Hurricane Leslie – A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability
Related Articles: Hurricane Leslie – A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Leslie – A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Hurricane Leslie – A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability

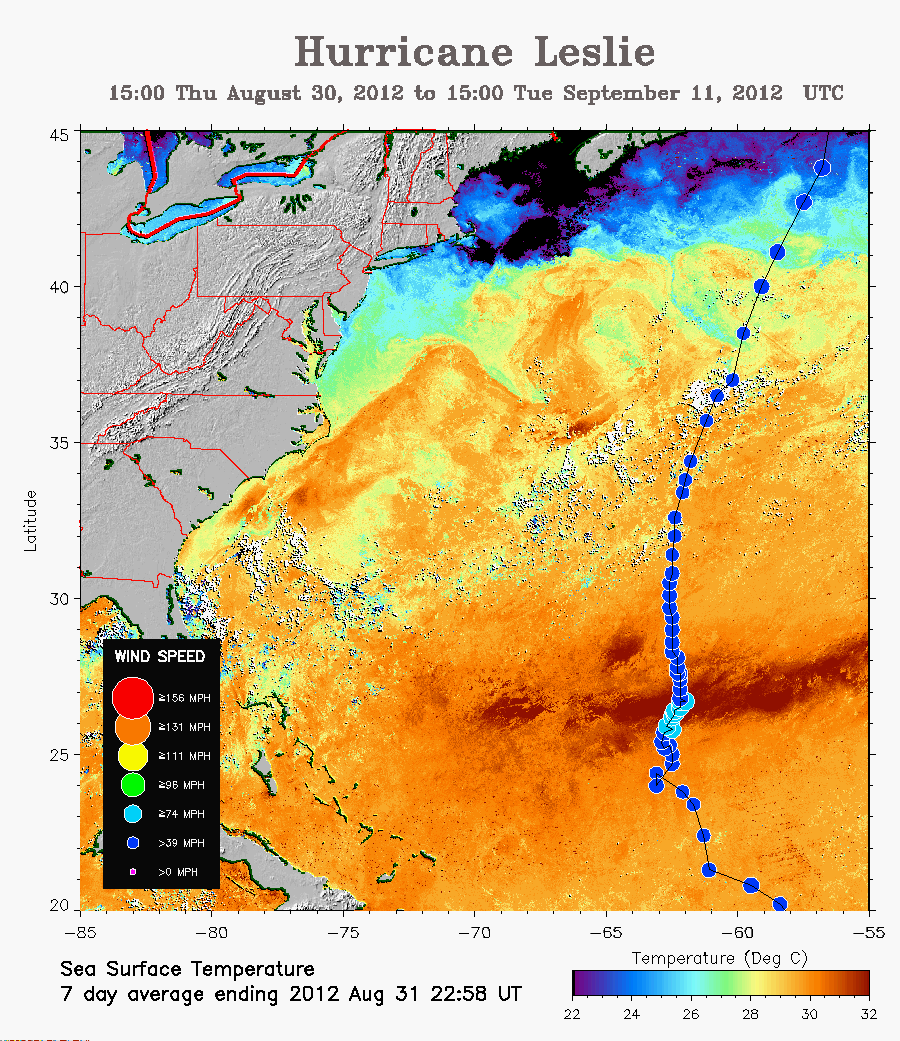
Hurricane Leslie was a powerful and long-lived hurricane that formed in the Atlantic Ocean in September 2003. It is notable for its unusual longevity, its extended path across the Atlantic, and its impact on multiple countries.
Formation and Development:
Hurricane Leslie originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on September 5th, 2003. This wave developed into a tropical depression on September 8th, and then into Tropical Storm Leslie on September 9th. The storm intensified rapidly, reaching hurricane status on September 10th.
Unusual Longevity and Path:
Hurricane Leslie defied typical hurricane behavior by persisting for an extended period and following an unusual path. It traversed the Atlantic Ocean for over two weeks, reaching Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale on September 12th.
The storm’s path took it far north, towards the Azores, a Portuguese archipelago in the mid-Atlantic. This trajectory was unusual, as most hurricanes track westward or northward towards the North American continent.
Impacts:
Hurricane Leslie caused significant impacts across the Atlantic. It brought heavy rainfall and strong winds to the Azores, resulting in power outages and damage to infrastructure. The storm also produced high waves and strong currents, posing dangers for maritime activities.
Hurricane Leslie also impacted Bermuda, bringing heavy rain and high winds. While the storm did not make landfall on the island, it caused some minor damage and disruptions.
Key Features and Significance:
Hurricane Leslie exemplifies the variability and unpredictability of Atlantic hurricanes. Its long duration, unusual path, and impacts on multiple countries highlight the importance of hurricane preparedness and monitoring.
The storm also provided valuable data for researchers studying hurricane dynamics and forecasting. It served as a case study for understanding how hurricanes can evolve and behave in unexpected ways.
