The Impact of Hurricane Beryl: A Comprehensive Look at a Significant Atlantic Storm
Related Articles: The Impact of Hurricane Beryl: A Comprehensive Look at a Significant Atlantic Storm
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Impact of Hurricane Beryl: A Comprehensive Look at a Significant Atlantic Storm. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Impact of Hurricane Beryl: A Comprehensive Look at a Significant Atlantic Storm

Hurricane Beryl, a significant storm that formed in the Atlantic Ocean in 2000, serves as a reminder of the potent and unpredictable nature of these powerful weather systems. While Beryl did not directly impact land, its path and intensity illustrate the importance of hurricane preparedness and the ongoing need to understand and predict these natural phenomena.
Hurricane Beryl’s Formation and Trajectory:
Beryl originated as a tropical wave that emerged off the coast of Africa on August 28, 2000. The wave quickly organized and strengthened, attaining tropical storm status on August 31st, and becoming a hurricane on September 1st. Beryl’s initial trajectory was westward, but it gradually curved northward, eventually reaching Category 1 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Beryl’s Impact and Significance:
Though Beryl never made landfall, its presence significantly impacted the weather patterns in the Atlantic region. The storm generated heavy rains and rough seas across a wide swathe of the ocean, impacting shipping and maritime activities. While the direct impact of Beryl was minimal, its trajectory and intensity highlighted the potential for significant damage should a hurricane of similar strength make landfall.
Understanding the Importance of Hurricane Beryl:
Hurricane Beryl serves as a valuable case study for understanding the complexities of hurricane formation and development. The storm’s trajectory and intensity were influenced by a number of factors, including the presence of a strong upper-level trough, the interaction with a nearby high-pressure system, and the prevailing wind patterns in the Atlantic. Analyzing these factors helps meteorologists refine their predictive models and improve hurricane forecasting.
