The Tropical Nine: A Cornerstone of Global Biodiversity
Related Articles: The Tropical Nine: A Cornerstone of Global Biodiversity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Tropical Nine: A Cornerstone of Global Biodiversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Tropical Nine: A Cornerstone of Global Biodiversity

The Earth’s biosphere is a complex tapestry woven from countless ecosystems, each harboring a unique assemblage of life. Among these ecosystems, the tropical regions stand out as hotspots of biodiversity, housing a disproportionately large share of the world’s species. Within this vibrant tapestry, a select group of nine countries, collectively known as the Tropical Nine, play a pivotal role in safeguarding global biodiversity.
Understanding the Tropical Nine
The Tropical Nine refers to the nine countries with the highest concentration of endemic plant and animal species:
- Brazil: Home to the Amazon rainforest, the world’s largest, Brazil boasts an extraordinary array of flora and fauna, including iconic species like the jaguar and the macaw.
- Colombia: With its diverse landscapes, including the Andes Mountains and the Amazon rainforest, Colombia is a haven for endemic species, such as the spectacled bear and the harlequin frog.
- Indonesia: Comprising thousands of islands, Indonesia harbors a rich biodiversity, with numerous endemic species like the Komodo dragon and the orangutan.
- Madagascar: An island nation off the coast of Africa, Madagascar is renowned for its unique flora and fauna, including the iconic lemur and the baobab tree.
- Mexico: With its varied topography, from deserts to rainforests, Mexico is home to a wide range of endemic species, such as the Mexican gray wolf and the vaquita.
- Peru: Sharing the Amazon rainforest with Brazil and Colombia, Peru is a biodiversity hotspot, with endemic species like the Andean condor and the giant otter.
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo: The Congo Basin rainforest is a major biodiversity reservoir, housing endemic species like the okapi and the bonobo.
- Ecuador: Nestled in the Andes Mountains, Ecuador is known for its diverse ecosystems, including the Galapagos Islands, which are home to unique and endemic species.
- Venezuela: With its vast rainforests and mountainous regions, Venezuela is a biodiversity hotspot, with endemic species like the Venezuelan Páramo tapir and the harpy eagle.
The Significance of the Tropical Nine
The Tropical Nine are not just repositories of biodiversity; they are critical to the health of the entire planet. Their ecosystems play a vital role in regulating global climate, providing essential ecosystem services like clean water and air, and supporting livelihoods through sustainable agriculture and tourism.
1. Climate Regulation: Tropical forests, particularly those found in the Tropical Nine, act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This helps mitigate climate change and its devastating effects.
2. Ecosystem Services: The Tropical Nine provide essential ecosystem services, including clean water, air purification, pollination, and soil fertility. These services are crucial for human well-being and economic development.
3. Biodiversity Conservation: The Tropical Nine are home to a disproportionate number of the world’s species, many of which are endemic to these countries. Their conservation is crucial for maintaining global biodiversity and preventing extinctions.
4. Sustainable Livelihoods: The Tropical Nine rely heavily on natural resources for their livelihoods. Sustainable agriculture, forestry, and tourism are vital sectors in these countries, and their continued success depends on the conservation of biodiversity.
Challenges Facing the Tropical Nine
Despite their significance, the Tropical Nine face numerous challenges that threaten their biodiversity and the well-being of their populations.
1. Habitat Loss and Degradation: Deforestation, driven by agriculture, logging, and mining, is a major threat to the Tropical Nine‘s ecosystems. Habitat loss and degradation lead to biodiversity loss, ecosystem dysfunction, and climate change.
2. Climate Change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are impacting the Tropical Nine‘s ecosystems, leading to species extinctions, habitat loss, and increased vulnerability to disease.
3. Illegal Wildlife Trade: The illegal trade in wildlife, driven by demand for exotic pets, traditional medicine, and bushmeat, is a major threat to the Tropical Nine‘s biodiversity.
4. Pollution: Industrial pollution, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste are contaminating the Tropical Nine‘s ecosystems, harming wildlife and human health.
5. Lack of Resources: The Tropical Nine often lack the financial and technical resources needed to effectively manage their biodiversity and address the challenges they face.
Solutions for the Tropical Nine
Addressing the challenges facing the Tropical Nine requires a multi-faceted approach that involves governments, communities, and international organizations.
1. Strengthening Conservation Efforts: Investing in protected areas, promoting sustainable land use practices, and tackling illegal wildlife trade are crucial for safeguarding biodiversity.
2. Addressing Climate Change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in renewable energy, and adapting to climate change are essential for mitigating its impacts on the Tropical Nine‘s ecosystems.
3. Promoting Sustainable Development: Developing sustainable economic activities, such as ecotourism and sustainable agriculture, can provide livelihoods while protecting biodiversity.
4. Empowering Local Communities: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts, promoting traditional ecological knowledge, and ensuring equitable benefit sharing are crucial for effective conservation.
5. International Cooperation: International cooperation, including financial assistance, technology transfer, and capacity building, is essential for supporting the Tropical Nine in their conservation efforts.
