Hurricane Kirk: A Case Study in Tropical Cyclone Development and Forecasting
Related Articles: Hurricane Kirk: A Case Study in Tropical Cyclone Development and Forecasting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Kirk: A Case Study in Tropical Cyclone Development and Forecasting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Hurricane Kirk: A Case Study in Tropical Cyclone Development and Forecasting
Hurricane Kirk, a Category 1 hurricane that formed in the eastern Atlantic Ocean in September 2003, offers a compelling case study for understanding the intricacies of tropical cyclone development and forecasting. While not a particularly powerful storm, Hurricane Kirk exhibited several characteristics that made it noteworthy, highlighting the challenges and advancements in hurricane prediction.
Formation and Development:
Hurricane Kirk originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the coast of Africa on September 1, 2003. This wave, a westward-moving disturbance in the trade winds, carried with it the potential for cyclonic development. Favorable conditions, including warm ocean waters and low wind shear, allowed the wave to organize and strengthen.
On September 4, the wave developed into a tropical depression, officially designated as Tropical Depression Nine. As the depression moved westward across the Atlantic, it intensified, becoming Tropical Storm Kirk on September 5.
The storm continued to strengthen, achieving hurricane status on September 7. Hurricane Kirk reached its peak intensity on September 8, with maximum sustained winds of 80 mph (130 km/h), classifying it as a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Track and Impact:
Hurricane Kirk followed a generally westward path across the Atlantic, passing south of the Cape Verde Islands on September 9. The storm then turned northward, skirting the Azores on September 13.
Despite reaching hurricane strength, Hurricane Kirk remained a relatively small and compact storm, with minimal impact on land. The storm’s primary impact was felt in the Azores, where it brought heavy rains and strong winds. However, the storm did not make landfall, avoiding any significant damage.
Forecasting Challenges and Advancements:
Hurricane Kirk presented several challenges for hurricane forecasters. The storm’s initial development was slow and uncertain, making accurate prediction difficult. Additionally, the storm’s track was somewhat erratic, particularly as it turned northward, posing a challenge for predicting its potential impact on land.
However, advancements in hurricane forecasting, including improved satellite imagery, numerical weather prediction models, and data assimilation techniques, allowed forecasters to track Hurricane Kirk with reasonable accuracy. The storm’s relatively weak intensity and its path away from major population centers minimized the potential for significant damage.
Related Searches:
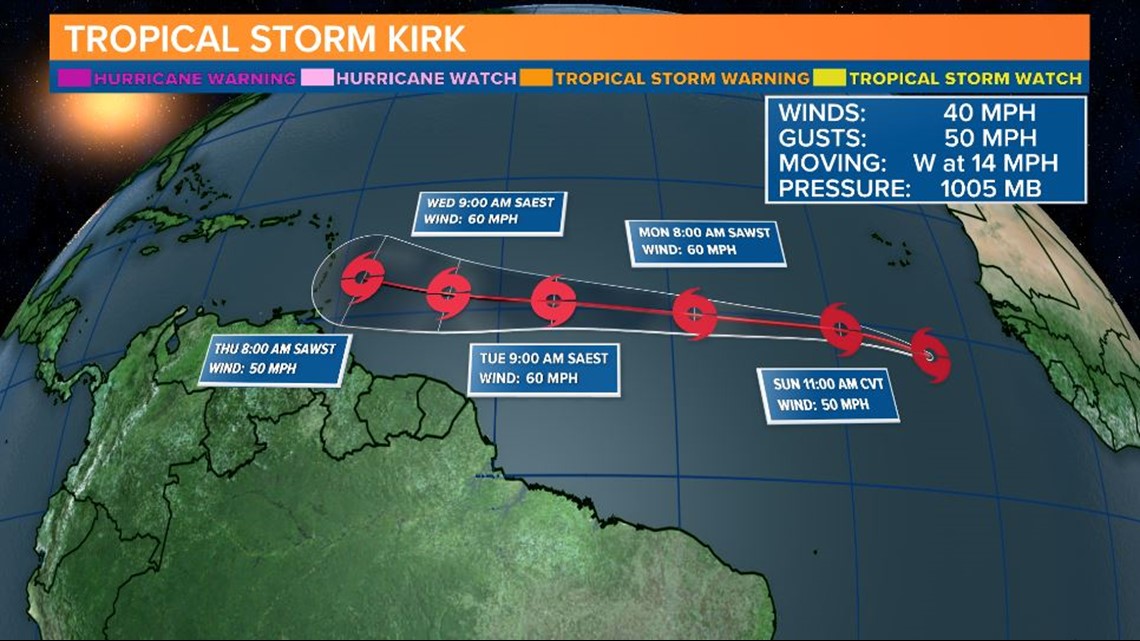
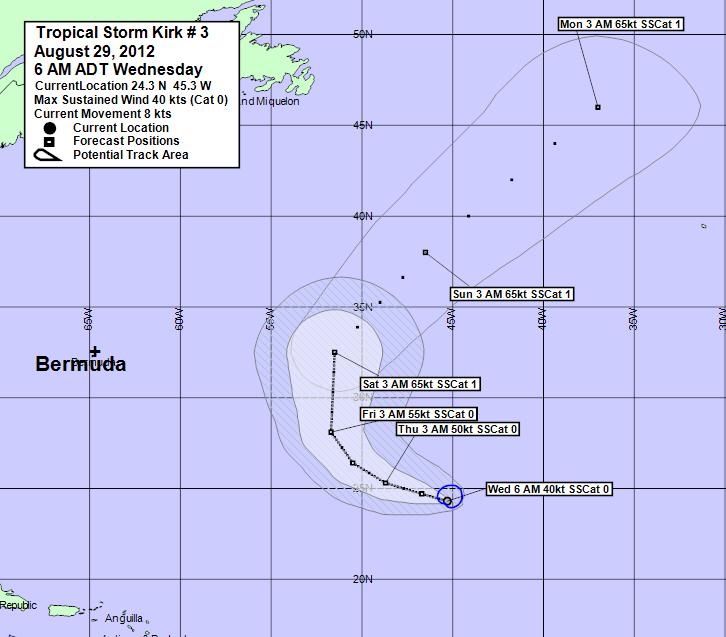
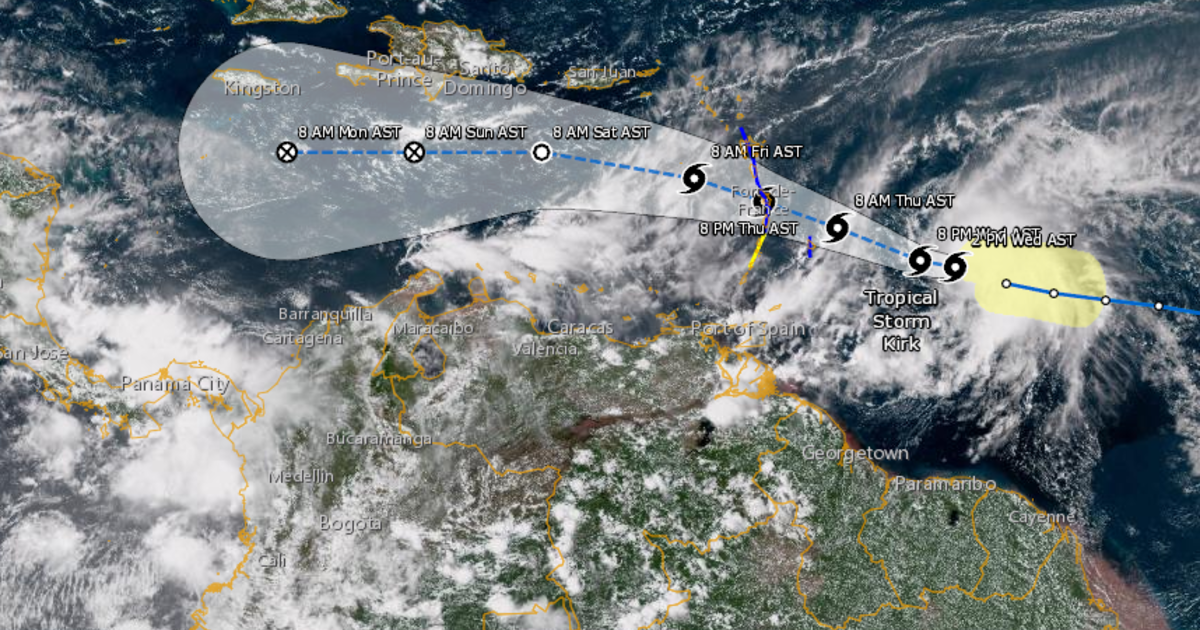
1. Hurricane Kirk Path: The track of Hurricane Kirk was characterized by its initial westward movement, followed by a northward turn. Understanding the factors influencing the storm’s path, such as steering currents and atmospheric pressure patterns, is crucial for accurate forecasting.
