The Genesis of a Hurricane: A Comprehensive Guide to the Formation and Development of a Powerful Storm
Related Articles: The Genesis of a Hurricane: A Comprehensive Guide to the Formation and Development of a Powerful Storm
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Genesis of a Hurricane: A Comprehensive Guide to the Formation and Development of a Powerful Storm. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Genesis of a Hurricane: A Comprehensive Guide to the Formation and Development of a Powerful Storm
Hurricanes, also known as cyclones or typhoons, are among nature’s most formidable forces. These rotating storms, characterized by intense winds, torrential rain, and storm surges, can cause widespread devastation. Understanding the formation and development of these powerful weather systems is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.
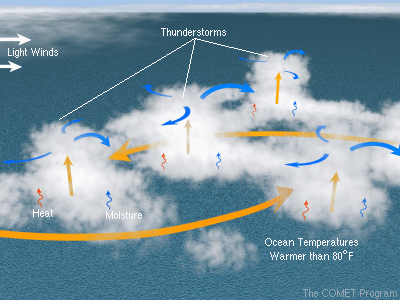
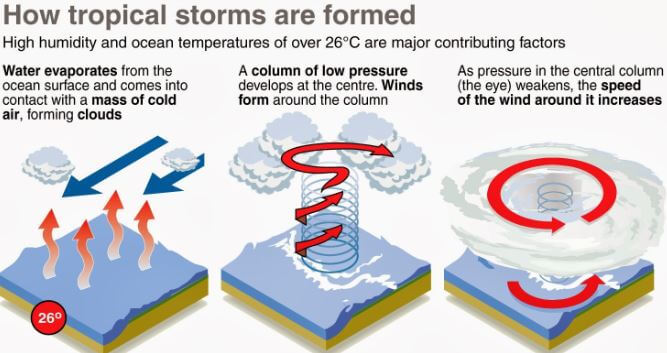
The Birthplace of a Hurricane: Warm Ocean Waters
Hurricanes are born over warm ocean waters, specifically in areas where the sea surface temperature is at least 80°F (26.5°C). This warm water provides the necessary heat and moisture to fuel the storm’s development. The