The Formation and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine
Related Articles: The Formation and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Formation and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Formation and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine

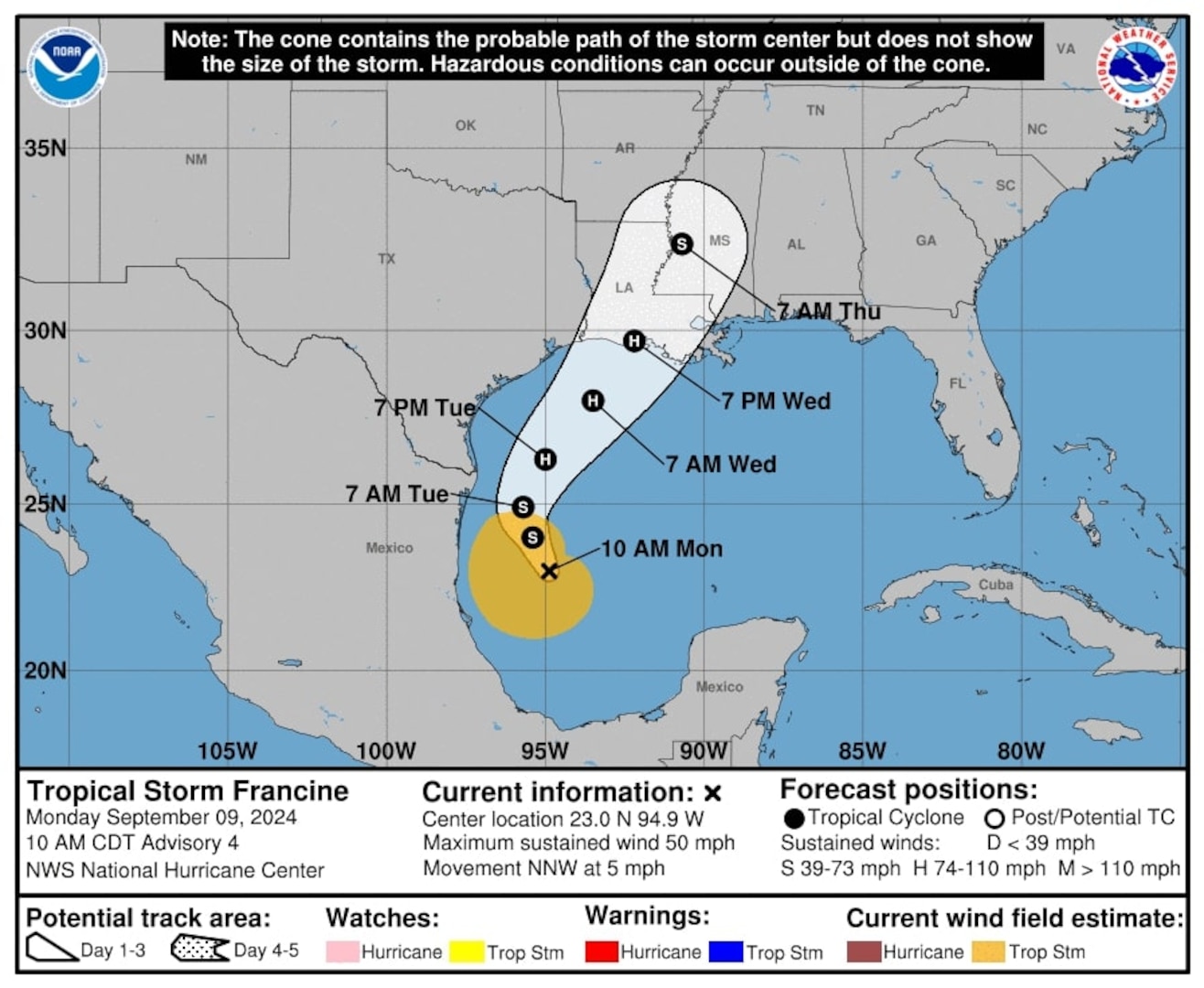
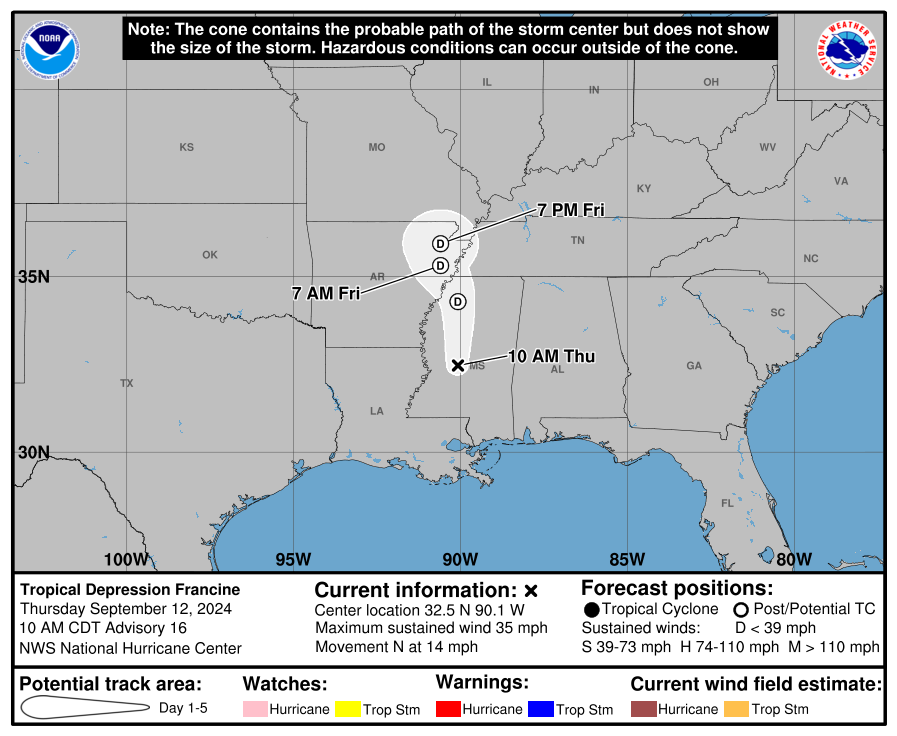
Tropical Storm Francine, a significant weather event in the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season, serves as a compelling case study in the complex dynamics of tropical cyclone formation and the potential for significant impact. While Francine ultimately did not reach hurricane strength, its formation and trajectory highlight key aspects of tropical meteorology and the importance of preparedness in coastal regions.
Understanding the Formation of Tropical Storm Francine
Tropical Storm Francine originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the coast of Africa on August 16, 2004. This wave, characterized by a low-pressure trough and associated thunderstorms, moved westward across the Atlantic, gradually gaining organization and strength. By August 20th, the system had developed into a tropical depression, with sustained winds reaching 35 mph.
The key factors contributing to Francine’s formation were:
- Favorable Atmospheric Conditions: The presence of warm, moist air in the lower atmosphere provided the necessary energy for the development of thunderstorms.
- Weak Vertical Wind Shear: Low wind shear, the change in wind speed and direction with height, allowed the thunderstorms to organize and develop into a coherent circulation.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: The tropical wave provided the initial seed for the development of a low-pressure center, which is crucial for the formation of a tropical cyclone.
As Francine moved westward, it encountered more favorable conditions, including warm ocean waters and a lack of significant upper-level winds. These factors allowed the storm to intensify further, becoming a tropical storm on August 21st.
The Path and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine
After reaching tropical storm status, Francine maintained a generally westward trajectory, passing north of the Lesser Antilles and then tracking northward into the western Atlantic. While the storm remained relatively weak, it brought significant impacts to several islands and coastal regions:
- Heavy Rainfall: Francine produced heavy rainfall across the Lesser Antilles, leading to localized flooding and mudslides.