2. Hurricane Kirk Wind Speed: Hurricane Kirk reached a maximum sustained wind speed of 80 mph (130 km/h), making it a Category 1 hurricane. This information is critical for assessing the potential impact of the storm, particularly on coastal areas.
3. Hurricane Kirk Rainfall: The storm brought heavy rains to the Azores, but its overall rainfall impact was relatively minor. Analyzing rainfall patterns associated with Hurricane Kirk provides insights into the storm’s structure and intensity.
4. Hurricane Kirk Formation: The formation of Hurricane Kirk from a tropical wave illustrates the process of tropical cyclone development. Studying the conditions that favor formation, such as warm ocean waters and low wind shear, helps in predicting the likelihood of tropical cyclone development.
5. Hurricane Kirk Impact: Hurricane Kirk primarily impacted the Azores, bringing heavy rains and strong winds. Understanding the storm’s impact on specific locations helps in assessing the potential for damage and preparing for future storms.
6. Hurricane Kirk Track: The track of Hurricane Kirk involved a westward movement followed by a northward turn. Analyzing the factors influencing the storm’s path, such as steering currents and atmospheric pressure patterns, is crucial for accurate forecasting.
7. Hurricane Kirk Duration: Hurricane Kirk lasted for approximately 13 days, from its formation as a tropical depression to its dissipation. Studying the duration of tropical cyclones provides insights into their life cycle and intensity.
8. Hurricane Kirk Significance: While not a particularly powerful storm, Hurricane Kirk provides valuable insights into tropical cyclone development and forecasting. Understanding the challenges and advancements in hurricane prediction, as exemplified by Hurricane Kirk, is crucial for mitigating potential risks associated with these natural hazards.
FAQs about Hurricane Kirk:
1. What was the highest wind speed recorded during Hurricane Kirk?
The highest sustained wind speed recorded during Hurricane Kirk was 80 mph (130 km/h), making it a Category 1 hurricane.
2. Where did Hurricane Kirk make landfall?
Hurricane Kirk did not make landfall during its lifespan. It primarily impacted the Azores, bringing heavy rains and strong winds.
3. What was the main impact of Hurricane Kirk on the Azores?
Hurricane Kirk brought heavy rains and strong winds to the Azores, but the storm did not cause any significant damage.
4. How long did Hurricane Kirk last?
Hurricane Kirk lasted for approximately 13 days, from its formation as a tropical depression to its dissipation.
5. What were the key challenges in forecasting Hurricane Kirk?
The key challenges in forecasting Hurricane Kirk included its slow initial development, uncertain track, and relatively small size.
6. What advancements in hurricane forecasting were used to track Hurricane Kirk?
Advancements in hurricane forecasting, such as improved satellite imagery, numerical weather prediction models, and data assimilation techniques, were used to track Hurricane Kirk with reasonable accuracy.
Tips for Preparing for a Hurricane:
1. Stay informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings issued by local authorities.
2. Develop an evacuation plan: Determine safe evacuation routes and designated meeting places for your family.
3. Secure your home: Secure loose objects, board up windows, and trim trees.
4. Stock up on supplies: Gather essential items such as food, water, batteries, and first-aid supplies.
5. Stay calm and follow instructions: During a hurricane, prioritize safety and follow instructions from emergency officials.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Kirk, while not a major hurricane, serves as a valuable case study for understanding the complexities of tropical cyclone development and forecasting. The storm’s relatively slow formation, erratic track, and minimal impact highlight the challenges faced by forecasters. However, advancements in hurricane prediction, including improved technology and data analysis, allow for more accurate tracking and warnings. By understanding the intricacies of tropical cyclone behavior and utilizing the latest forecasting tools, we can better prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with these natural hazards.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Kirk: A Case Study in Tropical Cyclone Development and Forecasting. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!