Hurricane Milton: A Powerful Storm in the 2005 Atlantic Hurricane Season
Related Articles: Hurricane Milton: A Powerful Storm in the 2005 Atlantic Hurricane Season
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Milton: A Powerful Storm in the 2005 Atlantic Hurricane Season. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Hurricane Milton: A Powerful Storm in the 2005 Atlantic Hurricane Season

Hurricane Milton was a powerful and destructive hurricane that formed in the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. It was the thirteenth named storm, the seventh hurricane, and the third major hurricane of the season.
Formation and Development:
Hurricane Milton originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the west coast of Africa on August 21, 2005. The wave moved westward across the Atlantic Ocean, gradually organizing and developing into a tropical depression on August 27th. It was upgraded to Tropical Storm Milton on August 28th and then to Hurricane Milton on August 29th.
Intensification and Peak Strength:
Hurricane Milton intensified rapidly as it moved westward across the Atlantic. It reached its peak intensity on September 1st, with maximum sustained winds of 130 miles per hour (215 km/h), making it a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Landfall and Weakening:
Hurricane Milton made landfall on the coast of Mexico near the city of Tuxpan, Veracruz, on September 2nd. It brought heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surge to the area. After landfall, Milton weakened rapidly and dissipated over land on September 4th.
Impact and Aftermath:
Hurricane Milton caused significant damage in Mexico, primarily in the states of Veracruz and Tamaulipas. It caused widespread power outages, flooding, and structural damage. Several deaths were reported, although the exact number remains uncertain.
Importance and Significance:
Hurricane Milton highlights the significant impact of hurricanes on coastal communities. Its rapid intensification and powerful winds emphasize the importance of preparedness and early warning systems for hurricane-prone regions. The storm also served as a reminder of the destructive potential of hurricanes and the need for continuous efforts to mitigate their impacts.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Milton Track:
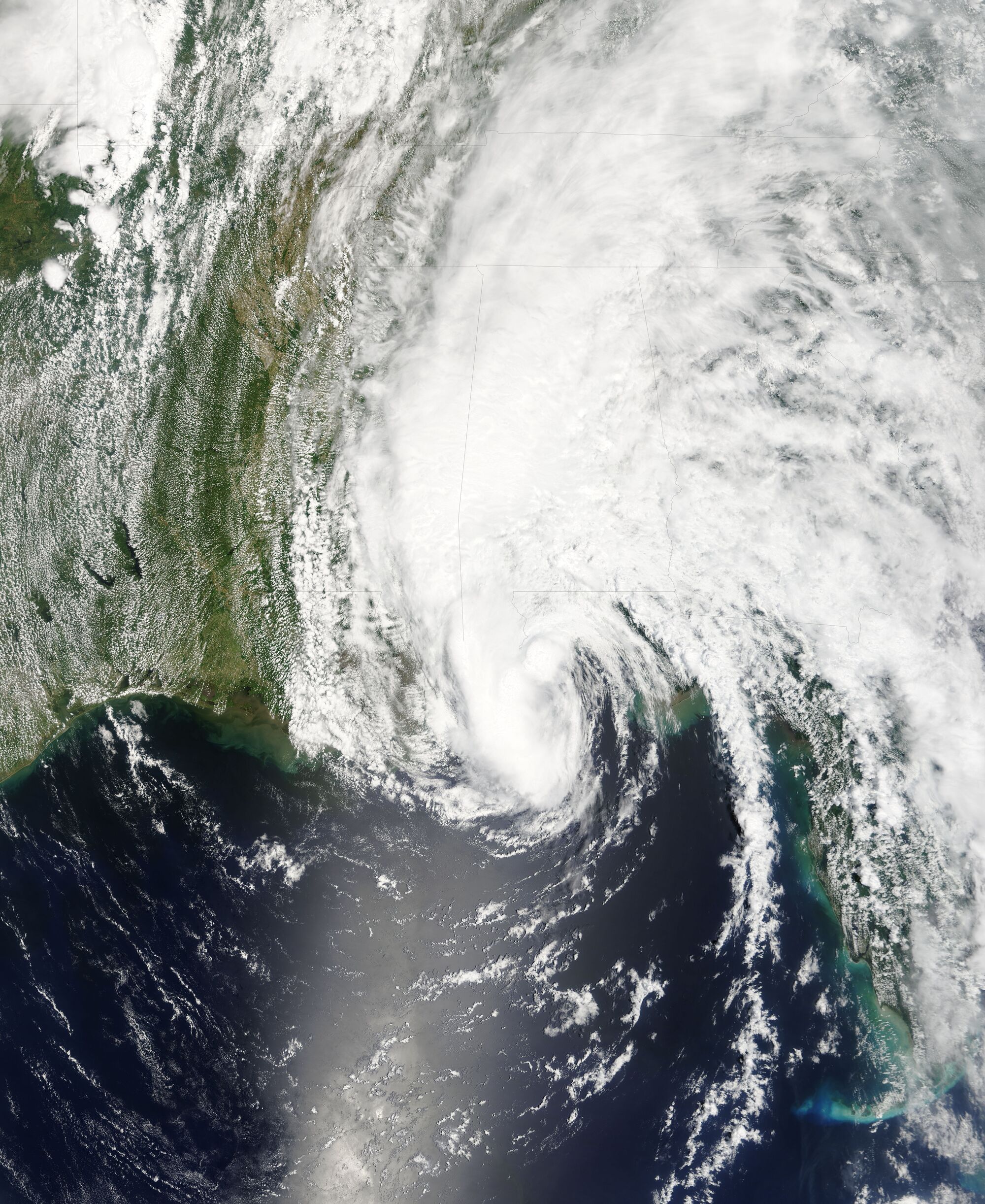
The track of Hurricane Milton was characterized by its westward movement across the Atlantic Ocean, culminating in its landfall on the Mexican coast. It initially moved slowly, allowing for ample time for preparations in the Caribbean and Central America. However, it accelerated significantly as it approached Mexico, leading to a shorter warning time for the coastal regions. Understanding the hurricane’s track is crucial for predicting its potential impact and issuing timely warnings.
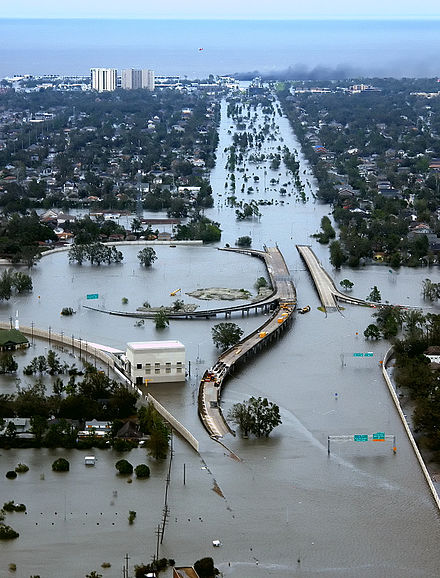
2. Hurricane Milton Damage:
Hurricane Milton caused significant damage in Mexico, primarily in the states of Veracruz and Tamaulipas. It brought heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surge to the area, resulting in widespread power outages, flooding, and structural damage. The impact of the storm varied depending on the specific location, with some areas experiencing more severe damage than others.
3. Hurricane Milton Deaths:
Hurricane Milton caused several deaths in Mexico, although the exact number remains uncertain. The storm’s strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge contributed to the fatalities. Accurate reporting of casualties following natural disasters can be challenging, and the number of deaths attributed to Hurricane Milton might have been underestimated.
4. Hurricane Milton Rainfall:
Hurricane Milton brought heavy rainfall to the Mexican coast, contributing significantly to flooding and landslides. The rainfall was heaviest in the immediate vicinity of the landfall location, with some areas receiving over 10 inches of rain. The intense rainfall exacerbated the storm’s impact, leading to widespread damage and disruption.
5. Hurricane Milton Wind Speed:
Hurricane Milton reached peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 130 miles per hour (215 km/h). These high wind speeds caused significant damage to infrastructure and vegetation, leading to widespread power outages and structural damage. The wind speeds also contributed to the storm surge that inundated coastal areas.
