The 2024 Hurricane Season: A Look at the Forecast and Preparations
Related Articles: The 2024 Hurricane Season: A Look at the Forecast and Preparations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The 2024 Hurricane Season: A Look at the Forecast and Preparations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The 2024 Hurricane Season: A Look at the Forecast and Preparations
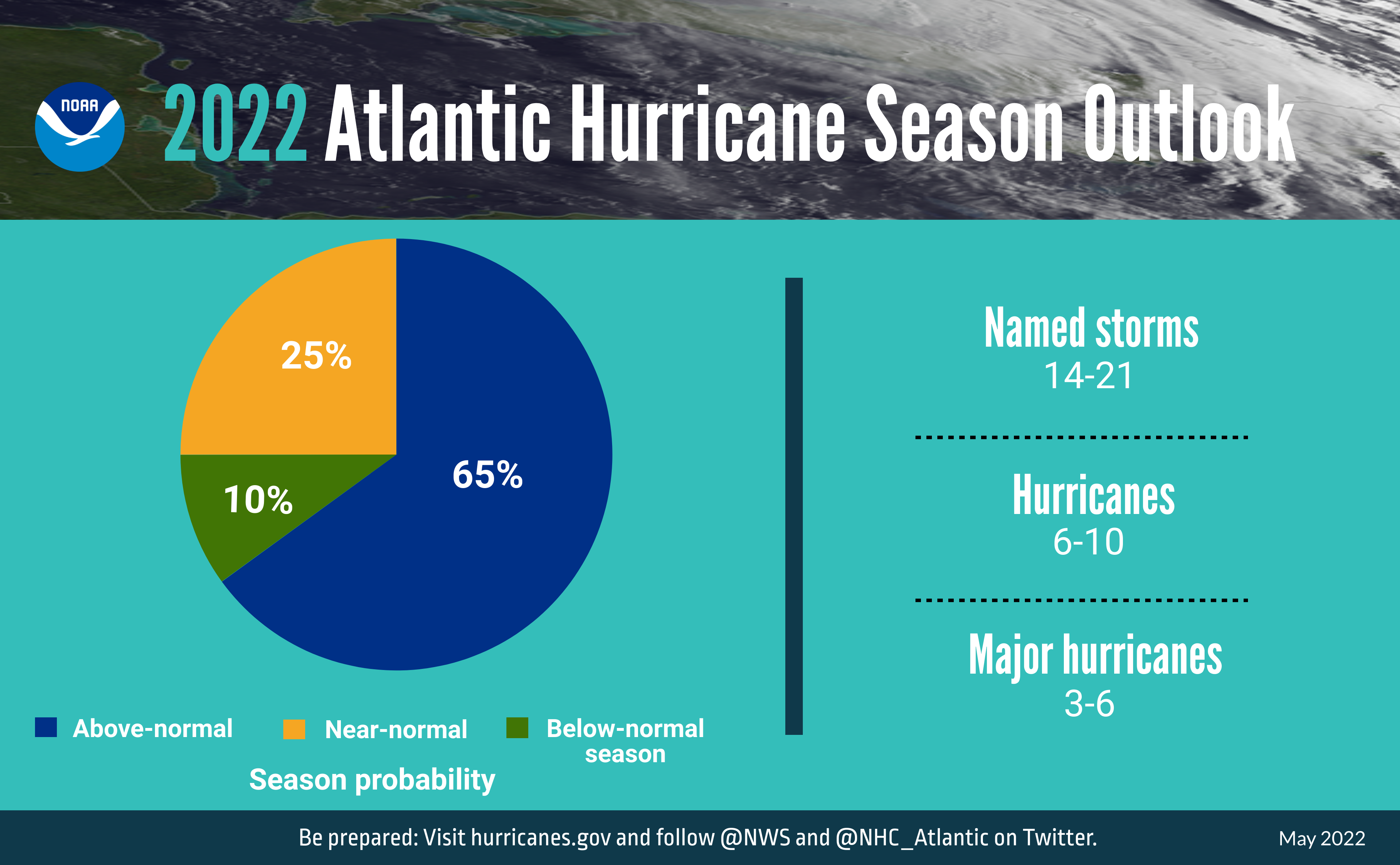
The Atlantic hurricane season officially runs from June 1st to November 30th each year, and while it’s impossible to predict the exact path or intensity of any given storm, scientists and meteorologists use a variety of data and models to forecast the overall activity for the season.
