The Journey of Tropical Storm Cindy: A Case Study in Hurricane Tracking
Related Articles: The Journey of Tropical Storm Cindy: A Case Study in Hurricane Tracking
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Journey of Tropical Storm Cindy: A Case Study in Hurricane Tracking. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Journey of Tropical Storm Cindy: A Case Study in Hurricane Tracking
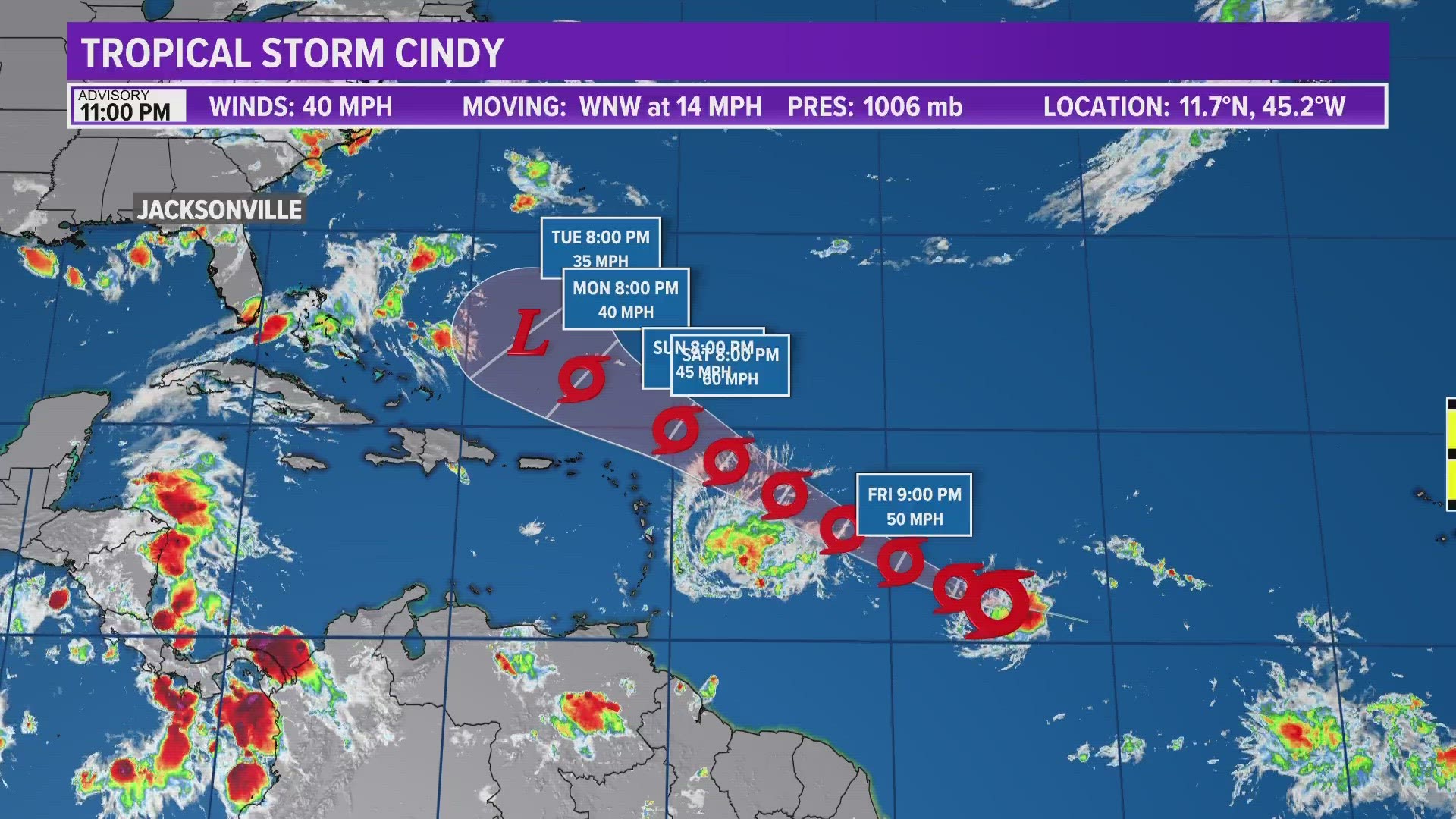
Tropical Storm Cindy, a relatively minor storm in the grand scheme of hurricane history, nevertheless serves as a valuable example of how meteorologists track and predict the path of tropical cyclones. Its journey in 2005, though not devastating, highlights the importance of understanding storm dynamics and the role of tropical storm Cindy path maps in mitigating potential damage.
Understanding the Path Map: A Visual Guide to Storm Progression
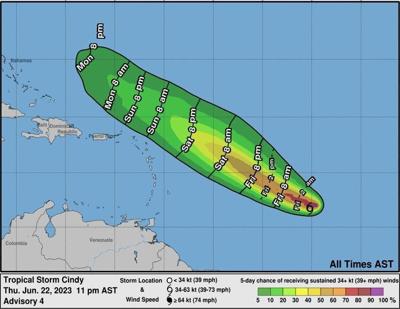
A tropical storm Cindy path map is a visual representation of the storm’s projected trajectory. It’s essentially a roadmap of the storm’s anticipated movement, factoring in factors like wind speed, direction, and pressure. These maps are crucial tools for:
- Public Safety: They provide vital information to emergency responders, enabling them to prepare for potential impacts and evacuate residents from vulnerable areas.
