Hurricane Helene: A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability
Related Articles: Hurricane Helene: A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Helene: A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Hurricane Helene: A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability
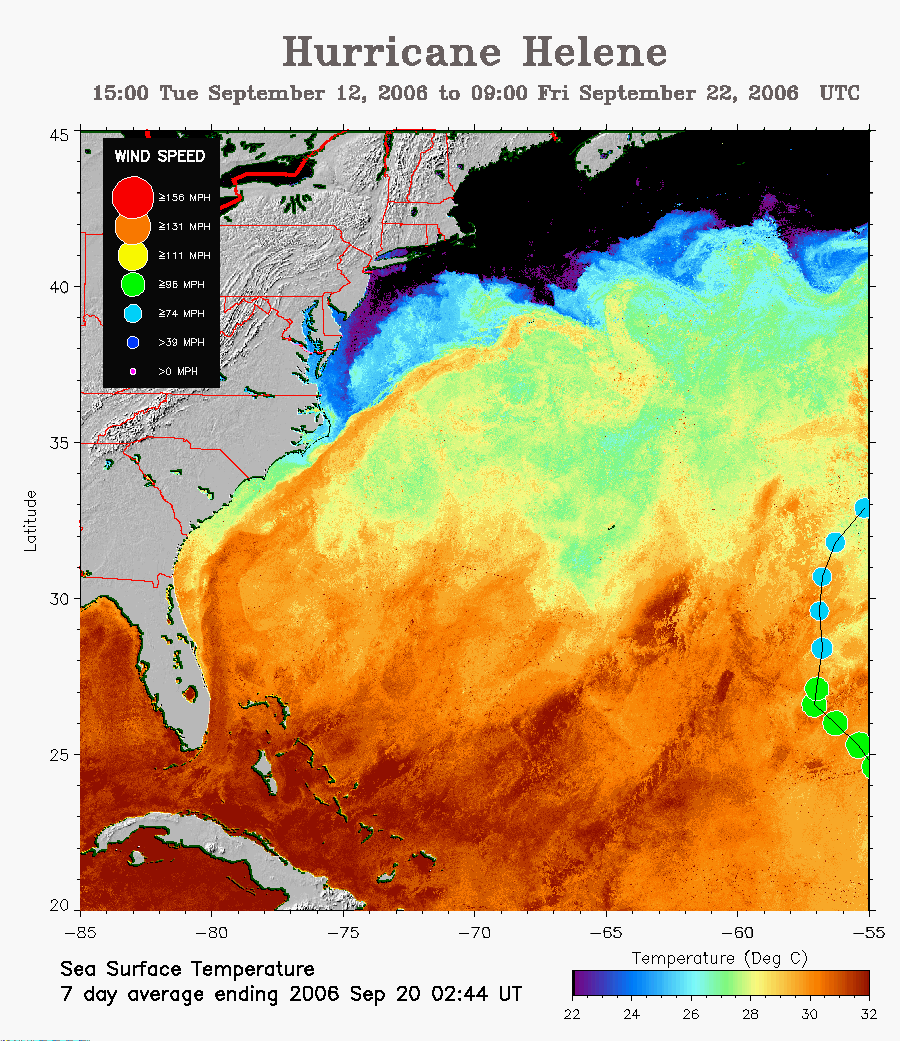
Hurricane Helene, a powerful Category 4 hurricane, traversed the Atlantic Ocean in September 2000, leaving a trail of destruction and highlighting the unpredictable nature of these powerful storms. This article delves into the genesis, development, and impact of Hurricane Helene, exploring its unique characteristics and the lessons learned from its destructive path.
Genesis and Development:
Hurricane Helene originated as a tropical wave that emerged off the coast of Africa on August 28, 2000. The wave moved westward across the tropical Atlantic, gradually organizing and intensifying. On September 1, it became a tropical depression, and by the next day, it had strengthened into Tropical Storm Helene.
The storm continued to intensify, reaching hurricane strength on September 3. It rapidly gained strength, becoming a Category 3 hurricane by September 5 and a Category 4 hurricane by September 7. This rapid intensification was fueled by exceptionally warm ocean temperatures and favorable atmospheric conditions.
Path and Impacts:
Hurricane Helene followed a somewhat unusual path, moving north-northwestward towards the Lesser Antilles. It then turned sharply westward, passing north of Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic. The storm then continued westward, approaching the southeastern United States.
Hurricane Helene caused significant damage across the Caribbean islands, particularly in Puerto Rico, where it brought heavy rains, strong winds, and coastal flooding. The storm also produced significant damage in the U.S. Virgin Islands and the Dominican Republic.