heat energy is transferred from the warm ocean to the air above, creating a cycle of rising air and condensation. This process releases latent heat, further warming the air and creating an unstable atmosphere.
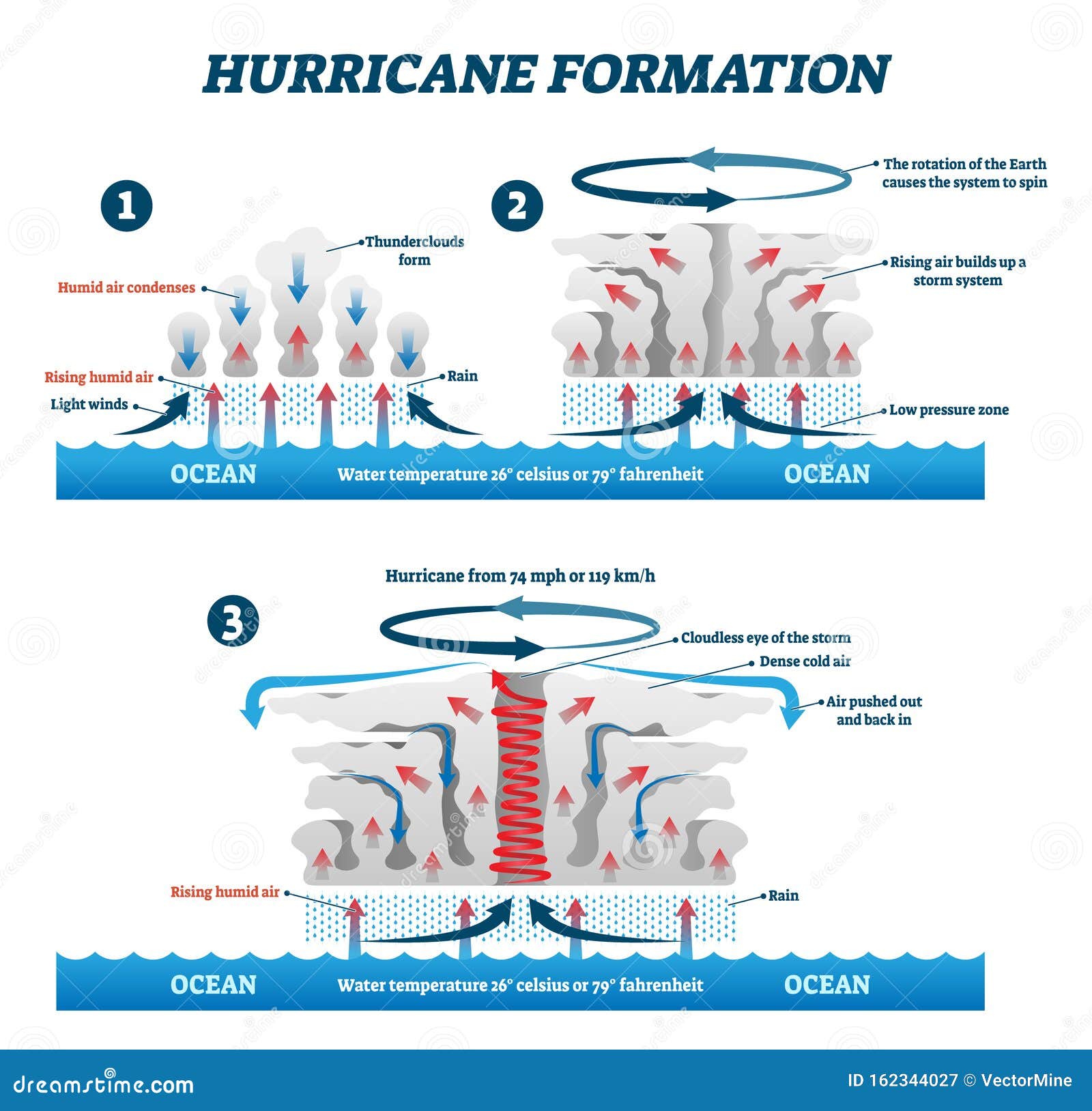
The Role of the Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect, a consequence of the Earth’s rotation, plays a crucial role in the formation of hurricanes. As air rises and rotates around a low-pressure center, the Earth’s rotation deflects the wind to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This deflection creates a spinning motion, allowing the storm to organize and intensify.
The Ingredients for a Hurricane’s Growth
For a tropical disturbance to develop into a hurricane, several additional factors must be present:
- Low Wind Shear: Wind shear, the change in wind speed or direction with altitude, can disrupt the organization of a storm. Low wind shear allows the storm’s central column of rising air, known as the eyewall, to remain intact and intensify.
- Pre-Existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave or an area of low pressure, provides the initial structure around which a hurricane can organize.
