The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm
Related Articles: The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm
- 3.1 Understanding Hurricane Formation and Development
- 3.2 Hurricane Hazards: Understanding the Risks
- 3.3 Preparing for a Hurricane: Essential Steps
- 3.4 Related Searches:
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Hurricanes on the East Coast:
- 3.6 Tips for Staying Safe During a Hurricane:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm
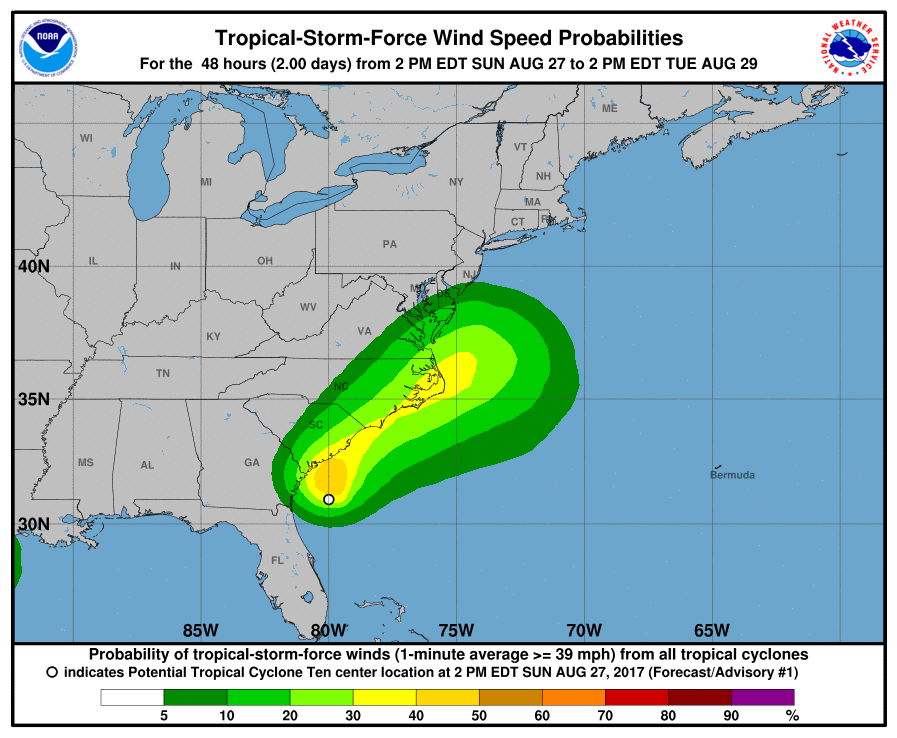
The Atlantic hurricane season, spanning from June 1st to November 30th, brings with it the annual threat of powerful storms that can devastate coastal communities. While the East Coast of the United States experiences its share of hurricanes each year, some years are marked by particularly intense storms. This article will delve into the intricacies of hurricanes impacting the East Coast, exploring their formation, potential dangers, and essential preparedness measures.
Understanding Hurricane Formation and Development
Hurricanes, categorized as tropical cyclones, are powerful rotating storms characterized by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges. They form over warm ocean waters, typically near the equator, where the water temperature is at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit.
1. Formation:
- Warm Ocean Water: The initial catalyst for hurricane formation is the presence of warm ocean water, which provides the necessary heat and moisture for the storm to develop. As warm, moist air rises, it cools and condenses, releasing latent heat that fuels the storm’s intensification.
- Low Wind Shear: Low wind shear, the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, is crucial for hurricane formation. Stable, low wind shear allows the storm’s circulation to develop and strengthen without being disrupted.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave or an area of low pressure, provides the initial spin and organization for the developing hurricane.
2. Development:
- Tropical Depression: A tropical depression is the initial stage of a hurricane, characterized by sustained winds of up to 38 miles per hour.
- Tropical Storm: As the storm intensifies, it becomes a tropical storm with sustained winds of 39-73 miles per hour. At this stage, the storm receives a name.
- Hurricane: When sustained winds reach 74 miles per hour or higher, the storm is classified as a hurricane. Hurricanes are further categorized into five categories based on wind speed, with Category 5 being the most intense.
3. Movement and Dissipation:
Hurricanes are guided by prevailing winds and steered by the Coriolis effect, a force caused by the Earth’s rotation. They typically move westward across the Atlantic, often curving northward as they encounter cooler waters or land.
