Navigating the Storms: A Comprehensive Guide to the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Storms: A Comprehensive Guide to the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Storms: A Comprehensive Guide to the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Storms: A Comprehensive Guide to the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map

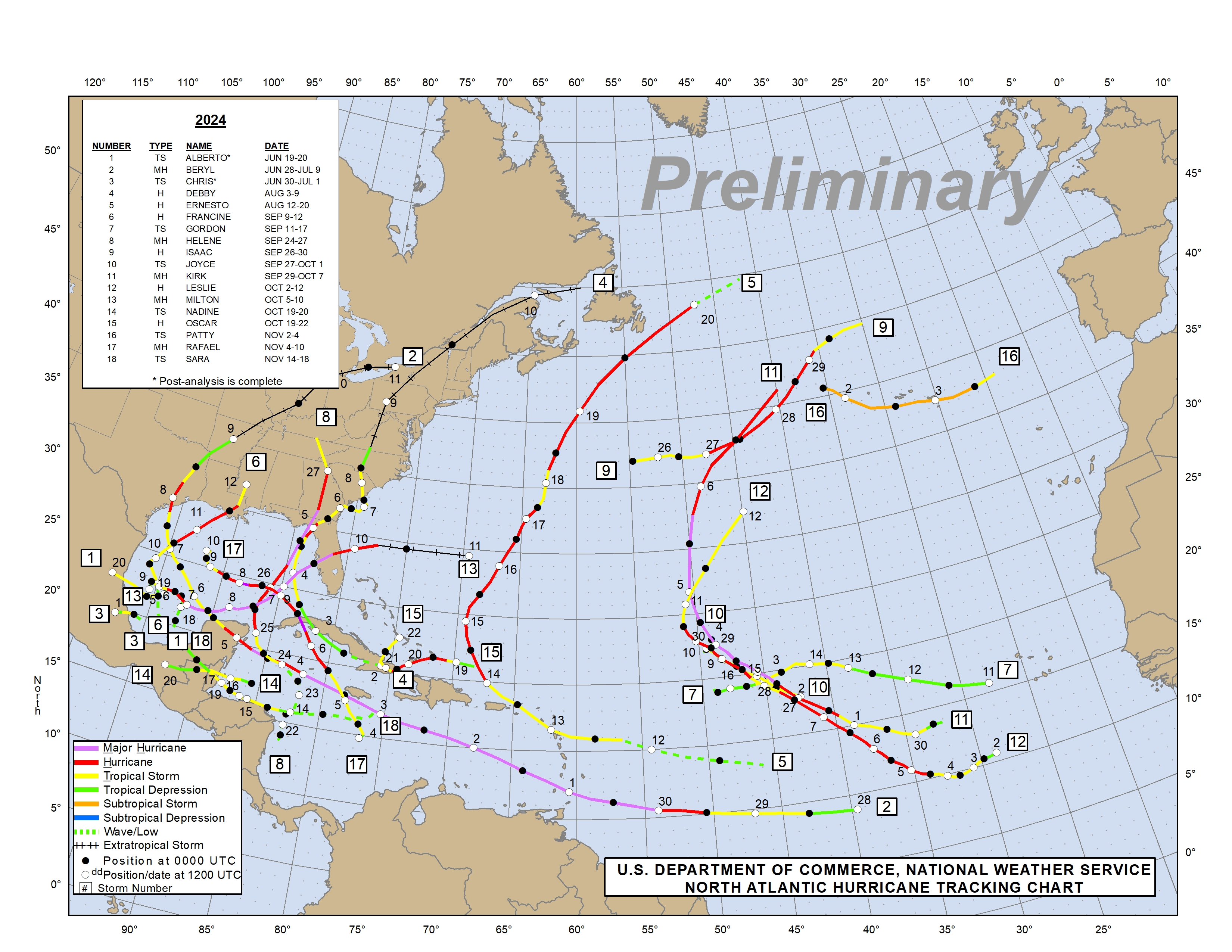
The Atlantic hurricane season, stretching from June 1st to November 30th, is a period of heightened anticipation and vigilance for millions along the Atlantic coast. The potential for destructive storms necessitates a robust system for monitoring and forecasting their paths, and this is where the Atlantic hurricane tracking map plays a pivotal role. This powerful tool provides a visual representation of the real-time locations and predicted trajectories of hurricanes, offering crucial information for preparedness and response.
Understanding the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
The Atlantic hurricane tracking map is a dynamic, constantly updating representation of hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin. It typically features:
- Hurricane Symbols: Each hurricane is represented by a distinct symbol, usually a circle with a tail indicating the storm’s direction of movement. The size of the circle corresponds to the hurricane’s intensity, with larger circles indicating stronger storms.
- Hurricane Tracks: Lines emanating from the hurricane symbols depict the storm’s predicted path over the next several days. These tracks are based on sophisticated computer models that factor in various meteorological data points.