- Infrastructure Protection: Utilities, transportation networks, and other vital infrastructure can be proactively secured, minimizing disruptions and potential damage.
- Economic Stability: Businesses can prepare for potential closures, supply chain disruptions, and other economic impacts, minimizing losses.
The Genesis of Tropical Storm Cindy
Tropical Storm Cindy formed on June 27, 2005, in the central Atlantic Ocean. The storm’s initial path was relatively straightforward, moving westward at a moderate speed. However, as it approached the Caribbean Sea, it encountered complex atmospheric conditions that significantly altered its trajectory.
The Impact of Atmospheric Conditions
The tropical storm Cindy path map showed a significant shift in the storm’s direction as it encountered a complex interplay of atmospheric forces:
- Steering Currents: The prevailing winds in the region, known as steering currents, exerted a powerful influence on Cindy’s path. The storm’s interaction with these currents caused a noticeable change in its trajectory.
- High-Pressure Systems: High-pressure systems, characterized by descending air, can act as barriers to storm movement. Cindy’s path was noticeably affected by the presence of a high-pressure system to its north, forcing it to turn towards the west.
- Low-Pressure Systems: Low-pressure systems, characterized by rising air, can draw storms towards them. Cindy’s trajectory was also influenced by a low-pressure system to its south, pulling it westward.
Navigating the Caribbean: A Challenging Journey
As Cindy moved through the Caribbean, it encountered a complex tapestry of atmospheric conditions. The storm’s path became less predictable, and the tropical storm Cindy path map underwent frequent revisions.
- Island Chains: The presence of island chains, like the Lesser Antilles, can disrupt a storm’s flow, causing it to change direction or intensify. Cindy’s path was noticeably affected by its interaction with these island chains.
- Warm Ocean Waters: Warm ocean waters provide fuel for tropical cyclones, allowing them to gain strength and sustain themselves. Cindy’s passage over the warm waters of the Caribbean contributed to its intensification.
- Wind Shear: Wind shear, the change in wind speed or direction with altitude, can weaken or disrupt storms. Cindy experienced periods of wind shear, which contributed to its weakening as it moved westward.
The Storm’s Landfall and Dissipation
After traversing the Caribbean, Cindy made landfall on the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico on July 1, 2005. The storm weakened significantly upon landfall, losing much of its intensity. It continued westward across Mexico, eventually dissipating over land on July 2.
The Importance of Constant Monitoring and Adjustment
The tropical storm Cindy path map was a dynamic tool, constantly evolving as new data became available. Meteorologists continuously monitored Cindy’s progress, adjusting the path map as the storm’s trajectory changed. This dynamic approach ensured that the information provided was as accurate as possible, allowing for effective preparation and mitigation efforts.
Related Searches: 2005 Hurricane Season, Tropical Cyclone Formation, Hurricane Tracking Technology, Hurricane Forecasting, Weather Prediction Models, Natural Disaster Preparedness, Hurricane Impacts, Caribbean Climate
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A: A tropical storm is classified as a tropical cyclone with sustained wind speeds between 39 and 73 mph. A hurricane is a more intense tropical cyclone with sustained wind speeds of 74 mph or higher.
Q: Why is it important to track the path of a tropical storm?
A: Tracking the path of a tropical storm is crucial for public safety, infrastructure protection, and economic stability. It allows for timely warnings and preparation measures to minimize potential damage.
Q: What factors influence the path of a tropical storm?
A: The path of a tropical storm is influenced by various factors, including steering currents, high-pressure systems, low-pressure systems, island chains, warm ocean waters, and wind shear.
Q: How do meteorologists predict the path of a tropical storm?
A: Meteorologists use sophisticated computer models and weather data to predict the path of a tropical storm. They analyze factors like wind speed, direction, pressure, and atmospheric conditions.
Q: What are the potential impacts of a tropical storm?
A: Tropical storms can cause significant damage, including flooding, storm surge, high winds, landslides, and power outages.
Tips
- Stay informed: Follow official weather reports and advisories from reputable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
- Have a plan: Develop a family emergency plan that includes evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies.
- Prepare your home: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and ensure your home is properly insured.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to weather warnings and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
Conclusion
The journey of Tropical Storm Cindy, though not a major event, serves as a powerful illustration of the importance of tropical storm Cindy path maps. These maps are essential tools for understanding the dynamics of tropical cyclones, allowing for timely preparation and mitigation efforts. By tracking the path of storms like Cindy, we can better prepare for the challenges they pose, minimizing potential damage and ensuring the safety of communities.




![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Journey of Tropical Storm Cindy: A Case Study in Hurricane Tracking. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!