Hurricanes can dissipate in several ways:
- Landfall: When a hurricane makes landfall, it loses its primary source of energy, warm ocean water. Friction with the land also weakens the storm.
- Cool Waters: As a hurricane moves over cooler waters, it loses its heat source and weakens.
- Wind Shear: High wind shear can disrupt the storm’s circulation, preventing it from strengthening or causing it to weaken.
Hurricane Hazards: Understanding the Risks
Hurricanes pose significant threats to coastal communities, including:
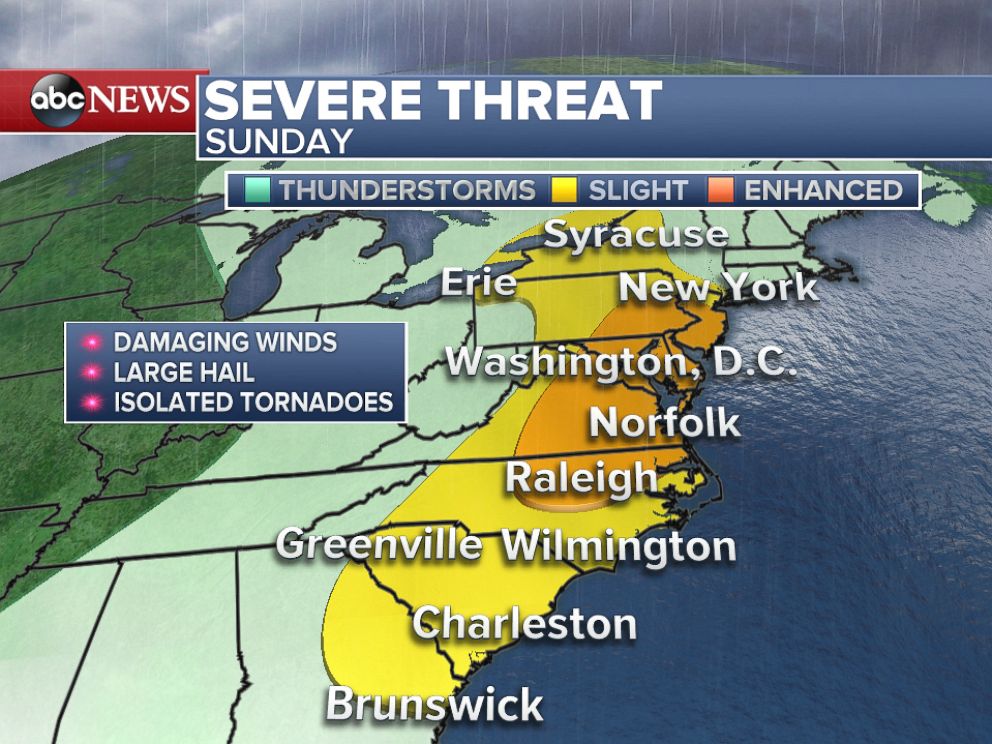
1. High Winds: Hurricane-force winds can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, trees, and power lines. These winds can also create dangerous flying debris, posing a serious threat to life and property.
2. Heavy Rainfall: Hurricanes produce torrential rainfall, leading to flooding, landslides, and erosion. Heavy rainfall can also overwhelm drainage systems, causing widespread damage and disruption.
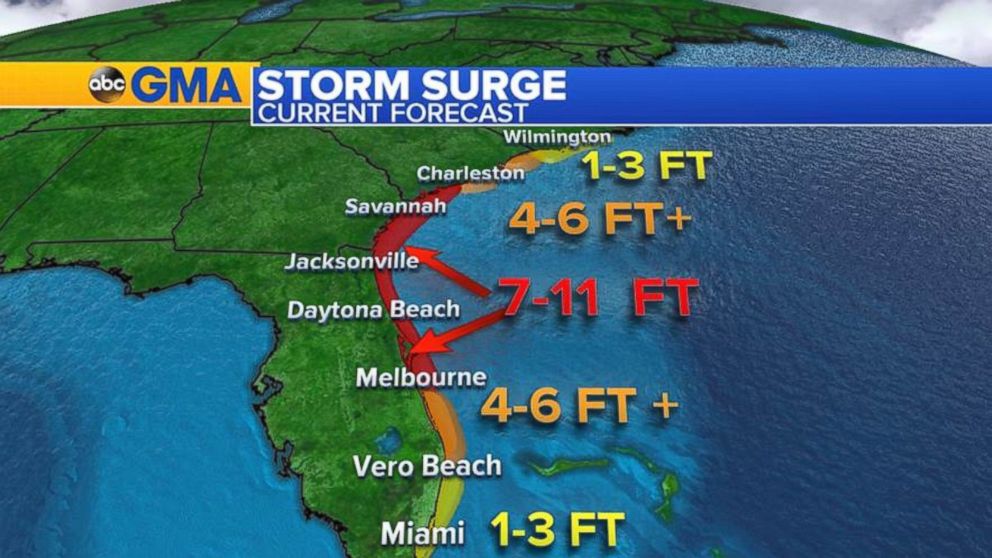
3. Storm Surge: One of the most devastating aspects of hurricanes is storm surge, a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds pushing water towards the shore. Storm surge can inundate coastal areas, causing significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
4. Tornadoes: Hurricanes can spawn tornadoes, which are intense rotating columns of air that can cause significant damage to structures and property.