6. Hurricane Milton Storm Surge:
Hurricane Milton generated a significant storm surge along the Mexican coast, inundating coastal areas and causing widespread flooding. The surge was most pronounced near the landfall location, where the storm’s intensity was highest. The storm surge contributed significantly to the overall damage caused by Hurricane Milton.
7. Hurricane Milton History:
Hurricane Milton’s history is part of the broader context of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season, which was one of the most active on record. The storm’s rapid intensification and destructive potential highlight the importance of understanding hurricane dynamics and developing effective mitigation strategies. Studying Hurricane Milton’s history can provide valuable insights into hurricane behavior and its potential impact.
8. Hurricane Milton Satellite Images:
Satellite imagery provided crucial information about Hurricane Milton’s development, track, and intensity. The images allowed meteorologists to monitor the storm’s progress and issue timely warnings to affected areas. Satellite imagery also provided valuable data for post-storm assessments, helping to understand the extent of the damage and the impact of the storm.
FAQs about Hurricane Milton:
1. What was the strongest category Hurricane Milton reached?
Hurricane Milton reached Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, with maximum sustained winds of 130 miles per hour (215 km/h).
2. Where did Hurricane Milton make landfall?
Hurricane Milton made landfall on the coast of Mexico near the city of Tuxpan, Veracruz, on September 2nd, 2005.
3. How long did Hurricane Milton last?
Hurricane Milton lasted for approximately a week, from its formation on August 27th to its dissipation over land on September 4th.
4. What was the impact of Hurricane Milton?
Hurricane Milton caused significant damage in Mexico, primarily in the states of Veracruz and Tamaulipas. It brought heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surge to the area, resulting in widespread power outages, flooding, and structural damage. Several deaths were reported.
5. What were the key factors that contributed to Hurricane Milton’s intensification?
Hurricane Milton intensified rapidly due to a combination of factors, including warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and a favorable atmospheric environment.
6. How did Hurricane Milton compare to other hurricanes in the 2005 season?
The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was one of the most active on record. Hurricane Milton was the seventh hurricane of the season and the third major hurricane (Category 3 or higher).
7. What lessons can be learned from Hurricane Milton?
Hurricane Milton highlights the importance of preparedness and early warning systems for hurricane-prone regions. It also underscores the destructive potential of hurricanes and the need for continuous efforts to mitigate their impacts.
8. How has the understanding of hurricanes evolved since Hurricane Milton?
Since Hurricane Milton, advancements in hurricane forecasting, modeling, and communication technologies have significantly improved our understanding of hurricane behavior and our ability to predict their impact.
Tips for Preparing for a Hurricane:
1. Stay Informed:
- Monitor weather reports and advisories from reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center (NHC).
- Familiarize yourself with your local hurricane preparedness plan.
- Understand evacuation routes and shelter locations.
2. Secure Your Property:
- Trim trees and secure loose objects that could become airborne.
- Protect windows with shutters or plywood.
- Secure your roof and make sure it is in good condition.
3. Prepare an Emergency Kit:
- Gather essential supplies such as water, food, first aid, medication, and a battery-powered radio.
- Include items for infants, elderly, and people with special needs.
- Consider a generator for power outages.
4. Develop an Evacuation Plan:
- Determine evacuation routes and have a plan for where you will go if you need to evacuate.
- Make arrangements for pets and other family members.
- Have a communication plan in case of separation.
5. Stay Safe During a Hurricane:
- Seek shelter in a safe place, preferably a hurricane-resistant structure.
- Avoid driving during the storm.
- Stay away from windows and doors.
- Be aware of potential hazards such as flooding, downed power lines, and flying debris.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Milton serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of hurricanes and the importance of preparedness in hurricane-prone regions. By understanding the history of Hurricane Milton, its impact, and the lessons learned from it, we can better prepare for future storms and mitigate their potential consequences. The continuous improvement of hurricane forecasting, early warning systems, and disaster response efforts are crucial for minimizing the impact of these powerful storms. It is essential to remain vigilant and prioritize preparedness to protect lives and property from the devastating effects of hurricanes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Milton: A Powerful Storm in the 2005 Atlantic Hurricane Season. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!