Related Searches:
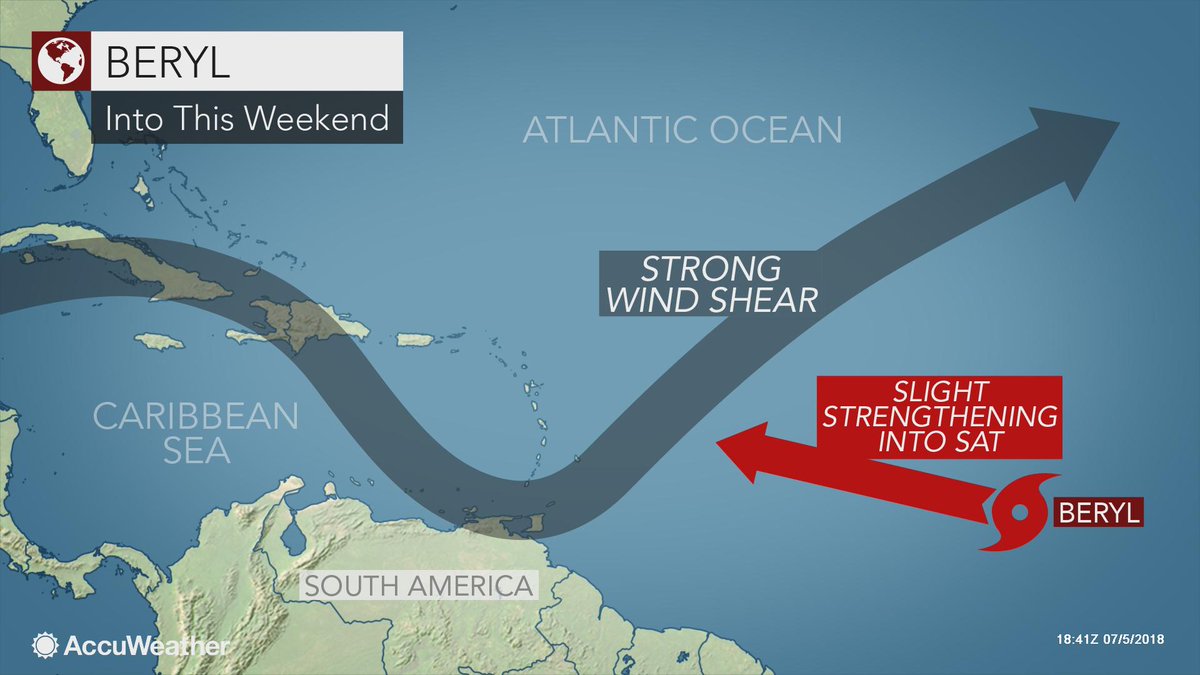
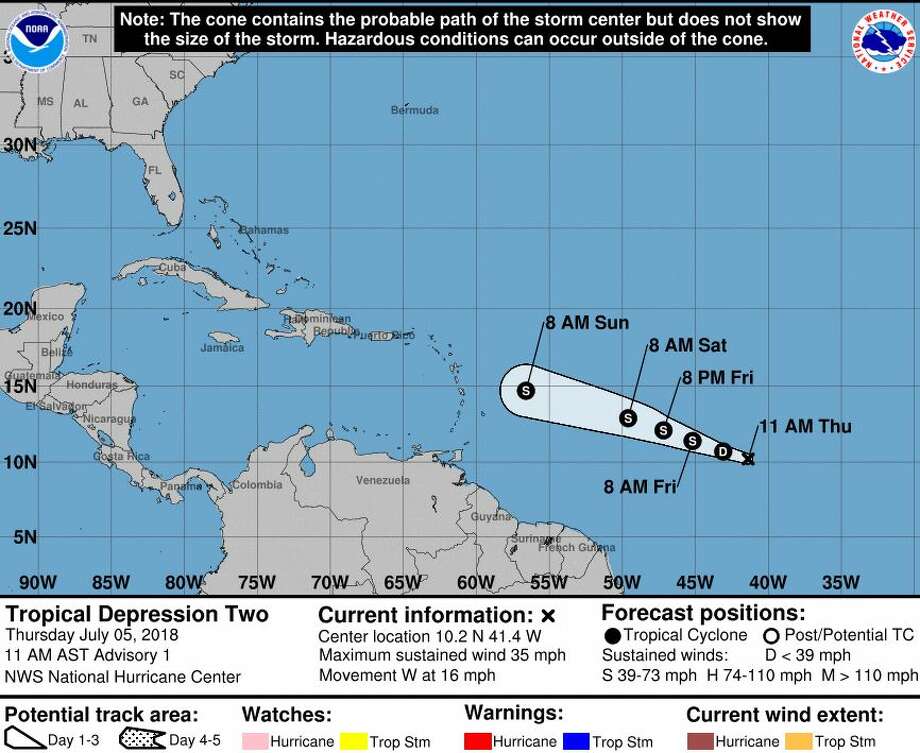
1. Hurricane Beryl Path: Beryl’s path was initially westward, but it gradually curved northward, eventually reaching a position east of the Bahamas. The storm’s trajectory was influenced by a number of factors, including the presence of a strong upper-level trough and the interaction with a nearby high-pressure system.
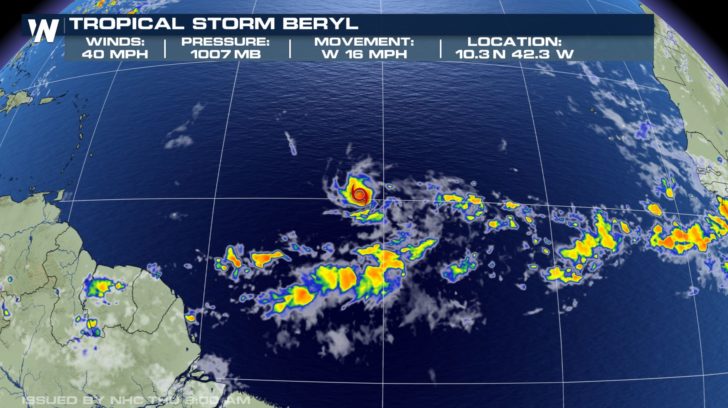
2. Hurricane Beryl Wind Speed: At its peak, Beryl reached Category 1 intensity with maximum sustained wind speeds of 75 mph (120 km/h). While Beryl did not make landfall, its strong winds posed a significant threat to shipping and maritime activities.
3. Hurricane Beryl Rainfall: Beryl generated heavy rainfall across a wide swathe of the Atlantic Ocean. The storm’s rainfall was particularly significant in the eastern Caribbean, where it caused localized flooding and landslides.
4. Hurricane Beryl Damage: While Beryl did not directly impact land, its heavy rains and strong winds caused significant damage to shipping and maritime infrastructure. The storm also disrupted air travel and caused power outages in some areas.
5. Hurricane Beryl History: Beryl was the eighth named storm of the 2000 Atlantic hurricane season. It was a relatively short-lived storm, lasting only about a week. However, Beryl’s intensity and trajectory highlighted the potential for significant damage should a hurricane of similar strength make landfall.
6. Hurricane Beryl Track: Beryl’s track was initially westward, but it gradually curved northward, eventually reaching a position east of the Bahamas. The storm’s track was influenced by a number of factors, including the presence of a strong upper-level trough and the interaction with a nearby high-pressure system.