- Forecast Cones: A cone of uncertainty, often depicted as a shaded area, surrounds the predicted track. This cone represents the range of possible locations where the storm’s center could be at a given time. The wider the cone, the greater the uncertainty in the forecast.
- Wind Speed and Pressure: The Atlantic hurricane tracking map often includes information about the hurricane’s maximum sustained wind speed and central pressure. These data points are crucial for determining the storm’s intensity and potential for damage.
- Storm Surge: Some maps may also display information about potential storm surge, the rise in sea level caused by a hurricane’s powerful winds. Storm surge can be particularly devastating, leading to widespread flooding.
The Importance of the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
The Atlantic hurricane tracking map serves as a vital tool for:
- Forecasting and Preparedness: By tracking the movement and intensity of hurricanes, meteorologists can issue timely warnings and alerts, allowing communities to prepare for potential impacts. This includes evacuations, securing property, and stocking up on essential supplies.
- Emergency Response: The map provides critical information for emergency responders, enabling them to anticipate the areas that will be most affected by the storm and to allocate resources accordingly.
- Public Awareness: The Atlantic hurricane tracking map serves as a valuable tool for public education, raising awareness about hurricane risks and promoting preparedness measures.
Key Benefits of the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
- Improved Forecasting: The use of sophisticated computer models and real-time data has significantly improved the accuracy of hurricane forecasts, giving communities more time to prepare.
- Enhanced Communication: The map facilitates clear and concise communication between meteorologists, emergency responders, and the public, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information.
- Increased Public Safety: By providing timely warnings and accurate predictions, the Atlantic hurricane tracking map contributes directly to public safety, minimizing the impact of hurricanes and saving lives.
Exploring Related Searches
Understanding the Atlantic hurricane tracking map is just the beginning. Here are some related searches that delve deeper into the complexities of hurricane tracking and preparedness:
1. Hurricane Forecast Models:
- National Hurricane Center (NHC) Models: The NHC utilizes several advanced computer models to predict hurricane paths, including the Global Forecast System (GFS), the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), and the Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF) model. Each model has its strengths and weaknesses, and meteorologists combine their outputs to create a comprehensive forecast.
- Ensemble Forecasting: Ensemble forecasting involves running multiple simulations of the same hurricane using slightly different initial conditions. This approach helps to account for the inherent uncertainties in weather prediction and provides a range of possible outcomes.
- Hurricane Intensity Forecasting: Predicting a hurricane’s intensity is a complex task, and researchers are constantly developing new models and techniques to improve accuracy. Factors like the hurricane’s environment, its internal structure, and the interaction with landmasses all play a role in determining its intensity.
2. Hurricane Naming Conventions:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO): The WMO maintains a list of hurricane names for each basin, rotating through the list every six years. This ensures that each storm is given a unique name, aiding in communication and record-keeping.
- Alternating Male and Female Names: In the Atlantic basin, hurricane names alternate between male and female, following a pre-determined list.
- Retired Names: If a hurricane causes significant damage or loss of life, its name may be retired to avoid future confusion or distress.
3. Hurricane Warning Systems:
- Hurricane Watches and Warnings: The NHC issues hurricane watches and warnings to alert communities of potential hurricane impacts. A hurricane watch indicates that hurricane conditions are possible within a specified area, while a hurricane warning indicates that hurricane conditions are expected within a specified area.
- Hurricane Categories: Hurricanes are categorized based on their maximum sustained wind speeds using the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. Category 1 hurricanes are the weakest, while Category 5 hurricanes are the most intense.
- Hurricane Preparedness Kits: It is essential to have a hurricane preparedness kit that includes essential supplies such as food, water, first aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
4. Hurricane History and Statistics:
- The Deadliest Hurricanes: The Atlantic basin has witnessed numerous devastating hurricanes throughout history, leaving behind a legacy of destruction and loss of life. Understanding the historical context helps to appreciate the importance of hurricane preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Hurricane Frequency and Intensity: Studies have shown that hurricane frequency and intensity are influenced by factors such as climate change and ocean temperatures. Analyzing historical data helps to identify trends and predict future hurricane activity.
- Hurricane Landfalls: Tracking hurricane landfalls provides valuable insight into the areas that are most vulnerable to hurricane impacts and helps to inform mitigation strategies.
5. Hurricane Mitigation Strategies:
- Building Codes and Construction Practices: Building codes and construction practices play a crucial role in mitigating hurricane damage. By incorporating hurricane-resistant features into buildings, communities can reduce the risk of structural collapse and injuries.
- Coastal Protection Measures: Coastal protection measures such as seawalls, breakwaters, and dune restoration help to reduce the impact of storm surge and erosion.
