The Path of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024: A Comprehensive Analysis
Related Articles: The Path of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Path of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024: A Comprehensive Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Path of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 marked the beginning of the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, a period characterized by the formation and development of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean. This storm, while relatively weak, served as a reminder of the potential hazards associated with these weather systems. Its path, though not particularly destructive, provided valuable insights into the dynamics of tropical storm formation and movement. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024’s path, exploring its formation, evolution, and impact.
Formation and Early Stages
Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the coast of Africa on June 1st, 2024. This wave, a trough of low pressure in the atmosphere, moved westward across the Atlantic Ocean, gradually organizing and developing into a tropical depression on June 4th. The depression intensified further, gaining tropical storm status on June 5th, 2024, and was officially named Arlene.
The storm’s early stages were characterized by a relatively slow movement across the Atlantic, with winds reaching up to 45 mph. This initial slow pace allowed for the storm to gather strength and develop a well-defined center of circulation.
Path and Evolution
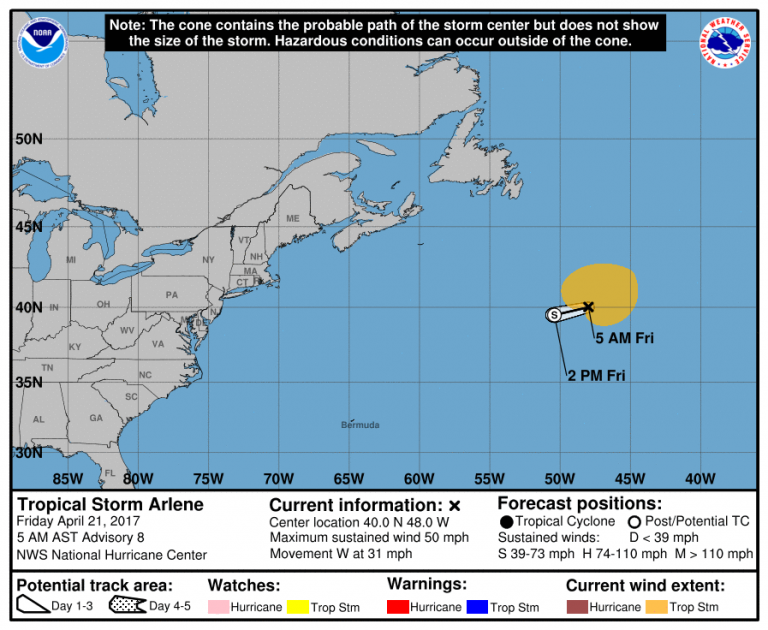
Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 followed a northward trajectory, moving towards the Lesser Antilles. Its path was influenced by the prevailing trade winds, which pushed the storm towards the west-northwest. As the storm progressed, it encountered a region of weak wind shear, a condition favorable for intensification.
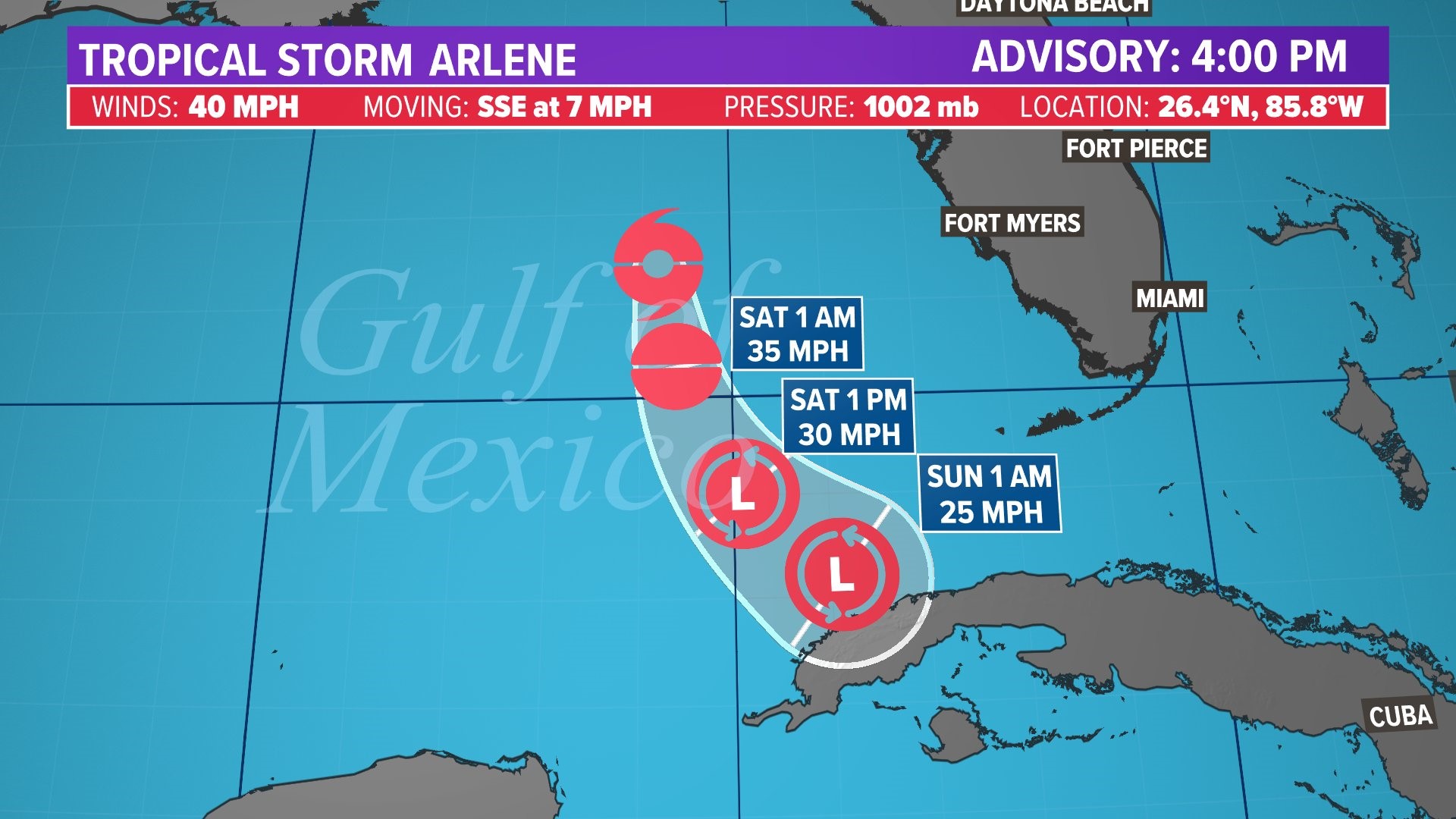
However, the storm’s path also led it into an area of cooler waters and dry air, factors that ultimately prevented Arlene from strengthening into a hurricane. Despite these limitations, the storm continued to move northward, reaching a peak intensity of 50 mph on June 7th, 2024.
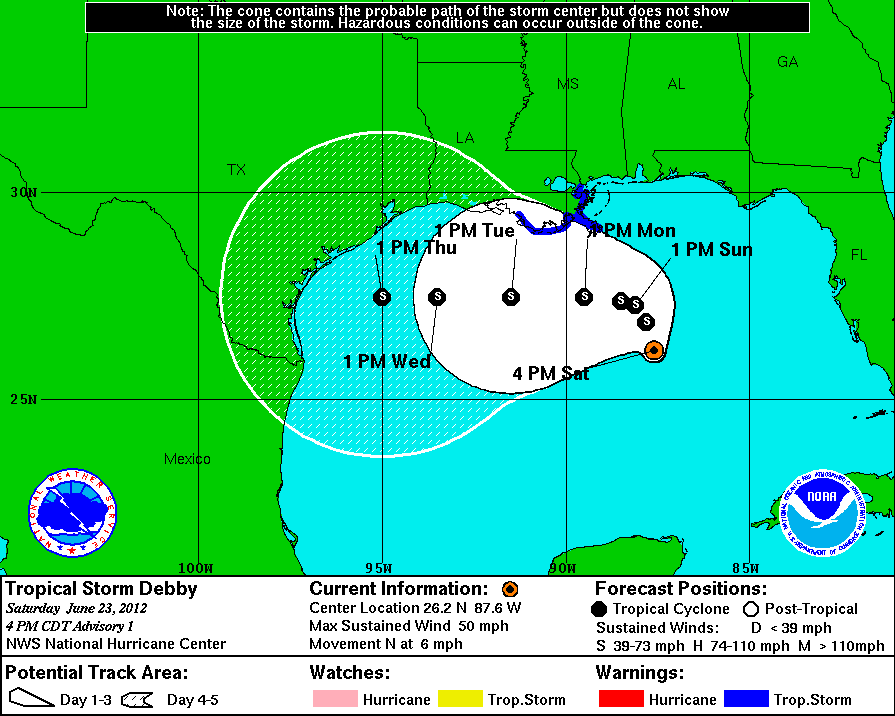
Impact and Landfall
Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 made landfall on the island of Bermuda on June 8th, 2024, with winds of 45 mph. While the storm’s impact on Bermuda was minimal, it brought heavy rainfall and gusty winds, causing some minor damage to infrastructure and disrupting travel. The storm’s passage over the island also led to localized flooding and coastal erosion.
Following its landfall in Bermuda, Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 continued its northward journey, losing intensity as it moved into colder waters. By June 9th, the storm had weakened to a tropical depression and subsequently dissipated over the open Atlantic Ocean.
Importance and Benefits
Despite its relatively short lifespan and limited impact, Tropical Storm Arlene 2024 provided valuable insights into the dynamics of tropical storm formation and movement. The storm’s path highlighted the influence of factors such as wind shear, water temperature, and air mass interaction on the development and intensification of tropical cyclones.
