The Devastating Legacy of Hurricane Mitch: A Case Study in Catastrophic Weather Events
Related Articles: The Devastating Legacy of Hurricane Mitch: A Case Study in Catastrophic Weather Events
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Devastating Legacy of Hurricane Mitch: A Case Study in Catastrophic Weather Events. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Devastating Legacy of Hurricane Mitch: A Case Study in Catastrophic Weather Events
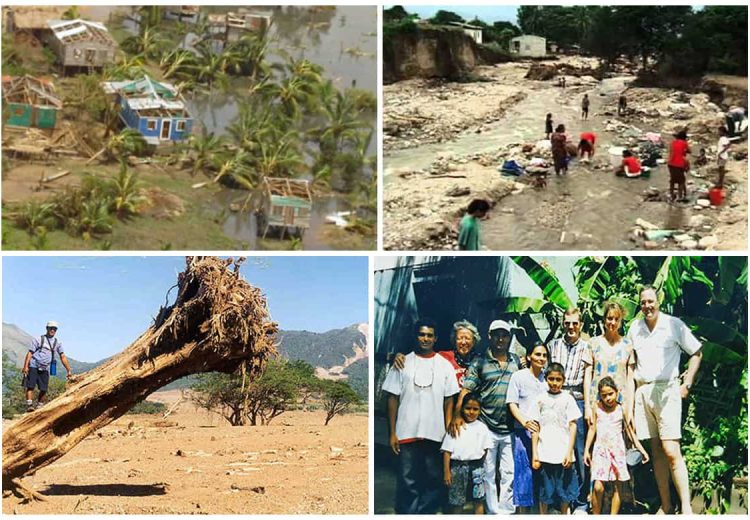

Determining the "worst hurricane ever" is a complex task, as different storms can be ranked based on various factors like wind speed, storm surge, rainfall, and the extent of damage caused. However, the catastrophic impact of Hurricane Mitch in 1998 makes it a compelling contender for this unfortunate title. This essay will examine the factors that contributed to Mitch’s devastating impact, explore the long-term consequences of this storm, and delve into related aspects like the science of hurricanes, historical comparisons, and future preparedness.
Understanding the Severity of Hurricane Mitch
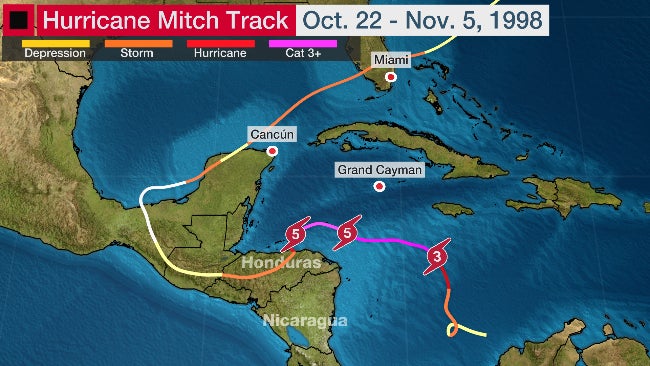
Hurricane Mitch formed in the western Caribbean Sea on October 22, 1998, and quickly intensified into a Category 5 storm. Its path took it across Nicaragua and Honduras, where it made landfall on October 26th. While the storm’s sustained wind speeds were high (180 mph), the most devastating factor was the torrential rainfall that accompanied it. Mitch dumped an unprecedented amount of rain, exceeding 75 inches in some areas, causing widespread flooding and mudslides.
The Impact of Mitch: A Human and Environmental Tragedy
The impact of Mitch was devastating, both in terms of human life and environmental damage.
- Loss of Life: The official death toll from Hurricane Mitch exceeded 11,000, with the majority of victims in Honduras and Nicaragua. The true number of fatalities is likely much higher, as many bodies were never recovered.
- Economic Devastation: The storm caused an estimated $5 billion in damages, crippling the economies of the affected countries. The agricultural sector was particularly hard hit, with widespread crop failures and livestock losses.
- Environmental Degradation: Mitch caused significant environmental damage, including deforestation, soil erosion, and contamination of water sources. The storm’s intense rainfall led to massive landslides that altered the landscape and destroyed ecosystems.
Factors Contributing to Mitch’s Devastating Impact
Several factors contributed to the severity of Hurricane Mitch’s impact:
- Slow Movement: Mitch moved slowly across Central America, allowing it to dump an extraordinary amount of rain over a prolonged period.