- Evacuation Plans: Developing comprehensive evacuation plans is essential for ensuring the safety of residents in hurricane-prone areas. These plans should include designated evacuation routes, shelters, and communication strategies.
6. Hurricane Research and Technology:
- Hurricane Doppler Radar: Doppler radar provides valuable information about the intensity and structure of hurricanes, allowing meteorologists to track their development and predict their paths.
- Hurricane Hunter Aircraft: Hurricane hunter aircraft fly directly into hurricanes, collecting data on wind speed, pressure, and other crucial parameters. This data is used to improve hurricane forecasts and understanding.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites provide a comprehensive view of hurricane activity, capturing images of the storm’s structure, cloud patterns, and intensity. This information is crucial for tracking hurricanes and predicting their paths.
7. Hurricane Impacts and Economic Consequences:
- Property Damage and Loss of Life: Hurricanes can cause widespread property damage, including structural damage to buildings, flooding, and power outages. They can also lead to loss of life due to high winds, storm surge, and flooding.
- Economic Disruptions: Hurricanes can cause significant economic disruptions, affecting businesses, infrastructure, and transportation systems. The cost of rebuilding and recovering from hurricane damage can be substantial.
- Insurance Costs: Hurricane risks are factored into insurance premiums, and the frequency and intensity of hurricanes can drive up insurance costs for residents in vulnerable areas.
8. Hurricane Climate Change:
- Rising Sea Levels: Rising sea levels due to climate change exacerbate the impact of storm surge, increasing the risk of coastal flooding.
- Warmer Ocean Temperatures: Warmer ocean temperatures provide fuel for hurricanes, potentially leading to more intense storms.
- Changes in Hurricane Tracks: Climate change may also influence hurricane tracks, potentially leading to storms making landfall in areas that are not typically affected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map
1. How Accurate are Hurricane Forecasts?
Hurricane forecasts have become increasingly accurate over the years, but they are still subject to inherent uncertainties. The accuracy of a forecast depends on factors such as the hurricane’s size, intensity, and the quality of available data.
2. What Does the Forecast Cone Mean?
The forecast cone represents the range of possible locations where the center of a hurricane could be at a given time. The cone is not a prediction of the storm’s path but rather a depiction of the uncertainty in the forecast.
3. How Often is the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map Updated?
The Atlantic hurricane tracking map is typically updated every few hours, reflecting the latest data and model predictions.
4. Where Can I Find the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map?
The Atlantic hurricane tracking map is readily available from various sources, including:
- National Hurricane Center (NHC): The NHC website provides a comprehensive Atlantic hurricane tracking map, along with detailed information about current and future hurricane activity.
- Weather Apps: Many weather apps, such as The Weather Channel, AccuWeather, and Weather Underground, offer Atlantic hurricane tracking maps and other hurricane-related information.
- News Websites: Major news organizations, such as CNN, The New York Times, and The Washington Post, also provide Atlantic hurricane tracking maps on their websites.
5. What Should I Do If a Hurricane is Approaching My Area?
If a hurricane is approaching your area, it is crucial to take the following steps:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather reports and updates from the NHC and local authorities.
- Prepare Your Home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and prepare a hurricane preparedness kit.
- Evacuate If Necessary: Follow evacuation orders issued by local authorities.
- Stay Safe: During a hurricane, stay indoors, avoid flooded areas, and be aware of potential hazards.
Tips for Using the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map Effectively
- Understand the Symbols and Terminology: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the Atlantic hurricane tracking map and the meaning of terms like "watch," "warning," and "cone of uncertainty."
- Focus on the Predicted Path: Pay attention to the predicted path of the hurricane and the areas that are expected to be affected.
- Consider the Forecast Cone: Remember that the forecast cone represents a range of possible locations, and the hurricane could deviate from the predicted path.
- Don’t Rely Solely on the Map: The Atlantic hurricane tracking map is just one tool for monitoring hurricane activity. Stay informed by listening to weather reports, following official advisories, and checking local news sources.
- Prepare for the Worst: Even if a hurricane is not expected to make landfall directly in your area, it is essential to be prepared for potential impacts such as heavy rain, flooding, and power outages.
Conclusion
The Atlantic hurricane tracking map is an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of hurricane season. It provides real-time information on hurricane locations, predicted paths, and intensity, enabling communities to prepare for potential impacts and mitigate risks. By understanding the map and its underlying data, individuals can make informed decisions to protect themselves and their families during hurricane season. However, it is crucial to remember that the Atlantic hurricane tracking map is just one component of hurricane preparedness. A comprehensive approach that includes staying informed, preparing for the worst, and following official advisories is essential for ensuring safety and minimizing the impact of these powerful storms.
/atlantictrackmap2010-56a9e13e3df78cf772ab33d0-5b882329c9e77c002ccda027.jpg)
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Storms: A Comprehensive Guide to the Atlantic Hurricane Tracking Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!