Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms
Related Articles: Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms
- 3.1 Formation and Early Development
- 3.2 Intensification and Landfall in the United States
- 3.3 The "Dual-Storm" Nature of Hurricane Leslie
- 3.4 The Transatlantic Journey of Hurricane Leslie
- 3.5 Impact on Europe
- 3.6 The Importance and Benefits of Hurricane Leslie (2000)
- 3.7 Related Searches
- 3.8 FAQs About Hurricane Leslie (2000)
- 3.9 Tips for Preparing for Hurricane Season
- 3.10 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms

Hurricane Leslie (2000) was a powerful and complex tropical cyclone that traversed the Atlantic basin in September 2000. It was notable for its unusual longevity, its impact on multiple regions, and its unique dual-storm nature. This article will delve into the intricacies of this hurricane, exploring its formation, evolution, and the significant effects it had on the United States and Europe.
Formation and Early Development
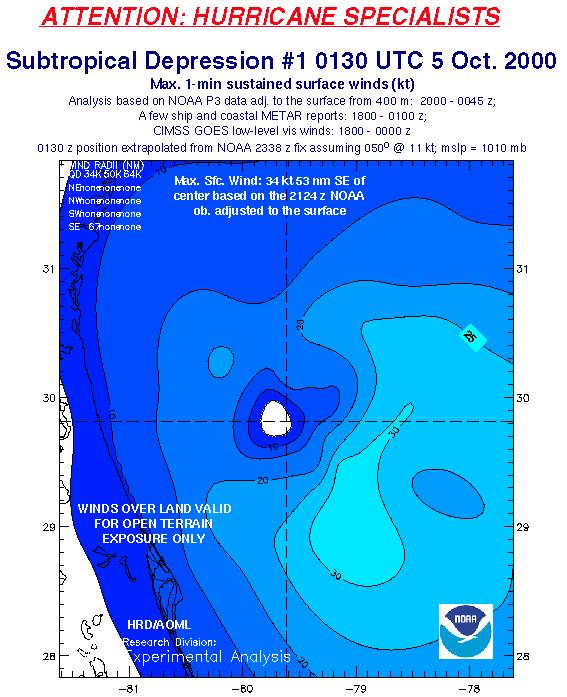
Hurricane Leslie originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on September 1, 2000. It slowly developed into a tropical depression on September 4th, then intensified into Tropical Storm Leslie on September 6th. The storm’s initial trajectory was westward, across the Atlantic towards the Caribbean. However, it was the interaction with a strong upper-level trough that propelled Hurricane Leslie on an unusual northward path, a rare occurrence for hurricanes in this region.
Intensification and Landfall in the United States
As Hurricane Leslie moved northward, it encountered favorable conditions for intensification. Warm ocean waters and low wind shear allowed the storm to rapidly strengthen. On September 10th, Leslie reached hurricane status, with maximum sustained winds of 80 mph. It continued to intensify, reaching Category 1 hurricane status on September 11th, with winds of 90 mph.