Understanding Hurricane Formation and Prediction
Hurricanes, also known as cyclones or typhoons depending on their location, are powerful storms that develop over warm ocean waters. They are characterized by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and potentially devastating storm surges. The formation of a hurricane requires specific conditions, including:
- Warm Ocean Waters: The ocean temperature must be at least 80 degrees Fahrenheit (26.5 degrees Celsius) to provide the necessary heat and moisture.
- Low Wind Shear: Vertical wind shear, the change in wind speed and direction with height, must be minimal to allow the storm to organize and intensify.
- Pre-existing Disturbance: A pre-existing weather disturbance, such as a tropical wave, is needed to provide the initial spin and organization.
The 2024 Hurricane Season Forecast
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) releases an annual hurricane outlook, predicting the number of named storms, hurricanes, and major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher) expected during the season. The 2024 forecast is expected to be released in May, and will provide valuable information for individuals, communities, and emergency responders to prepare for potential storm impacts.
Factors Influencing the 2024 Hurricane Season
Several factors contribute to the overall activity of a hurricane season, including:
- El Niño/La Niña: These climate patterns can influence wind shear and other atmospheric conditions, affecting hurricane development.
- Sea Surface Temperatures: Warmer-than-average ocean temperatures can fuel hurricane formation and intensification.
- Atmospheric Conditions: The presence of dust, aerosols, and other atmospheric factors can impact the development and strength of hurricanes.
Preparing for the Hurricane Season
The best way to mitigate the potential damage and disruption caused by hurricanes is to prepare well in advance. This includes:
- Developing a Hurricane Plan: Create a plan that outlines evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies to be gathered in case of a hurricane warning.
- Securing Your Home: Strengthen windows and doors, trim trees, and secure loose objects that could become projectiles during high winds.
- Building an Emergency Kit: Stock up on non-perishable food, water, batteries, first-aid supplies, and other essential items that may be needed if power or other services are disrupted.
- Staying Informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the guidance of local officials.
The Importance of Hurricane Preparedness
Hurricanes can cause significant damage to infrastructure, property, and human life. By taking proactive steps to prepare, individuals and communities can reduce the risk of loss and ensure a faster recovery process.
Related Searches
1. Hurricane Tracking:
- Hurricane Tracking Websites: Websites like the National Hurricane Center (NHC), the National Weather Service (NWS), and AccuWeather provide real-time tracking of hurricanes and tropical storms.
- Hurricane Tracking Apps: Mobile apps like Hurricane Tracker, MyRadar, and WeatherBug offer interactive maps, alerts, and detailed information about hurricanes.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide valuable data on hurricane development, intensity, and movement, allowing for better prediction and preparedness.
2. Hurricane Safety Tips:
- Evacuation Orders: Evacuate immediately if ordered by local authorities.
- Shelter in Place: If evacuation is not possible, seek shelter in a sturdy building, preferably on the lowest floor.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and official announcements for updates and instructions.
- Avoid Floodwaters: Floodwaters can be contaminated and pose a health risk.
3. Hurricane Damage and Recovery:
- Insurance Coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for hurricane damage to your property.
- Disaster Relief Resources: Organizations like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) provide financial assistance and other resources for disaster victims.
- Community Recovery Efforts: Community involvement is crucial for post-hurricane recovery, including debris removal, rebuilding efforts, and supporting those affected.
4. Hurricane History and Statistics:
- Historical Hurricane Records: The NHC maintains extensive records of past hurricanes, providing valuable insights into storm patterns and impacts.
- Hurricane Statistics: Statistical analysis of hurricane data helps predict future trends and inform preparedness efforts.
- Hurricane Naming Conventions: Hurricanes are named according to a pre-determined list, with names rotating every six years.
