The Powerful Dance of the Winds: Understanding Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Related Articles: The Powerful Dance of the Winds: Understanding Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Powerful Dance of the Winds: Understanding Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerful Dance of the Winds: Understanding Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones

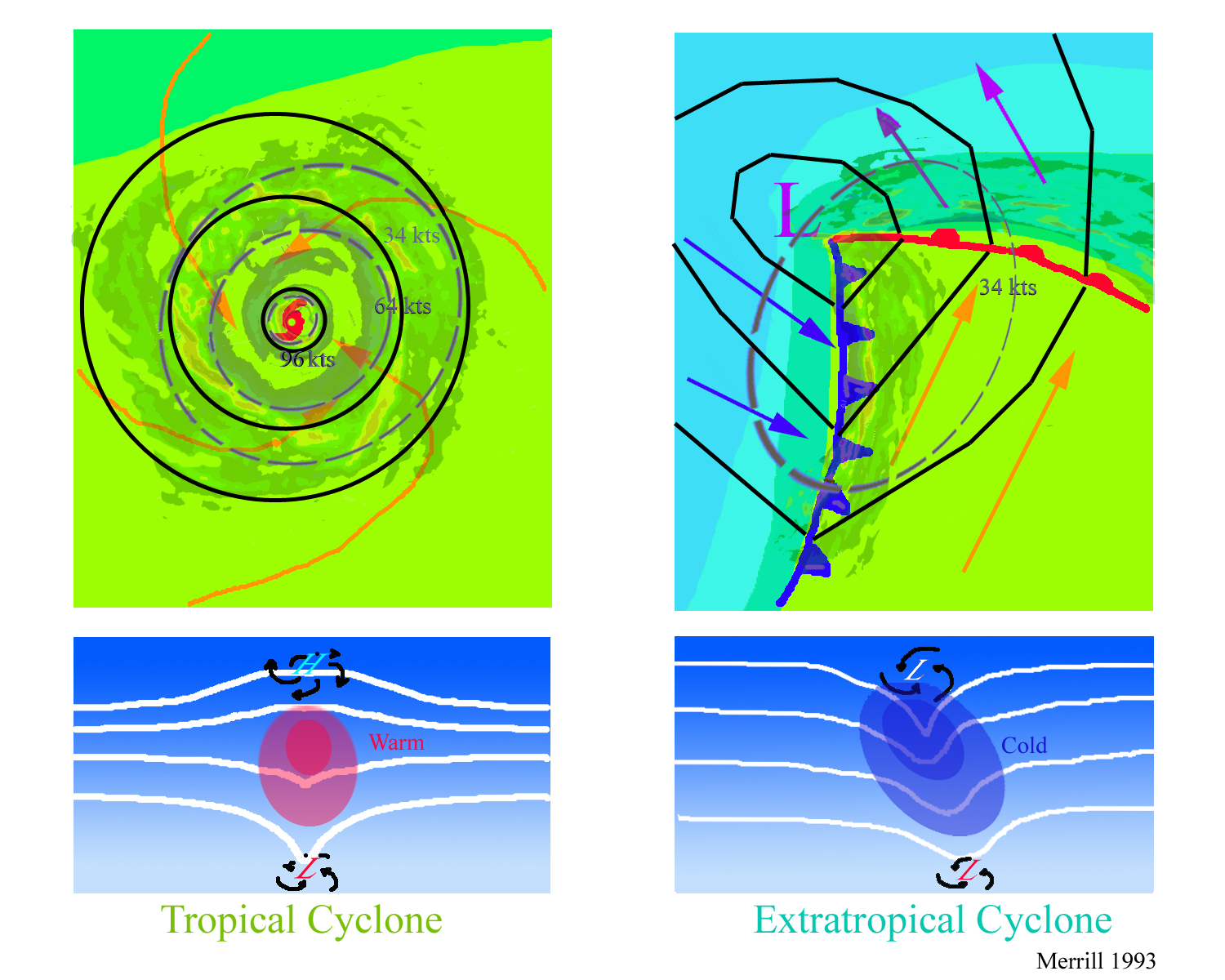
The Earth’s atmosphere is a dynamic system, constantly in motion. This movement manifests in various weather patterns, some mild and others incredibly powerful. Among these powerful forces of nature are tropical cyclones and extra-tropical cyclones, both capable of causing significant damage and disruption. While they share a common thread – rotating winds – they differ significantly in their formation, structure, and impact.