- Moist Air: Abundant moisture in the atmosphere is essential for the formation of clouds and rainfall, which are key components of a hurricane’s energy cycle.
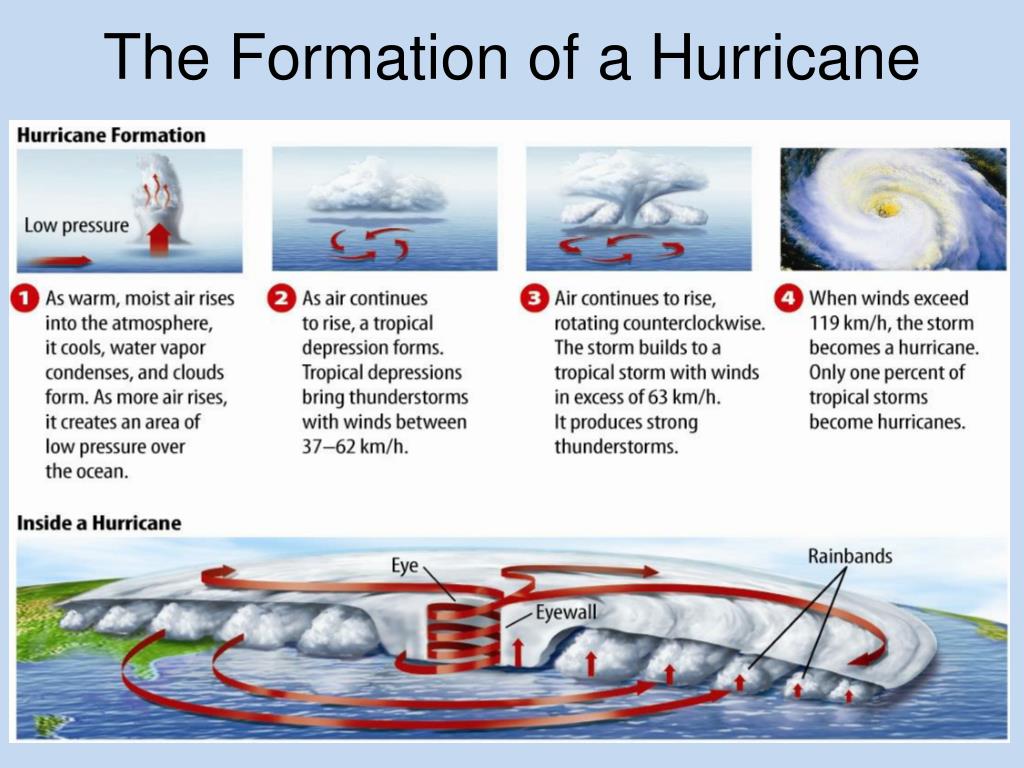
The Stages of Hurricane Development
Hurricanes develop in stages, each characterized by distinct features:
- Tropical Depression: A tropical depression is a closed circulation of winds with maximum sustained wind speeds of up to 38 mph (61 km/h). It is characterized by organized thunderstorms and a well-defined center of low pressure.
- Tropical Storm: A tropical storm is a more organized system with maximum sustained wind speeds between 39 mph (63 km/h) and 73 mph (117 km/h). It develops a more defined eyewall and a wider band of thunderstorms.
- Hurricane: A hurricane is a mature tropical cyclone with maximum sustained wind speeds of at least 74 mph (119 km/h). It possesses a distinct eye, a region of calm weather surrounded by the intense eyewall.
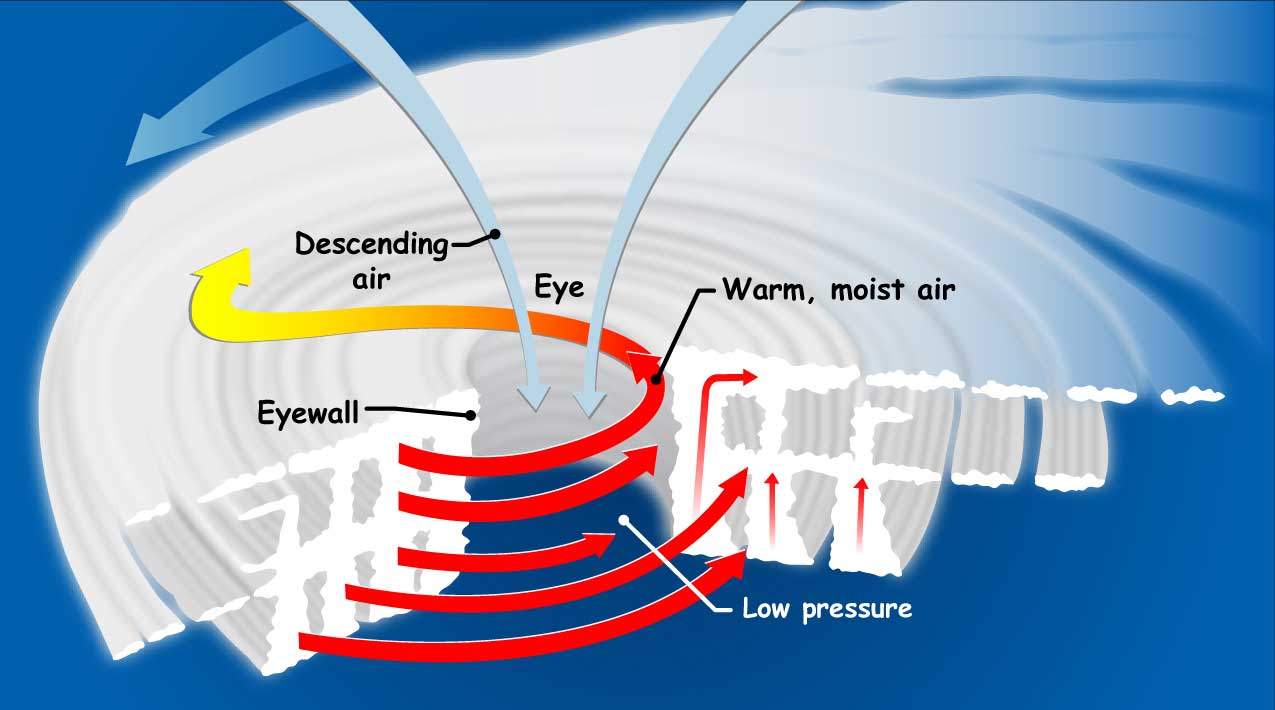
Hurricane Structure: A Closer Look
A hurricane’s structure is characterized by several key components:
- Eye: The eye is the calm center of a hurricane, typically 20-40 miles (32-64 km) wide. It is characterized by clear skies and light winds.