Related Searches
The Tropical Nine represent a focal point for understanding and addressing global biodiversity challenges. Further research and exploration into the following related topics can provide deeper insights:
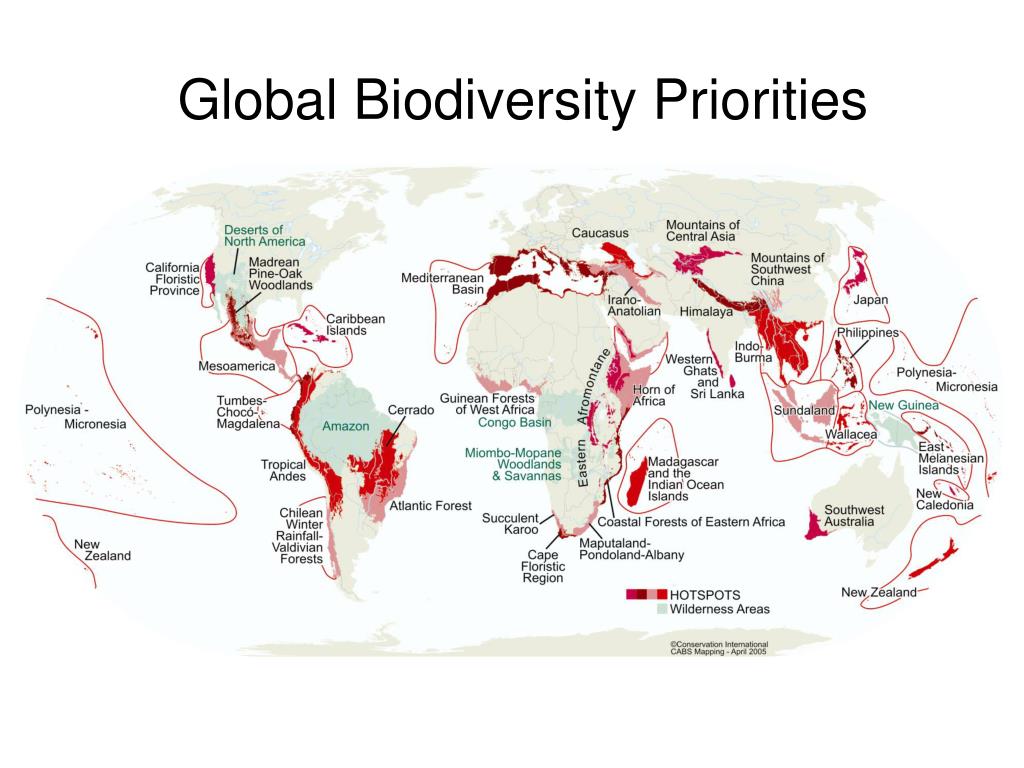
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The concept of biodiversity hotspots, including the Tropical Nine, and their importance in global conservation efforts.
- Endemic Species: A deeper understanding of endemic species, their unique adaptations, and the threats they face.
- Conservation Strategies: Exploring effective conservation strategies for protecting biodiversity, including protected areas, sustainable land management, and community-based conservation.
- Climate Change Impacts: Analyzing the specific impacts of climate change on the Tropical Nine, including changes in species distribution, habitat loss, and ecosystem services.
- Sustainable Development: Exploring sustainable development models that promote economic growth while protecting biodiversity, such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, and green technology.
- International Cooperation: Examining the role of international cooperation in supporting the Tropical Nine‘s conservation efforts, including financial assistance, technology transfer, and capacity building.
- Indigenous Knowledge: Recognizing and integrating indigenous knowledge and practices in biodiversity conservation efforts.
- Citizen Science: Exploring the role of citizen science in monitoring biodiversity and contributing to conservation efforts.
FAQs
1. Why are the Tropical Nine so important for global biodiversity?
The Tropical Nine are home to a disproportionately large share of the world’s species, many of which are endemic to these countries. Their ecosystems provide essential ecosystem services, regulate global climate, and support livelihoods.
2. What are the biggest threats to the Tropical Nine’s biodiversity?
The Tropical Nine face numerous threats, including habitat loss and degradation, climate change, illegal wildlife trade, pollution, and lack of resources.
3. What can be done to protect the Tropical Nine’s biodiversity?
Protecting the Tropical Nine‘s biodiversity requires a multi-faceted approach that involves strengthening conservation efforts, addressing climate change, promoting sustainable development, empowering local communities, and fostering international cooperation.
4. How can I help protect the Tropical Nine?
You can help protect the Tropical Nine by supporting conservation organizations, choosing sustainable products, reducing your carbon footprint, and advocating for policies that protect biodiversity.
Tips
- Learn about the Tropical Nine: Educate yourself about the biodiversity of the Tropical Nine, the challenges they face, and the conservation efforts underway.
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working to protect the Tropical Nine‘s biodiversity.
- Choose Sustainable Products: Support companies that practice sustainable forestry, agriculture, and tourism.
- Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Take steps to reduce your carbon footprint, such as using public transportation, conserving energy, and reducing consumption.
- Advocate for Biodiversity Protection: Contact your elected officials and advocate for policies that protect biodiversity and promote sustainable development.
Conclusion
The Tropical Nine are a vital part of the global biosphere, playing a critical role in maintaining biodiversity, regulating climate, and supporting livelihoods. Their conservation is essential for the well-being of the planet and its inhabitants. By understanding the challenges facing the Tropical Nine, supporting conservation efforts, and promoting sustainable development, we can help ensure that these biodiversity hotspots continue to thrive for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tropical Nine: A Cornerstone of Global Biodiversity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!