5. Hurricane Forecasting Technology:
- Computer Models: Sophisticated computer models use atmospheric data to predict hurricane paths and intensity.
- Hurricane Research: Scientists are constantly improving hurricane forecasting technology through research and development.
- Hurricane Observation: Advanced observation techniques, including radar and satellite imagery, provide real-time data on hurricane development.
6. Hurricane Impacts on the Environment:
- Coastal Erosion: Hurricanes can cause significant coastal erosion, impacting beaches and coastal ecosystems.
- Storm Surge Flooding: Storm surge, the rise in sea level caused by a hurricane, can inundate coastal areas and cause widespread flooding.
- Rainfall and Flooding: Hurricanes can produce heavy rainfall, leading to flooding and landslides.
7. Hurricane Impacts on Society:
- Economic Losses: Hurricanes can cause significant economic losses due to property damage, business disruptions, and lost productivity.
- Displaced Populations: Hurricanes can displace large numbers of people, requiring temporary housing and other assistance.
- Social Impacts: Hurricanes can have long-lasting social impacts, including mental health challenges and community recovery efforts.
8. Hurricane Mitigation and Adaptation:
- Seawalls and Levees: Infrastructure projects like seawalls and levees can help protect coastal areas from storm surge flooding.
- Building Codes: Strengthening building codes can reduce the risk of structural damage during hurricanes.
- Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems, including weather alerts and evacuation orders, can help save lives and minimize damage.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A: A tropical storm is a rotating weather system with maximum sustained winds of 39-73 mph (63-118 km/h). Once the maximum sustained winds reach 74 mph (119 km/h) or higher, it is classified as a hurricane.
Q: How are hurricanes named?
A: Hurricanes are named according to pre-determined lists, alternating between male and female names. The names are chosen in alphabetical order, with the list rotating every six years.
Q: What is the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale?
A: The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a five-category scale that classifies hurricanes based on their maximum sustained wind speeds. Category 1 is the weakest, while Category 5 is the strongest.
Q: What is a storm surge?
A: Storm surge is the rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s winds pushing water towards the shore. It can be a major cause of flooding and damage during hurricanes.
Q: What are the signs of an approaching hurricane?
A: Signs of an approaching hurricane include increasing winds, heavy rainfall, rising tides, and falling barometric pressure.
Tips
- Stay informed: Monitor weather reports and follow the guidance of local officials.
- Prepare a hurricane kit: Include non-perishable food, water, batteries, first-aid supplies, and other essential items.
- Secure your home: Strengthen windows and doors, trim trees, and secure loose objects.
- Develop a hurricane plan: Outline evacuation routes, communication strategies, and essential supplies.
- Know your evacuation routes: Identify safe evacuation routes and practice them with your family.
- Be aware of flood risks: Avoid floodwaters as they can be contaminated and pose a health risk.
- Have a communication plan: Establish a way to communicate with family and friends in case of a hurricane.
- Check your insurance coverage: Ensure adequate insurance coverage for hurricane damage.
- Be patient and cooperative: Follow instructions from emergency responders and be patient during the recovery process.
Conclusion
The 2024 hurricane season is a reminder of the potential dangers posed by these powerful storms. By understanding the factors influencing hurricane formation, staying informed about the forecast, and taking proactive steps to prepare, individuals and communities can mitigate the risks and ensure a safer and more resilient future. It is crucial to remember that even a seemingly small storm can cause significant damage and disruption. Being prepared and following safety guidelines are essential for protecting lives and property during hurricane season.