- Eyewall: The eyewall is a ring of intense thunderstorms surrounding the eye. It is the area of strongest winds, heaviest rainfall, and highest storm surge.
- Spiral Bands: Spiral bands are bands of thunderstorms extending outward from the eyewall. They produce heavy rain and gusty winds, but are generally weaker than the eyewall.
The Lifespan of a Hurricane
Hurricanes are dynamic systems, constantly evolving and changing. Their lifespan can vary significantly, ranging from a few days to several weeks. Factors that influence a hurricane’s lifespan include:
- Ocean Temperature: As a hurricane moves over cooler waters, its energy supply diminishes, weakening the storm.
- Land Interaction: When a hurricane makes landfall, it loses its primary source of energy and begins to weaken.
- Wind Shear: Increased wind shear can disrupt a hurricane’s structure and weaken its intensity.
The Impact of Hurricanes: Devastation and Resilience
Hurricanes have the potential to cause widespread devastation, impacting coastal areas and inland regions alike. The primary hazards associated with hurricanes include:
- Strong Winds: Hurricane-force winds can cause significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and trees.
- Torrential Rainfall: Heavy rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and erosion.
- Storm Surge: Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the hurricane’s winds pushing water towards the shore. It can cause widespread flooding and coastal erosion.
- Tornadoes: Hurricanes can spawn tornadoes, which can cause significant damage to property and infrastructure.
Hurricane Preparedness and Mitigation
Effective hurricane preparedness is essential for minimizing the impact of these powerful storms. Steps individuals and communities can take include:
- Developing an Evacuation Plan: In areas prone to hurricanes, it is crucial to have a well-defined evacuation plan in place.
- Securing Property: Protecting homes and businesses from hurricane damage involves securing windows, doors, and roofs.
- Building Resilience: Investing in hurricane-resistant construction methods and infrastructure can help mitigate damage.
- Staying Informed: Staying informed about hurricane warnings and forecasts is crucial for making timely decisions.
FAQs about Hurricane Formation:
Q: What is the difference between a hurricane, a cyclone, and a typhoon?
A: These terms refer to the same type of storm system but are used in different regions of the world. Hurricanes are typically found in the North Atlantic, Central North Pacific, and Eastern North Pacific. Cyclones are found in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean. Typhoons are found in the Western North Pacific.
Q: Can hurricanes form over land?
A: Hurricanes cannot form over land because they require warm ocean waters as their energy source. However, a hurricane that makes landfall can still cause significant damage and flooding.
Q: What is the role of climate change in hurricane formation?
A: While the exact relationship between climate change and hurricane formation is still being studied, research suggests that warmer ocean temperatures due to climate change could lead to more intense and potentially longer-lasting hurricanes.
Q: How are hurricanes tracked and monitored?
A: Hurricanes are tracked and monitored using a combination of satellite imagery, radar systems, and weather buoys. This information is used to predict the storm’s path, intensity, and potential impact.
Tips for Hurricane Preparedness:
- Prepare an emergency kit: This should include essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a radio.
- Secure your home: Board up windows, trim trees, and move valuables to higher ground.
- Know your evacuation route: Identify a safe place to go in case of an evacuation order.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and follow instructions from local authorities.
Conclusion
Hurricanes are powerful and destructive forces of nature. Understanding their formation, development, and impact is essential for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies. By staying informed, taking preventative measures, and responding appropriately to warnings, individuals and communities can minimize the risks associated with these devastating storms. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, understanding and preparing for hurricanes will become increasingly critical in the years to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Genesis of a Hurricane: A Comprehensive Guide to the Formation and Development of a Powerful Storm. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!