Unveiling the Essence of Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones are intense weather systems characterized by a low-pressure center and rotating winds that spiral inwards. They form over warm ocean waters near the equator, drawing energy from the latent heat released as warm, moist air rises and condenses. This process fuels the cyclone’s intensification, leading to powerful winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges.
The Birth of a Tropical Cyclone
The genesis of a tropical cyclone requires specific conditions:
- Warm Ocean Waters: The ocean surface temperature must be at least 26.5°C (80°F) to provide the necessary heat and moisture for the storm’s development.
- Low Wind Shear: Vertical wind shear, the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, must be minimal to allow the storm’s central low-pressure area to develop and intensify.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave or a cluster of thunderstorms, provides the initial trigger for the formation of a tropical cyclone.
The Anatomy of a Tropical Cyclone
A mature tropical cyclone exhibits a distinct structure:
- Eye: The calm center of the storm, characterized by clear skies and light winds.
- Eyewall: A ring of intense thunderstorms surrounding the eye, where the strongest winds and heaviest rainfall occur.
- Spiral Bands: Bands of thunderstorms extending outward from the eyewall, spiraling inwards towards the center of the storm.
Classifying the Intensity of Tropical Cyclones
The intensity of a tropical cyclone is measured by its wind speed, using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale for storms in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific basins, and the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale for storms in the Southern Hemisphere. These scales categorize storms based on wind speed into categories ranging from 1 (weakest) to 5 (strongest).
The Global Dance of Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones are known by different names depending on their location:
- Hurricanes: In the North Atlantic, Central North Pacific, and Eastern North Pacific.
- Typhoons: In the Northwest Pacific.
- Cyclones: In the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
While these names vary, the underlying phenomenon remains the same – a powerful rotating storm fueled by warm ocean waters.
The Impacts of Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones can cause significant damage and disruption, impacting human lives and infrastructure:
- Strong Winds: High-velocity winds can cause widespread damage to buildings, trees, and power lines.
- Heavy Rainfall: Torrential rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and infrastructure damage.
- Storm Surge: The rise in sea level caused by the storm’s powerful winds can inundate coastal areas, causing significant damage and loss of life.
- Coastal Erosion: Powerful waves and storm surge can erode coastlines, impacting coastal ecosystems and infrastructure.
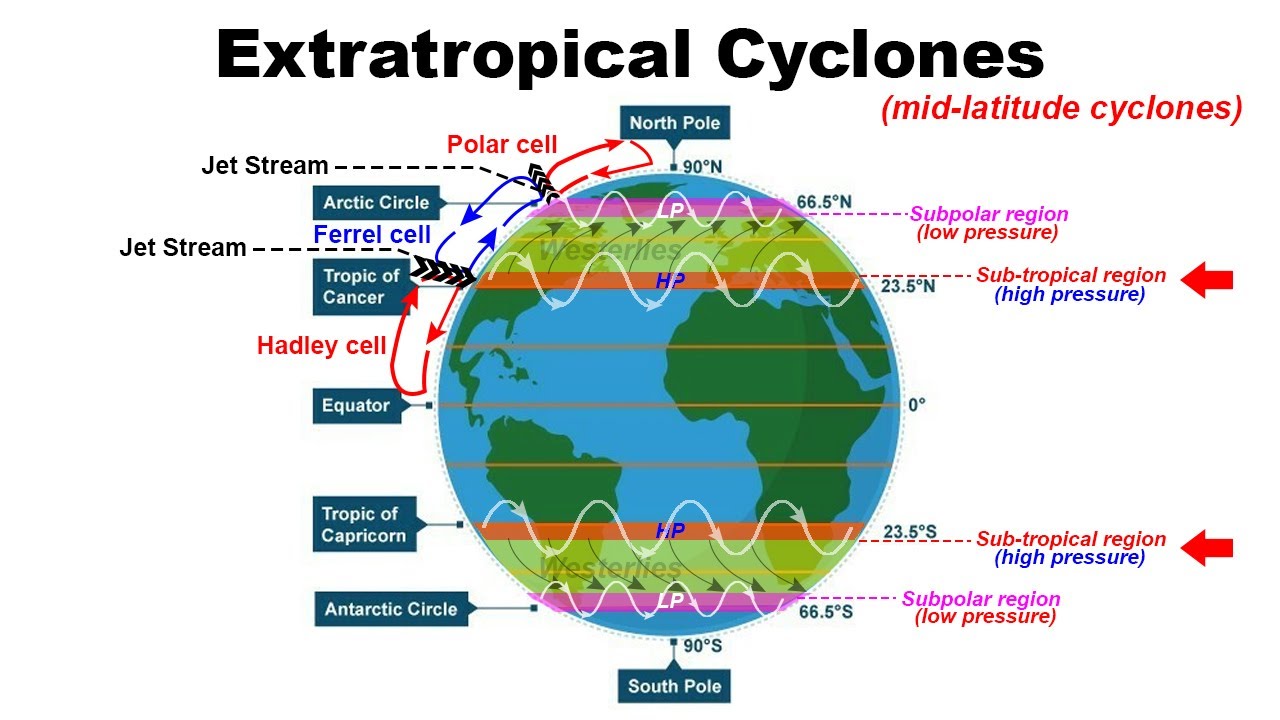
Understanding Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Unlike tropical cyclones, extra-tropical cyclones are large-scale weather systems that form in mid-latitudes, typically at the boundary between cold and warm air masses. They are driven by the temperature difference between these air masses, leading to a complex interplay of pressure gradients, wind patterns, and precipitation.