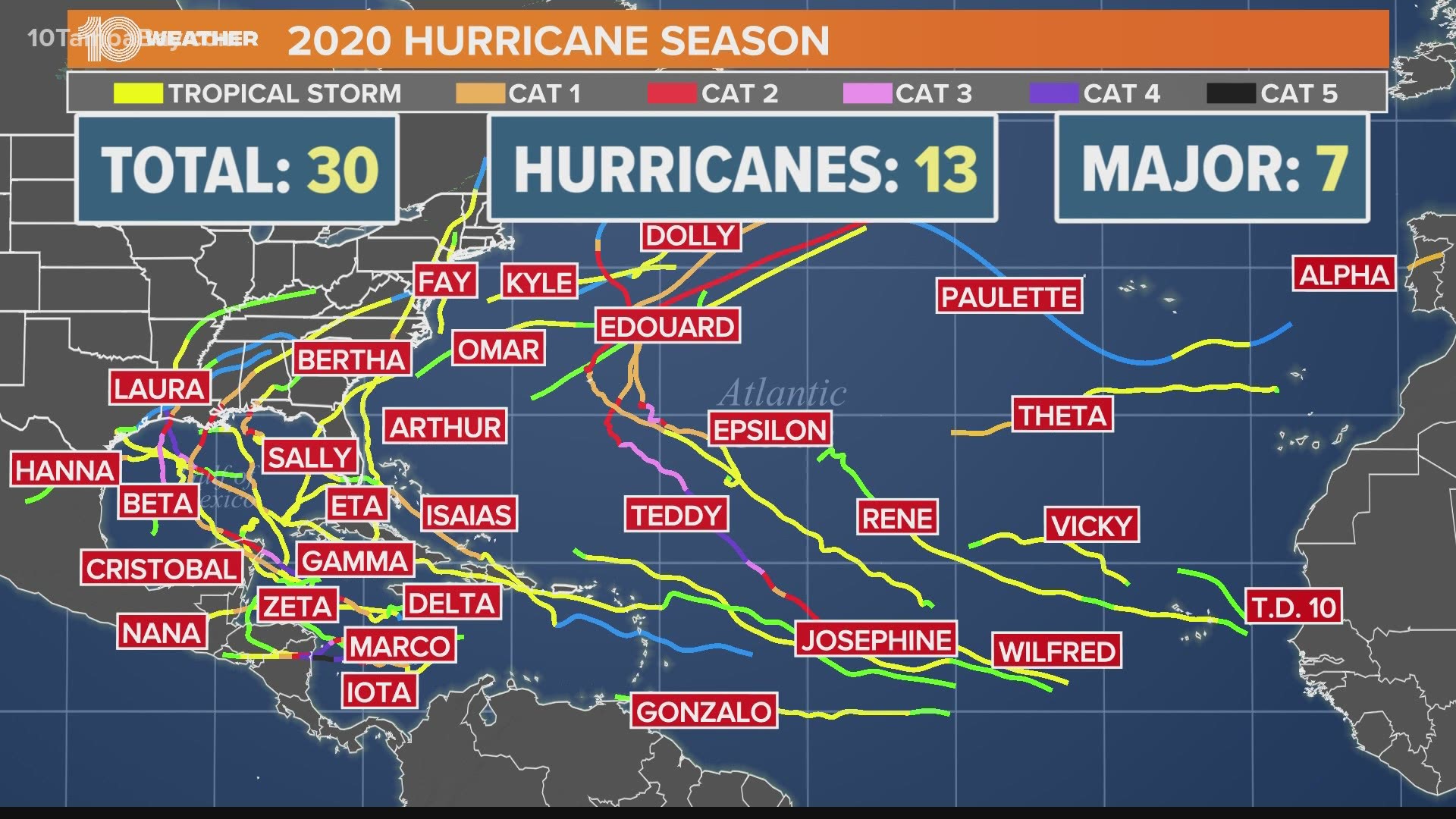
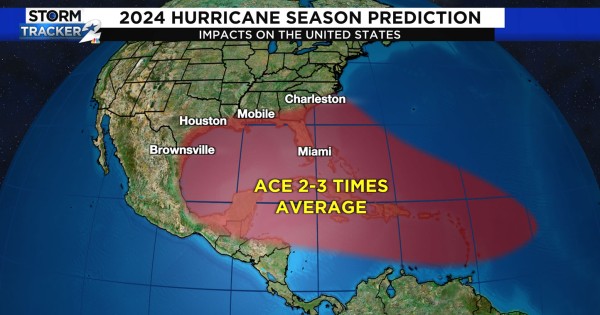
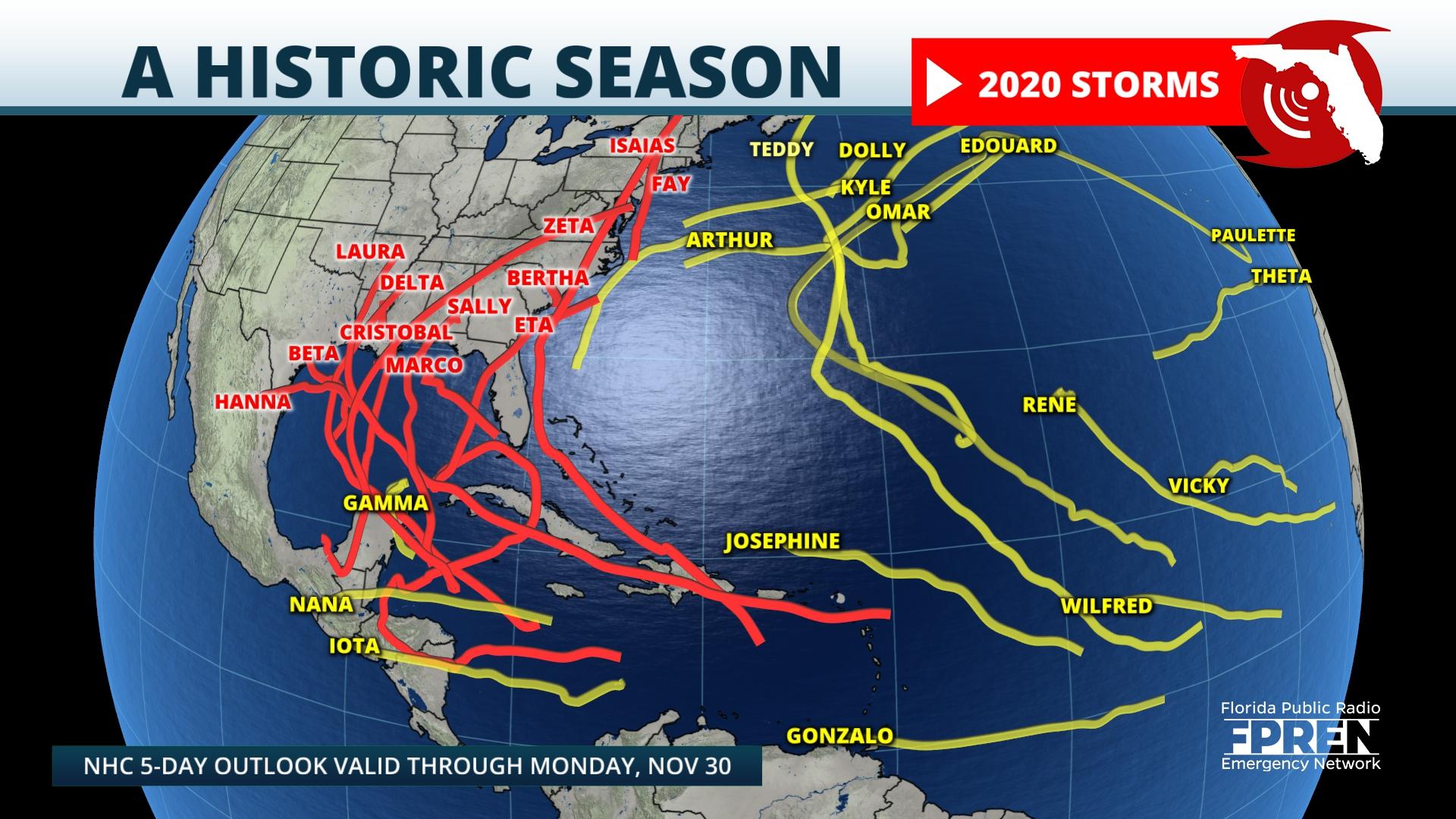



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The 2024 Hurricane Season: A Look at the Forecast and Preparations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!