Landfall and Aftermath:
Hurricane Helene made landfall in the southeastern United States on September 10, near Charleston, South Carolina. At landfall, it had weakened to a Category 1 hurricane, but it still brought strong winds, heavy rains, and significant coastal flooding. The storm caused extensive damage to infrastructure, power lines, and trees.
The aftermath of Hurricane Helene was marked by widespread power outages, downed trees, and road closures. Recovery efforts were hampered by the extensive damage and heavy rainfall.
Key Characteristics and Lessons Learned:
Hurricane Helene was a complex and powerful storm that exhibited several unusual characteristics. These included:
- Rapid Intensification: Hurricane Helene intensified rapidly, reaching Category 4 strength in just a few days. This rapid intensification was fueled by exceptionally warm ocean temperatures and favorable atmospheric conditions.
- Unusual Path: Hurricane Helene followed an unusual path, turning sharply westward after initially moving north-northwestward. This shift in direction was influenced by a combination of factors, including the steering currents in the atmosphere and the interaction with other weather systems.
- Significant Damage: Hurricane Helene caused significant damage across the Caribbean islands and the southeastern United States. The storm’s heavy rains, strong winds, and coastal flooding resulted in widespread destruction.
The experience with Hurricane Helene highlighted the importance of:
- Improved Forecasting: The rapid intensification of Hurricane Helene underscored the need for improved hurricane forecasting models to better predict the rapid changes in storm intensity.
- Enhanced Disaster Preparedness: The extensive damage caused by Hurricane Helene emphasized the importance of robust disaster preparedness measures, including evacuation plans, emergency supplies, and community awareness programs.
- Climate Change Impacts: Hurricane Helene occurred during a period of unusually warm ocean temperatures, which contributed to its rapid intensification. The potential impact of climate change on hurricane intensity and frequency remains a critical area of research.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Helene Path: Understanding the path of Hurricane Helene provides insights into its impact and the factors that influenced its trajectory.
2. Hurricane Helene Damage: Assessing the damage caused by Hurricane Helene is crucial for understanding the storm’s impact and the subsequent recovery efforts.
3. Hurricane Helene Wind Speeds: Analyzing the wind speeds of Hurricane Helene is essential for understanding its intensity and the level of damage it caused.
4. Hurricane Helene Rainfall: Examining the rainfall associated with Hurricane Helene is crucial for evaluating its impact on flooding and water resources.
5. Hurricane Helene Storm Surge: Assessing the storm surge generated by Hurricane Helene is vital for understanding its impact on coastal areas and infrastructure.