The Formation of Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Extra-tropical cyclones develop as a result of:
- Air Mass Contrast: The presence of a sharp temperature difference between cold and warm air masses.
- Jet Stream Interactions: The interaction of the jet stream, a fast-flowing current of air high in the atmosphere, with the temperature contrast can trigger the formation of a cyclone.
- Frontal Systems: The convergence of cold and warm fronts, leading to the development of a low-pressure center and the formation of a cyclone.
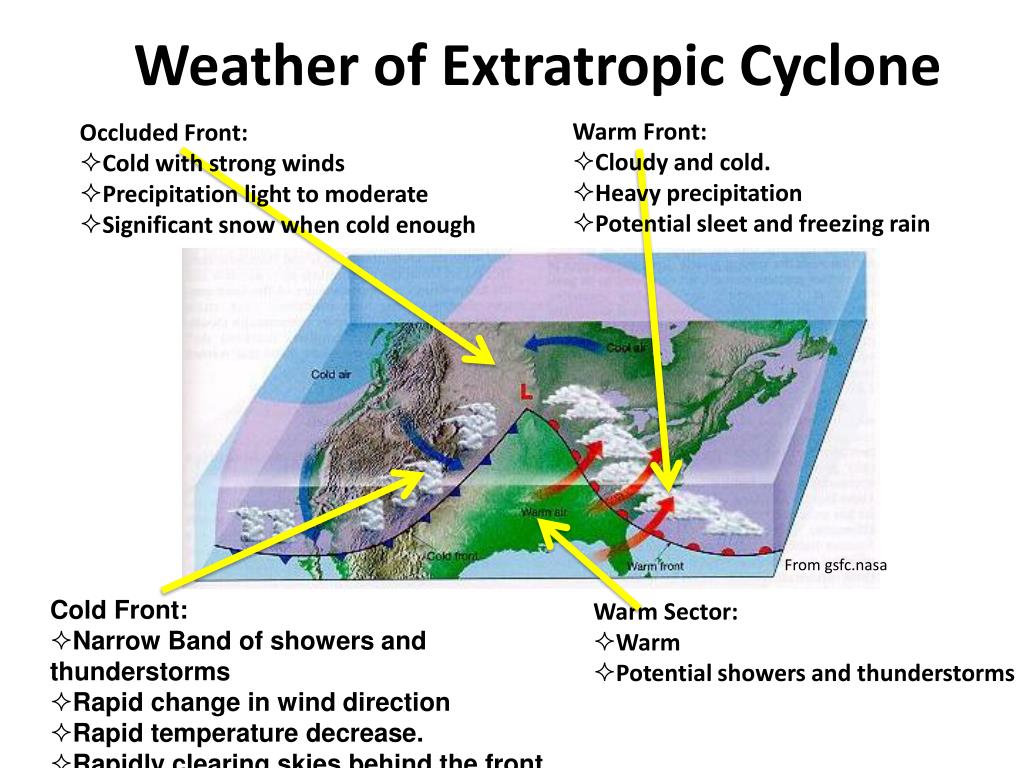
The Structure of Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Extra-tropical cyclones are characterized by:
- Wide Area: They cover a much larger area than tropical cyclones, spanning hundreds or even thousands of kilometers.
- Fronts: They are associated with distinct frontal systems, such as cold fronts, warm fronts, and stationary fronts.
- Wind Patterns: They exhibit a complex wind pattern, with winds rotating counter-clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Precipitation: They are often associated with widespread precipitation, including rain, snow, and sleet.