- Geographic Location: The mountainous terrain of Central America amplified the impact of the storm, as rainfall runoff caused flash floods and mudslides in vulnerable areas.
- Deforestation: Extensive deforestation in the region, particularly in Honduras, exacerbated the effects of the storm. The lack of vegetation contributed to soil erosion and increased the vulnerability of slopes to landslides.
- Pre-existing Poverty: The affected countries were already struggling with poverty and limited resources. The storm’s impact further strained their infrastructure and ability to respond to the disaster.
Historical Comparisons: Placing Mitch in Context
Hurricane Mitch’s impact was unprecedented in Central America. While other hurricanes have caused significant damage, Mitch’s combination of intense rainfall, slow movement, and the region’s vulnerability made it a particularly devastating event.
- Hurricane Fifi-Orlene (1974): This hurricane caused widespread flooding and landslides in Honduras, killing an estimated 8,000 people.
- Hurricane Flora (1963): This storm caused widespread flooding in Cuba and Haiti, killing an estimated 1,500 people.
These historical comparisons highlight the importance of understanding the unique factors that contribute to the severity of each hurricane. While wind speeds are often the focus, rainfall, storm surge, and the vulnerability of the affected area are crucial factors in determining a hurricane’s overall impact.
The Long-Term Consequences of Hurricane Mitch
The impact of Hurricane Mitch was not limited to the immediate aftermath of the storm. The long-term consequences continue to affect the affected countries.
- Economic Recovery: The economic recovery from Mitch was slow and challenging. The damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and tourism sectors took years to rebuild.
- Social Impact: The storm exacerbated existing social problems, including poverty, displacement, and food insecurity. The loss of livelihoods and homes led to increased migration and social unrest.
- Environmental Recovery: The environmental damage caused by Mitch continues to have long-term consequences. Soil erosion and deforestation have led to increased vulnerability to future natural disasters.
Related Searches and FAQs
1. What is a hurricane?
Hurricanes are powerful storms characterized by intense rotating winds and heavy rainfall. They form over warm ocean waters near the equator and are fueled by the heat and moisture released from the ocean surface.
2. What are the different categories of hurricanes?
Hurricanes are categorized based on their sustained wind speed, with Category 5 being the most intense. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is used to classify hurricanes based on their wind speed and potential damage.
3. How often do hurricanes occur?
Hurricane season varies depending on the region, but generally occurs during the summer and fall months. The Atlantic hurricane season runs from June 1st to November 30th, while the Pacific hurricane season can extend year-round.
4. What are the warning signs of a hurricane?
Warning signs of a hurricane include a drop in barometric pressure, rising tides, and increased wind speeds. Coastal communities are advised to monitor weather reports and heed official warnings.
5. What is the difference between a hurricane, a typhoon, and a cyclone?
Hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones are all the same type of storm, but the names differ depending on the location where they form. Hurricanes are found in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific, typhoons in the Northwest Pacific, and cyclones in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
6. How can we prepare for a hurricane?
Hurricane preparedness involves several steps, including:
- Creating an emergency plan
- Stocking supplies like food, water, and batteries
- Securing your home and property
- Understanding evacuation routes
7. What are the effects of climate change on hurricanes?
Climate change is expected to increase the intensity and frequency of hurricanes. Rising sea levels and warmer ocean temperatures contribute to stronger storms with higher storm surges.
8. What are the long-term impacts of hurricanes?
Hurricanes can have long-term impacts on ecosystems, economies, and societies. They can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and coastal areas. The recovery process can take years and require significant resources.
Tips for Preparing for Hurricane Season
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and heed official warnings from local authorities.
- Create an emergency plan: This should include evacuation routes, communication plans, and a list of essential supplies.
- Stock up on supplies: Gather non-perishable food, bottled water, batteries, first-aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Secure your home and property: Trim trees, secure loose objects, and prepare your home for potential flooding.
- Know your evacuation routes: Be familiar with the designated evacuation routes and have a plan for where you will go in case of a hurricane.
Conclusion
Hurricane Mitch serves as a stark reminder of the devastating power of nature and the importance of preparedness. While the storm’s impact was unprecedented, it highlights the vulnerability of human societies to extreme weather events. Understanding the factors that contribute to hurricane intensity, promoting sustainable development practices, and investing in disaster preparedness are crucial steps in mitigating the risks of future storms. By learning from the lessons of Mitch, we can work towards building more resilient communities that are better equipped to withstand the challenges of a changing climate.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Devastating Legacy of Hurricane Mitch: A Case Study in Catastrophic Weather Events. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!