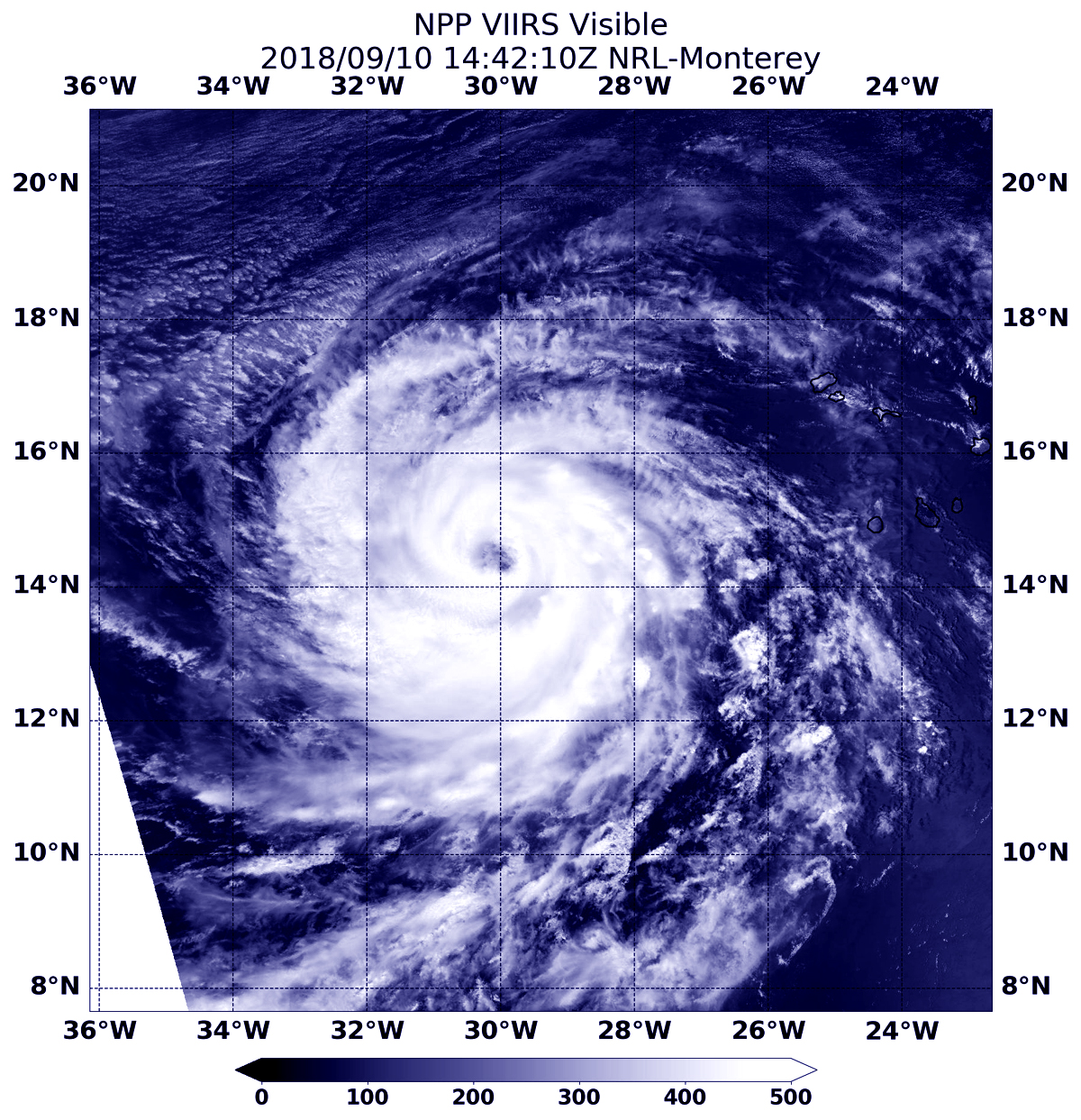
6. Hurricane Helene Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery provides a comprehensive view of Hurricane Helene’s development and movement, aiding in forecasting and understanding its impact.
7. Hurricane Helene History: Examining the historical context of Hurricane Helene allows for comparisons with other hurricanes and helps to understand its significance.
8. Hurricane Helene Impacts on Puerto Rico: Understanding the specific impact of Hurricane Helene on Puerto Rico is essential for assessing the storm’s effects on the island’s infrastructure and population.
FAQs:
Q: What was the strongest category reached by Hurricane Helene?
A: Hurricane Helene reached Category 4 strength on September 7, 2000.
Q: Where did Hurricane Helene make landfall?
A: Hurricane Helene made landfall near Charleston, South Carolina, on September 10, 2000.
Q: What were the primary impacts of Hurricane Helene?
A: Hurricane Helene caused significant damage across the Caribbean islands and the southeastern United States. Its impacts included heavy rains, strong winds, coastal flooding, power outages, downed trees, and road closures.
Q: What lessons were learned from Hurricane Helene?
A: Hurricane Helene highlighted the need for improved hurricane forecasting, enhanced disaster preparedness, and a deeper understanding of climate change’s impact on hurricane intensity and frequency.
Q: How did Hurricane Helene contribute to the understanding of hurricane variability?
A: Hurricane Helene’s rapid intensification and unusual path demonstrated the unpredictable nature of hurricanes and the need for ongoing research to improve forecasting models and disaster preparedness strategies.
Tips:
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on hurricane forecasts and warnings from reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
- Prepare for Storms: Develop a hurricane preparedness plan that includes evacuation routes, emergency supplies, and communication strategies.
- Be Aware of Risks: Understand the potential risks associated with hurricanes, including flooding, wind damage, and power outages.
- Support Recovery Efforts: Contribute to relief efforts for communities affected by hurricanes, whether through financial donations, volunteering, or providing supplies.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Helene serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of hurricanes and the importance of being prepared for these powerful storms. Its rapid intensification, unusual path, and significant impacts highlighted the need for continuous improvements in hurricane forecasting, disaster preparedness, and climate change research. By understanding the lessons learned from Hurricane Helene, we can better prepare for future hurricane events and mitigate their devastating effects.