The Impacts of Extra-Tropical Cyclones
Extra-tropical cyclones can cause a range of impacts:
- Strong Winds: While not as intense as tropical cyclones, they can still produce strong winds that can cause damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Heavy Precipitation: They can produce heavy rain, snow, and sleet, leading to flooding, power outages, and transportation disruptions.
- Coastal Impacts: They can generate strong waves and storm surge, impacting coastal areas.
- Winter Storms: In colder regions, they can lead to severe winter storms, characterized by heavy snow, blizzards, and dangerously low temperatures.
Related Searches: Exploring Deeper Insights
- Tropical Cyclone Formation: This search explores the specific conditions and processes that lead to the formation of tropical cyclones, including the role of warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and pre-existing disturbances.
- Tropical Cyclone Intensity: This search focuses on the factors that influence the intensity of tropical cyclones, including the strength of the low-pressure center, the organization of thunderstorms, and the availability of heat and moisture.
- Tropical Cyclone Tracks: This search examines the movement of tropical cyclones, exploring the factors that influence their paths, including steering currents, wind patterns, and land interaction.
- Extra-Tropical Cyclone Formation: This search delves into the mechanisms behind the formation of extra-tropical cyclones, including the role of air mass contrast, jet stream interactions, and frontal systems.
- Extra-Tropical Cyclone Impacts: This search explores the various impacts of extra-tropical cyclones, including strong winds, heavy precipitation, coastal impacts, and winter storms.
- Tropical Cyclone Forecasting: This search investigates the methods and tools used to forecast the development, track, and intensity of tropical cyclones, highlighting the importance of accurate forecasting for disaster preparedness.
- Extra-Tropical Cyclone Forecasting: This search explores the challenges and advancements in forecasting extra-tropical cyclones, emphasizing the need for accurate predictions to mitigate their potential impacts.
- Climate Change and Cyclones: This search examines the potential influence of climate change on the frequency, intensity, and track of both tropical and extra-tropical cyclones, highlighting the importance of understanding these connections for future preparedness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the difference between a tropical cyclone and an extra-tropical cyclone?
A: The primary difference lies in their formation and energy source. Tropical cyclones form over warm ocean waters and are fueled by the release of latent heat, while extra-tropical cyclones form in mid-latitudes at the boundary between cold and warm air masses and are driven by the temperature difference between these air masses.
Q: How are tropical cyclones classified?
A: Tropical cyclones are classified based on their wind speed using scales such as the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale and the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale. These scales categorize storms into different categories based on their wind speed, ranging from 1 (weakest) to 5 (strongest).
Q: What are the dangers associated with tropical cyclones?
A: Tropical cyclones pose a variety of dangers, including strong winds, heavy rainfall, storm surge, coastal erosion, and landslides. These hazards can cause significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and ecosystems, and can lead to loss of life.
Q: What are the dangers associated with extra-tropical cyclones?
A: Extra-tropical cyclones can cause strong winds, heavy precipitation, coastal impacts, and winter storms. These hazards can result in damage to buildings, infrastructure, and transportation systems, and can lead to power outages, flooding, and other disruptions.
Q: How can we prepare for tropical and extra-tropical cyclones?
A: Preparation for tropical and extra-tropical cyclones involves understanding the potential risks, developing evacuation plans, securing property, and having emergency supplies readily available. Staying informed about weather forecasts and following official advisories is crucial for ensuring safety.
Tips for Staying Safe During Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and advisories from reliable sources.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit that includes essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Secure Your Home: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and board up windows.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Know your evacuation routes and have a plan for where you will go in case of an evacuation order.
- Follow Official Instructions: Heed warnings and instructions from authorities.
- Stay Indoors: During the storm, stay indoors and avoid unnecessary travel.
- Be Aware of Flooding: Stay away from flooded areas and avoid driving through floodwaters.
- Check on Neighbors: Check on elderly or disabled neighbors to ensure their safety.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power and Importance of Cyclones
Tropical and extra-tropical cyclones are powerful forces of nature that can cause significant damage and disruption. Understanding their formation, structure, and impacts is crucial for mitigating their effects and ensuring safety. By staying informed, preparing for potential hazards, and following official guidelines, we can minimize the risks associated with these storms and protect ourselves and our communities. While these cyclones can be destructive, they also play a crucial role in the global climate system, influencing weather patterns and distributing heat and moisture across the planet. Recognizing both the power and the importance of cyclones allows us to better understand and appreciate the complex dynamics of our planet’s atmosphere.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerful Dance of the Winds: Understanding Tropical and Extra-Tropical Cyclones. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!