5. Coastal Erosion: The combined forces of high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge can cause significant coastal erosion, leading to beach loss and damage to coastal infrastructure.
Preparing for a Hurricane: Essential Steps
1. Develop a Hurricane Plan: Create a plan that outlines evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies for your family.
2. Build an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit that includes non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, a battery-powered radio, flashlights, and other essential items.
3. Secure Your Home: Take steps to protect your home from hurricane damage, such as securing loose objects, trimming trees, and boarding up windows.
4. Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the instructions of local authorities.
5. Evacuate if Necessary: If authorities issue an evacuation order, heed the warning and evacuate to a safe location.
6. Be Prepared for Power Outages: Hurricanes can cause widespread power outages, so have a backup power source, such as a generator.
7. Check on Neighbors: Check on elderly neighbors or those with special needs to ensure their safety.
8. Be Patient: Recovery from a hurricane can take time. Be patient and follow the instructions of authorities.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Tracking Websites:
- National Hurricane Center (NHC): The NHC is the official source for hurricane information and forecasts. Their website provides real-time tracking of hurricanes, storm warnings, and advisories.
- NOAA National Weather Service: The National Weather Service provides detailed weather information and forecasts for the entire United States, including hurricane warnings and updates.
- AccuWeather: AccuWeather is a private weather forecasting service that provides detailed forecasts for hurricanes and other weather events.
2. Hurricane Preparedness Resources:
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): FEMA provides comprehensive resources on hurricane preparedness, including evacuation plans, emergency kit checklists, and disaster recovery assistance.
- American Red Cross: The Red Cross offers guidance on hurricane preparedness, including first-aid training, shelter information, and disaster relief services.
- Ready.gov: Ready.gov is a government website that provides comprehensive information on disaster preparedness, including hurricane preparedness tips and resources.
3. Hurricane History and Statistics:
- Hurricane History: The National Hurricane Center maintains a comprehensive database of past hurricanes, including their tracks, intensities, and damage records. This information is valuable for understanding historical hurricane patterns and predicting future events.
- Hurricane Statistics: The National Hurricane Center also compiles statistical data on hurricanes, such as the average number of storms each year, the most active hurricane seasons, and the strongest hurricanes on record.
4. Hurricane Impacts on Coastal Communities:
- Coastal Erosion: Hurricanes can cause significant coastal erosion, leading to beach loss, property damage, and increased vulnerability to future storms.
- Infrastructure Damage: Hurricanes can damage infrastructure, including roads, bridges, power lines, and communication systems, leading to disruptions in transportation, communication, and essential services.
- Economic Impacts: Hurricanes can have significant economic impacts, including lost revenue, property damage, and increased insurance costs.
5. Hurricane Safety Tips:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Evacuate if Necessary: If authorities issue an evacuation order, heed the warning and evacuate to a safe location.
- Secure Your Home: Take steps to protect your home from hurricane damage, such as securing loose objects, trimming trees, and boarding up windows.
- Be Prepared for Power Outages: Hurricanes can cause widespread power outages, so have a backup power source, such as a generator.
- Check on Neighbors: Check on elderly neighbors or those with special needs to ensure their safety.
6. Hurricane Recovery Efforts:
- Disaster Relief: The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provides financial assistance and other forms of disaster relief to individuals and communities affected by hurricanes.
- Community Recovery: Local communities often come together to help with hurricane recovery efforts, providing volunteer support, donating supplies, and rebuilding damaged infrastructure.