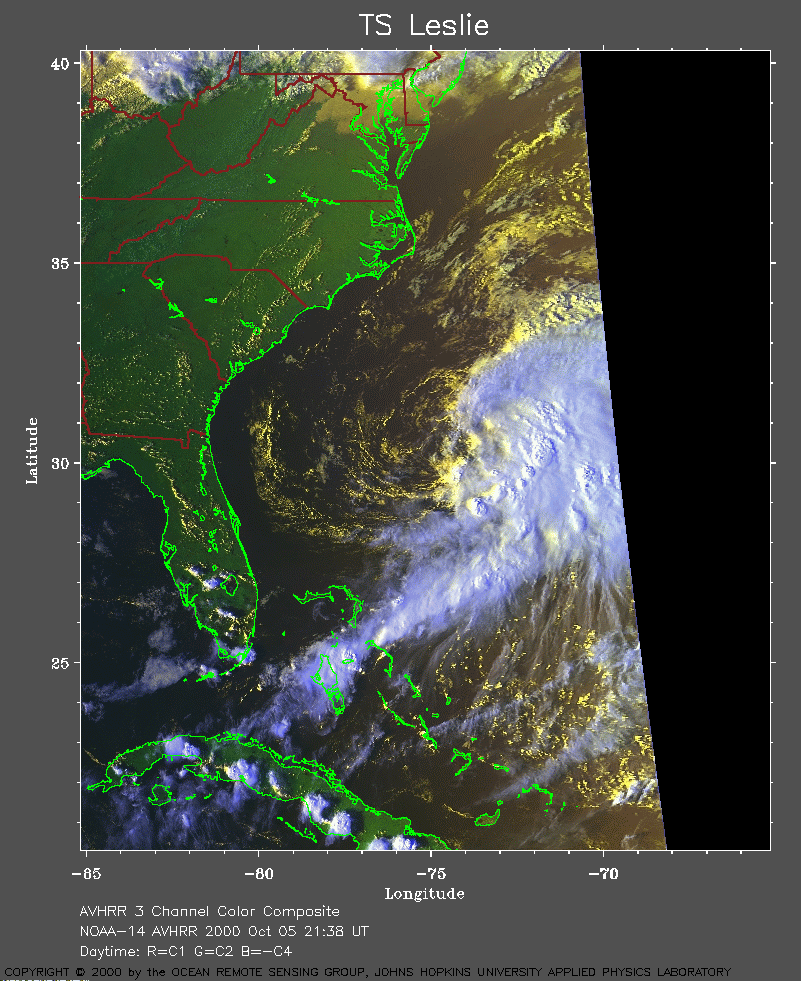
On September 12th, Hurricane Leslie made landfall near Cape Lookout, North Carolina, as a Category 1 hurricane. The storm brought heavy rainfall and strong winds to the Outer Banks, resulting in widespread coastal flooding and power outages. While the impact was significant, it was thankfully less severe than initially anticipated.
The "Dual-Storm" Nature of Hurricane Leslie
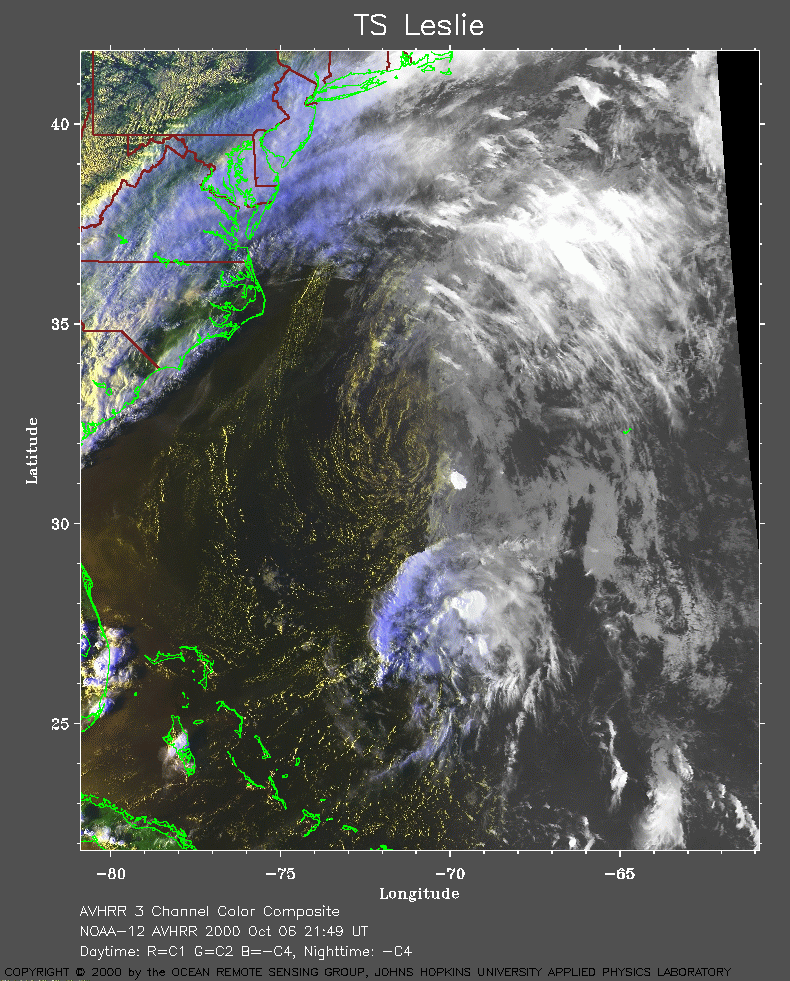
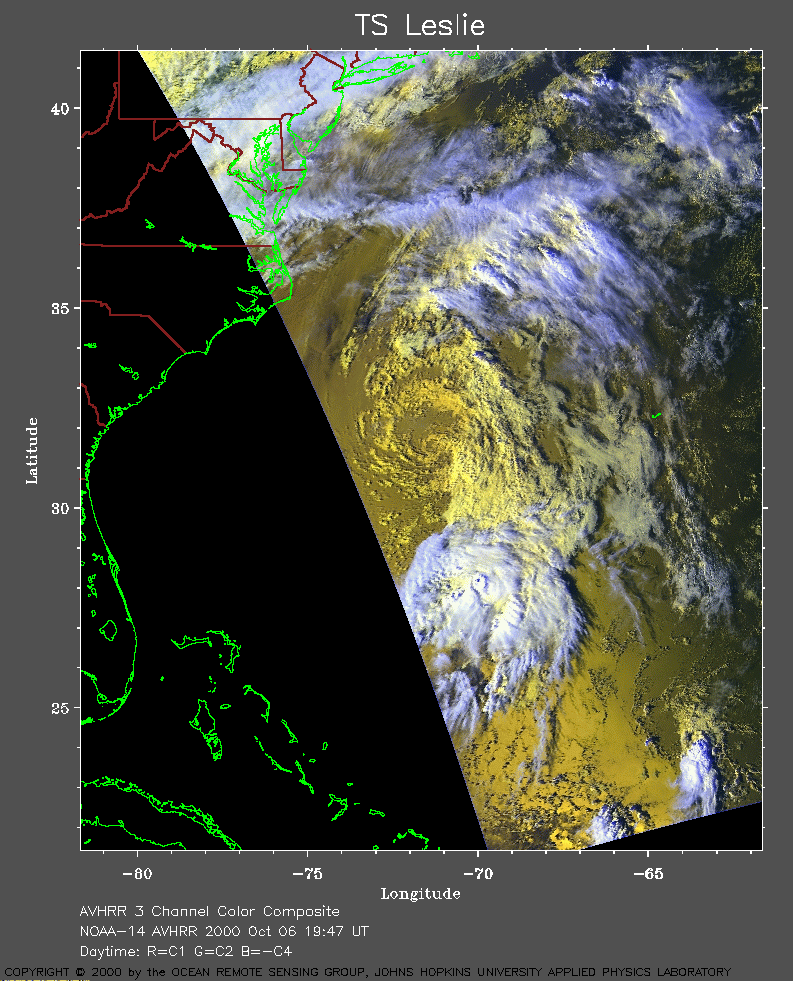
One of the most fascinating aspects of Hurricane Leslie was its unique dual-storm nature. After making landfall in North Carolina, the storm weakened rapidly, losing hurricane status and becoming a tropical storm again. However, the remnants of Hurricane Leslie interacted with a cold front over the northeastern United States, triggering a secondary development.
This interaction spawned a new low-pressure system, which was initially designated as a "post-tropical cyclone." This newly formed system, although not technically a hurricane, continued to bring strong winds and heavy rainfall to the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. It was this second storm that caused the most significant damage, leading to widespread power outages and flooding in regions such as New York, Massachusetts, and Nova Scotia.
The Transatlantic Journey of Hurricane Leslie
Remarkably, Hurricane Leslie wasn’t done yet. After its impact on the United States, the storm’s remnants moved out over the Atlantic, where it re-intensified into a tropical storm once again. It then embarked on an unusual journey across the Atlantic, a path rarely seen for a tropical cyclone.
Hurricane Leslie tracked towards Europe, a region not accustomed to such storms. On September 20th, it made landfall near the Azores, bringing heavy rainfall and strong winds to the islands. The storm then continued its eastward journey, weakening as it moved across the eastern Atlantic.
Impact on Europe
Although Hurricane Leslie had lost its hurricane status by the time it reached Europe, it still had a significant impact on the continent. It brought strong winds and heavy rainfall to parts of Portugal, Spain, and France. The storm also caused significant damage to crops and infrastructure in these regions.
