- Know your evacuation route: Identify the safest evacuation route and have a plan for where you will go if necessary.
- Listen to authorities: Follow instructions from local officials during a hurricane.
Conclusion: Another Hurricane Brewing
The term "another hurricane brewing" might sound ominous, but it highlights the cyclical nature of these powerful storms. While we cannot control the formation of hurricanes, understanding their dynamics, potential impacts, and taking necessary precautions can significantly reduce their devastating effects. By staying informed, preparing for the worst, and following official guidance, we can minimize the risks associated with these powerful storms.



![Dynamics of air flow in hurricane [16] Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pushpendra_Jain4/publication/281612751/figure/download/fig5/AS:670546983415823@1536882267338/Dynamics-of-air-flow-in-hurricane-16.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unseen Force: Understanding the Dynamics of Hurricane Formation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!