- Long-Term Recovery: Hurricane recovery is a long-term process, requiring ongoing efforts to rebuild infrastructure, revitalize economies, and address the social and environmental impacts of the storm.
7. Hurricane Research and Forecasting:
- Hurricane Forecasting: Advances in hurricane forecasting technology have significantly improved the accuracy of hurricane predictions, allowing for more effective warnings and evacuation plans.
- Climate Change and Hurricanes: Climate change is expected to influence hurricane activity, potentially leading to more intense and frequent storms. Research on the impacts of climate change on hurricanes is ongoing.
8. Hurricane Awareness and Education:
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about hurricane risks and preparedness is crucial for minimizing the impacts of these storms.
- Education Programs: Schools and community organizations can play a vital role in educating the public about hurricane safety, preparedness, and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Hurricanes on the East Coast:
1. What is the hurricane season on the East Coast?
The Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1st to November 30th. However, hurricanes can form outside of this period, although they are less common.
2. How often do hurricanes hit the East Coast?
The frequency of hurricanes hitting the East Coast varies from year to year. Some years experience multiple hurricanes, while others see none. The average number of hurricanes that make landfall on the East Coast is about one per year.
3. What are the most common hurricane threats to the East Coast?
The most common threats from hurricanes on the East Coast are:
- High winds: Hurricane-force winds can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, trees, and power lines.
- Heavy rainfall: Hurricanes produce torrential rainfall, leading to flooding, landslides, and erosion.
- Storm surge: Storm surge, a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds pushing water towards the shore, can inundate coastal areas, causing significant damage.
4. What are the best ways to prepare for a hurricane?
The best ways to prepare for a hurricane include:
- Developing a hurricane plan: This plan should outline evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies for your family.
- Building an emergency kit: This kit should include non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, a battery-powered radio, flashlights, and other essential items.
- Securing your home: Take steps to protect your home from hurricane damage, such as securing loose objects, trimming trees, and boarding up windows.
- Staying informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Evacuating if necessary: If authorities issue an evacuation order, heed the warning and evacuate to a safe location.
5. What should I do during a hurricane?
During a hurricane, it is crucial to:
- Stay indoors: Seek shelter in a safe location, preferably in a basement or on the lowest floor of your home.
- Avoid windows: Stay away from windows and doors to avoid flying debris.
- Listen to the radio: Monitor local radio stations for updates and instructions from authorities.
- Follow evacuation orders: If authorities issue an evacuation order, evacuate immediately.
- Be prepared for power outages: Hurricanes can cause widespread power outages, so have a backup power source, such as a generator.
6. What should I do after a hurricane?
After a hurricane, it is important to:
- Check for injuries: Check yourself and your family for injuries and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Assess damage: Assess the damage to your home and property and take steps to secure your home.
- Stay informed: Monitor local news and radio stations for updates on recovery efforts and safety guidelines.
- Avoid floodwaters: Stay away from floodwaters, as they can be contaminated with sewage and other hazardous materials.
- Be patient: Recovery from a hurricane can take time. Be patient and follow the instructions of authorities.
Tips for Staying Safe During a Hurricane:
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the instructions of local authorities.
- Evacuate if necessary: If authorities issue an evacuation order, evacuate immediately.
- Secure your home: Take steps to protect your home from hurricane damage, such as securing loose objects, trimming trees, and boarding up windows.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Assemble a kit that includes non-perishable food, water, first-aid supplies, a battery-powered radio, flashlights, and other essential items.
- Have a communication plan: Establish a plan for how to communicate with family and friends during and after the storm.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to potential hazards, such as downed power lines, flooding, and debris.
- Stay away from windows: During the storm, stay away from windows and doors to avoid flying debris.
- Listen to the radio: Monitor local radio stations for updates and instructions from authorities.
- Check on neighbors: Check on elderly neighbors or those with special needs to ensure their safety.
- Be patient: Recovery from a hurricane can take time. Be patient and follow the instructions of authorities.
Conclusion:
Hurricanes are powerful storms that can devastate coastal communities. Understanding the risks posed by these storms, preparing for their arrival, and following safety guidelines during and after a hurricane are essential steps for minimizing the impacts of these natural disasters. By staying informed, taking precautions, and working together, we can mitigate the risks and ensure the safety and well-being of our communities.
![]()





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Threat of Hurricanes on the East Coast: Understanding the Risks and Preparing for the Storm. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!