The Importance and Benefits of Hurricane Leslie (2000)
While the storm caused significant damage and disruption, Hurricane Leslie (2000) was also an important event for meteorological research. Its unusual path, dual-storm nature, and its impact on multiple regions provided valuable insights into the complex dynamics of tropical cyclones.
Hurricane Leslie highlighted the importance of accurate forecasting and preparedness for extreme weather events. The storm also served as a reminder of the global nature of weather patterns and the potential for tropical cyclones to impact regions far from their origins.
Related Searches
Here are some related searches that offer further insight into the intricacies of Hurricane Leslie (2000):
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Path: This search will provide detailed information on the storm’s trajectory, from its formation off the coast of Africa to its final dissipation over the Atlantic.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Damage: This search will reveal the extent of the damage caused by the storm, including the impact on infrastructure, agriculture, and human life.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Rainfall: This search will provide information about the amount of rainfall associated with the storm, highlighting the areas that received the heaviest precipitation.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Wind Speeds: This search will delve into the wind speeds associated with the storm, providing insights into the intensity of the storm at different stages of its development.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Impact on North Carolina: This search will focus on the specific impact of the storm on North Carolina, including the areas most affected and the nature of the damage.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Impact on Europe: This search will provide information about the storm’s impact on European countries, including the areas affected, the type of damage, and the response to the event.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Forecast: This search will explore the accuracy of the forecasts for Hurricane Leslie, highlighting the challenges of predicting the path and intensity of such complex storms.
- Hurricane Leslie 2000 Aftermath: This search will delve into the aftermath of the storm, including the recovery efforts, the long-term effects on the affected areas, and the lessons learned from the event.
FAQs About Hurricane Leslie (2000)
1. What was the strongest intensity of Hurricane Leslie?
Hurricane Leslie reached Category 1 status on September 11th, 2000, with maximum sustained winds of 90 mph.
2. How long did Hurricane Leslie last?
Hurricane Leslie lasted for over three weeks, from its formation on September 1st to its final dissipation over the Atlantic on September 24th.
3. Where did Hurricane Leslie make landfall?
Hurricane Leslie made landfall near Cape Lookout, North Carolina, on September 12th, 2000.
4. What was the most significant impact of Hurricane Leslie?
While Hurricane Leslie caused damage in both the United States and Europe, the most significant impact was from the secondary storm that formed after the remnants of Hurricane Leslie interacted with a cold front over the northeastern United States. This secondary storm caused widespread power outages and flooding in the region.
5. What lessons were learned from Hurricane Leslie?
Hurricane Leslie highlighted the importance of accurate forecasting and preparedness for extreme weather events, especially for unusual storms like this one. It also underscored the global nature of weather patterns and the need for international cooperation in monitoring and responding to such events.
6. Was Hurricane Leslie a rare event?
Hurricane Leslie was a rare event due to its unusual path, its dual-storm nature, and its impact on multiple regions. While hurricanes are not uncommon in the Atlantic, the combination of these factors made Hurricane Leslie a unique and significant storm.
Tips for Preparing for Hurricane Season
- Stay informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
- Develop a hurricane plan: This should include evacuation routes, emergency supplies, and communication plans.
- Secure your property: Trim trees, secure loose objects, and bring in outdoor furniture.
- Have an emergency kit: This should include food, water, first-aid supplies, batteries, and a weather radio.
- Know your flood risk: If you live in a flood-prone area, take steps to protect your home from flooding.
- Be prepared to evacuate: If authorities issue an evacuation order, do not hesitate to evacuate.
Conclusion
Hurricane Leslie (2000) was a complex and powerful storm that demonstrated the unpredictable nature of tropical cyclones. Its unique trajectory, dual-storm nature, and impact on both the United States and Europe provided valuable insights into the dynamics of hurricanes. While the storm caused significant damage and disruption, it also served as a reminder of the importance of preparedness, accurate forecasting, and international cooperation in responding to extreme weather events. The lessons learned from Hurricane Leslie continue to guide efforts to improve our understanding of tropical cyclones and to mitigate their potential impacts.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Leslie (2000): A Tale of Two Storms. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!