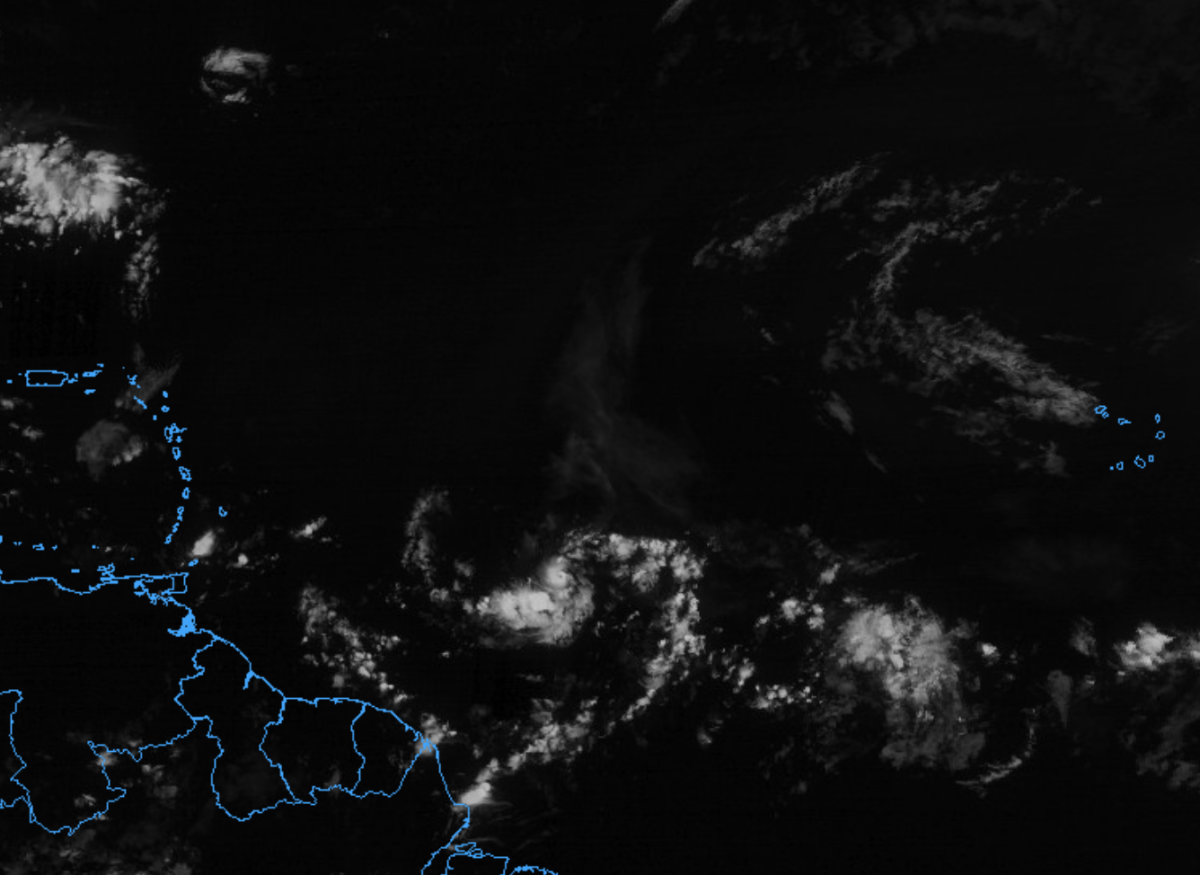
7. Hurricane Beryl Satellite Images: Satellite images of Hurricane Beryl provided valuable insights into the storm’s structure and development. These images allowed meteorologists to track the storm’s movement and intensity, and to predict its potential impact.
8. Hurricane Beryl Forecast: Forecasts for Hurricane Beryl were relatively accurate, predicting the storm’s trajectory and intensity with a high degree of confidence. These accurate forecasts allowed authorities to issue timely warnings and prepare for the storm’s potential impact.
FAQs about Hurricane Beryl:
Q: Did Hurricane Beryl make landfall?
A: No, Hurricane Beryl did not make landfall. The storm remained out at sea throughout its duration.
Q: What was the highest category of Hurricane Beryl?
A: Hurricane Beryl reached Category 1 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Q: How long did Hurricane Beryl last?
A: Hurricane Beryl lasted for approximately one week, from August 28th to September 4th, 2000.
Q: What were the main impacts of Hurricane Beryl?
A: Hurricane Beryl generated heavy rains and rough seas across a wide swathe of the Atlantic Ocean, impacting shipping and maritime activities. The storm also caused localized flooding and landslides in the eastern Caribbean.
Tips for Preparing for Hurricanes:
1. Develop a Hurricane Plan: Create a plan that outlines your family’s evacuation route, communication strategy, and emergency supplies.
2. Secure Your Home: Strengthen your home’s structure by securing windows, doors, and roofs. Trim trees and remove loose objects from your yard.
3. Assemble an Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit that includes essential items such as food, water, medicine, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
4. Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from local authorities. Be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
5. Stay Safe: If you are in a hurricane’s path, take shelter in a safe location. Avoid driving during the storm, and be aware of downed power lines and other hazards.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Beryl, while not directly impacting land, serves as a reminder of the potential dangers posed by hurricanes. The storm’s trajectory and intensity highlight the importance of hurricane preparedness and the ongoing need to understand and predict these powerful weather systems. By learning from events like Hurricane Beryl, we can better prepare for future storms and minimize their potential impact.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Impact of Hurricane Beryl: A Comprehensive Look at a Significant Atlantic Storm. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!