Furthermore, Arlene served as a reminder of the importance of preparedness during the hurricane season. The storm’s passage over Bermuda prompted authorities to implement emergency response protocols, ensuring the safety of residents and minimizing potential damage.
Related Searches
1. Atlantic Hurricane Season 2024
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 1st and ends on November 30th. This period is characterized by the formation and development of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has predicted an above-average hurricane season, with 12-17 named storms, 5-9 hurricanes, and 1-4 major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher). Understanding the seasonal outlook and potential hazards is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
2. Tropical Storm Formation
Tropical storms develop from tropical waves, disturbances in the atmosphere characterized by low pressure and organized thunderstorms. These waves, originating primarily from the coast of Africa, move westward across the Atlantic Ocean. Favorable conditions for tropical storm formation include warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and a pre-existing area of low pressure.
3. Wind Shear and Tropical Cyclones
Wind shear, a change in wind speed or direction with height, can significantly impact the development of tropical cyclones. Strong wind shear can disrupt the storm’s internal circulation, preventing its intensification. Conversely, weak wind shear allows for the formation of a well-defined center and the upward transport of moisture, contributing to the storm’s strengthening.
4. Hurricane Track Prediction
Predicting the path of a hurricane is a complex process involving multiple factors, including atmospheric pressure gradients, wind patterns, and the Coriolis effect. Meteorologists use sophisticated computer models and satellite imagery to track the storm’s movement and forecast its future trajectory. These predictions are essential for issuing timely warnings and evacuations, minimizing potential damage and loss of life.
5. Hurricane Preparedness
Hurricane preparedness involves taking proactive measures to minimize the impact of a storm. This includes developing emergency plans, securing homes and property, stocking emergency supplies, and staying informed about weather updates and warnings. Effective preparedness can significantly reduce the risk of injury, property damage, and disruption to daily life.
6. Hurricane Hazards
Hurricanes pose a multitude of hazards, including strong winds, heavy rainfall, storm surge, and tornadoes. These hazards can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, disrupt transportation systems, and lead to power outages. Understanding the specific hazards associated with a particular storm is crucial for effective mitigation and response efforts.
7. Bermuda’s Hurricane History
Bermuda, a small island nation located in the North Atlantic Ocean, has a long history of hurricane activity. The island has been struck by numerous hurricanes over the centuries, resulting in significant damage and loss of life. Understanding Bermuda’s hurricane history is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies and ensuring the island’s resilience to future storms.
8. Climate Change and Hurricanes
Climate change is expected to influence the intensity and frequency of hurricanes. Rising sea levels, warmer ocean temperatures, and changes in atmospheric circulation patterns are all factors that could contribute to more intense and destructive hurricanes. Understanding the potential impacts of climate change on hurricanes is crucial for developing long-term adaptation and mitigation strategies.
FAQs
1. What is a tropical storm?
A tropical storm is a rotating weather system characterized by sustained wind speeds of 39-73 mph. These storms typically form over tropical or subtropical waters and are classified as a stage in the development of a hurricane.
2. What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
The primary difference lies in wind speed. A hurricane is a more intense tropical cyclone with sustained wind speeds of 74 mph or higher. While both systems can bring heavy rainfall and storm surge, hurricanes are typically associated with more significant damage and potential for loss of life.
3. How does wind shear affect tropical storm development?
Wind shear, a change in wind speed or direction with height, can disrupt the internal circulation of a tropical storm, preventing its intensification. Strong wind shear can shear off the storm’s top, disrupting the upward transport of moisture and heat, which are essential for its growth.
4. What are the main hazards associated with tropical storms?
Tropical storms can pose a variety of hazards, including strong winds, heavy rainfall, storm surge, and tornadoes. These hazards can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, disrupt transportation systems, and lead to power outages.
5. How can I prepare for a tropical storm?
Hurricane preparedness involves taking proactive measures to minimize the impact of a storm. This includes developing emergency plans, securing homes and property, stocking emergency supplies, and staying informed about weather updates and warnings.
Tips
1. Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings issued by official sources such as the National Hurricane Center (NHC).
2. Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a plan that outlines evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies.
3. Secure Your Home: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and reinforce windows and doors.
4. Stock Emergency Supplies: Gather a supply of food, water, medicine, batteries, and other essential items.
5. Stay Safe During the Storm: Seek shelter during heavy winds and rainfall, avoid flooded areas, and stay informed about potential hazards.
Conclusion
Tropical Storm Arlene 2024, though relatively weak, served as a valuable reminder of the importance of hurricane preparedness and the complex dynamics of tropical storm formation and movement. The storm’s path highlighted the influence of factors such as wind shear, water temperature, and air mass interaction on the development and intensification of tropical cyclones.
The experience with Arlene underscores the need for continuous monitoring of weather patterns, proactive preparedness measures, and effective communication strategies to mitigate the risks associated with hurricane activity. By understanding the science behind these storms and taking appropriate precautions, we can minimize their impact and ensure the safety and well-being of communities in the path of future tropical cyclones.

![]()
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Path of Tropical Storm Arlene 2024: A Comprehensive Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!