- High Winds: The storm’s sustained winds, while not hurricane-force, caused damage to infrastructure and downed trees, particularly on the islands of Antigua and Barbuda.
- Coastal Flooding: Francine’s surge caused minor coastal flooding in some areas, particularly in Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands.
The Importance of Tropical Storm Francine
Despite its relatively weak intensity, Tropical Storm Francine serves as a reminder of the importance of:
- Monitoring Tropical Systems: The rapid development of Francine from a tropical wave to a tropical storm underscores the importance of closely monitoring tropical systems in their early stages.
- Preparedness for Coastal Communities: Even relatively weak storms can cause significant damage and disruptions. Coastal communities need to be prepared for the possibility of heavy rainfall, high winds, and coastal flooding.
- Understanding the Dynamics of Tropical Cyclones: Francine’s trajectory and intensity highlight the complex interplay of atmospheric and oceanic factors that contribute to the formation and development of tropical cyclones.
Related Searches
1. Tropical Storm Formation: Understanding the conditions necessary for the formation of tropical storms, including warm ocean temperatures, low wind shear, and pre-existing disturbances.
2. Tropical Storm Tracks: Analyzing the historical paths of tropical storms to better predict future storm trajectories and potential impacts.
3. Tropical Storm Intensity: Investigating the factors that influence the intensity of tropical storms, including the interaction of atmospheric and oceanic conditions.
4. Tropical Storm Impacts: Assessing the potential impacts of tropical storms on coastal communities, including flooding, high winds, and storm surge.
5. Hurricane Forecasting: Exploring the latest advancements in hurricane forecasting, including the use of computer models and satellite imagery.
6. Hurricane Preparedness: Providing guidance on how individuals and communities can prepare for hurricanes, including developing evacuation plans and securing property.
7. Hurricane Mitigation: Examining strategies for reducing the impacts of hurricanes, including building codes and infrastructure improvements.
8. Hurricane History: Learning from past hurricane events to improve preparedness and mitigation efforts for future storms.
FAQs
Q: What are the key differences between a tropical depression, a tropical storm, and a hurricane?
A: The primary difference lies in wind speed. A tropical depression has sustained winds of less than 38 mph, a tropical storm has sustained winds between 39 and 73 mph, and a hurricane has sustained winds of 74 mph or higher.
Q: How are tropical storms tracked and monitored?
A: Tropical storms are tracked using a combination of satellite imagery, radar data, and aircraft reconnaissance. These data are used to determine the storm’s location, intensity, and movement.
Q: What are the primary hazards associated with tropical storms?
A: Tropical storms can cause a variety of hazards, including heavy rainfall, high winds, storm surge, and tornadoes.
Q: How can I stay safe during a tropical storm?
A: It is important to stay informed about the storm’s progress and to follow the instructions of local authorities. This may include evacuating to higher ground, securing your property, and stocking up on essential supplies.
Tips
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and advisories from reputable sources such as the National Hurricane Center.
- Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a plan for your family that includes evacuation routes, communication methods, and a designated meeting place.
- Prepare Your Home: Secure loose objects outside, trim trees, and stock up on essential supplies such as water, non-perishable food, batteries, and first-aid supplies.
- Be Aware of Coastal Hazards: Understand the risks of storm surge and coastal flooding and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
- Stay Safe During the Storm: Avoid driving during the storm, stay indoors, and avoid contact with downed power lines.
Conclusion
Tropical Storm Francine serves as a reminder of the constant threat posed by tropical cyclones. While Francine did not achieve hurricane strength, its formation and trajectory highlight the importance of understanding the dynamics of these storms and the need for preparedness in coastal communities. By staying informed, developing emergency plans, and taking preventative measures, individuals and communities can mitigate the potential impacts of these powerful weather events.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Formation and Impact of Tropical Storm Francine. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!