Related Searches and FAQs:
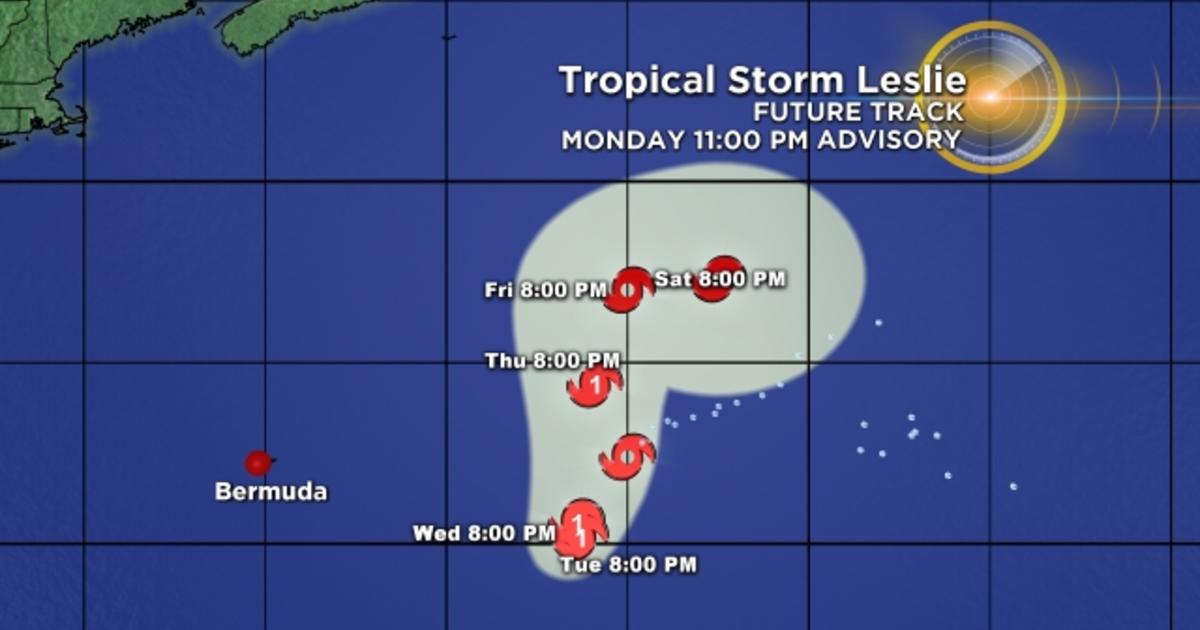
1. Hurricane Leslie Path:
Hurricane Leslie followed a unique path, initially moving westward across the Atlantic before turning sharply northward towards the Azores. This unusual trajectory was influenced by a combination of factors, including the steering currents in the upper atmosphere and the presence of a strong high-pressure system to the north.
2. Hurricane Leslie Track:
The track of Hurricane Leslie can be traced using satellite imagery, radar data, and weather models. This information allows meteorologists to track the storm’s movement and predict its potential impacts.
3. Hurricane Leslie History:
Hurricane Leslie was a significant event in Atlantic hurricane history due to its longevity and unusual path. Its impacts on the Azores and Bermuda provide valuable insights into the potential risks associated with hurricanes.
4. Hurricane Leslie Landfall:
While Hurricane Leslie did not make landfall in the traditional sense, it did bring strong winds and heavy rain to the Azores and Bermuda. These impacts were significant enough to be considered landfall-like events.
5. Hurricane Leslie Damage:
The damage caused by Hurricane Leslie was primarily focused on the Azores, where the storm caused power outages, infrastructure damage, and disruptions to transportation. The storm also caused some minor damage to Bermuda.
6. Hurricane Leslie Wind Speed:
Hurricane Leslie reached Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, with maximum sustained wind speeds of 125 mph.
7. Hurricane Leslie Rainfall:
Hurricane Leslie produced significant rainfall across the Azores, resulting in localized flooding and landslides. The storm also brought heavy rain to Bermuda.
8. Hurricane Leslie Category:
Hurricane Leslie reached Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, making it a major hurricane.
Tips for Hurricane Preparedness:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings issued by your local authorities and the National Hurricane Center.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Stock up on essential supplies such as food, water, first-aid kit, batteries, and a weather radio.
- Secure Your Home: Protect your windows and doors, trim trees, and secure loose objects that could be blown away by strong winds.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: If you live in an area prone to hurricanes, know your evacuation routes and have a plan in place for where you will go if you need to evacuate.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Leslie stands as a testament to the unpredictable nature of Atlantic hurricanes. Its extended duration, unusual path, and impacts on multiple countries highlight the importance of hurricane preparedness and the need for continuous research and monitoring. By understanding the dynamics of hurricanes and learning from past events, we can improve our ability to mitigate their risks and protect ourselves from their destructive forces.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Leslie – A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!