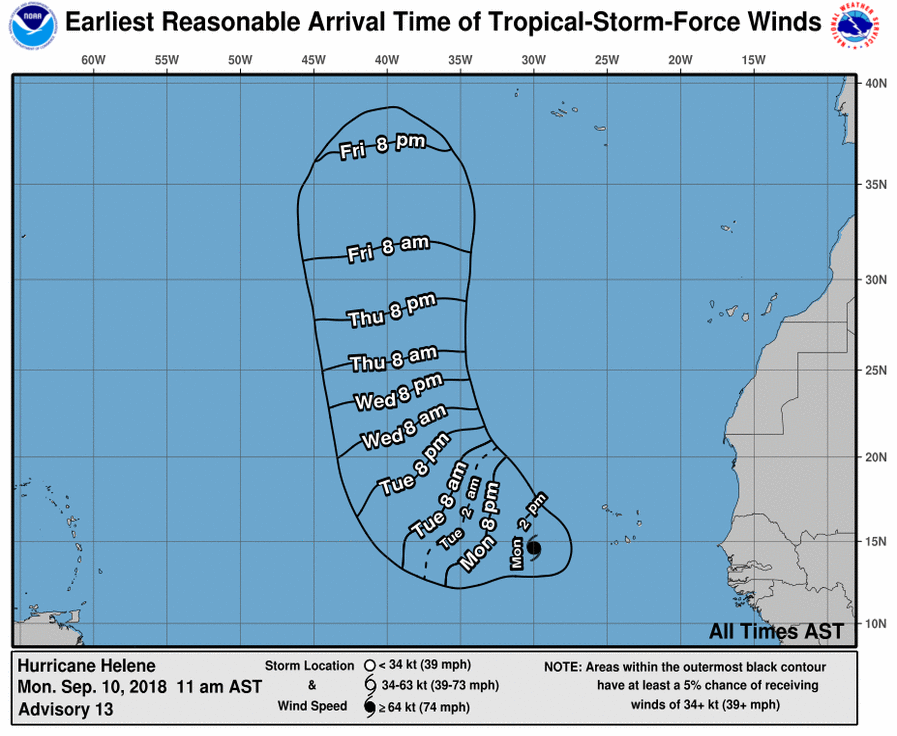



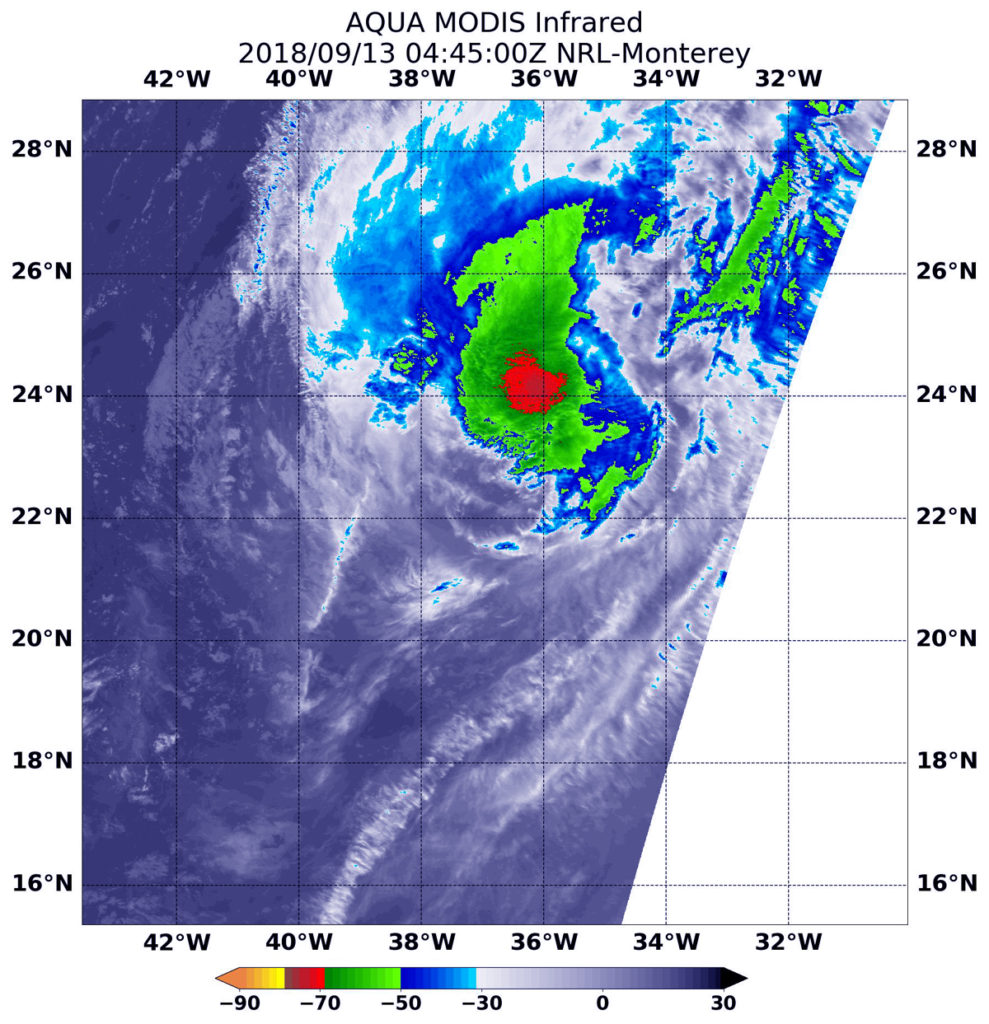
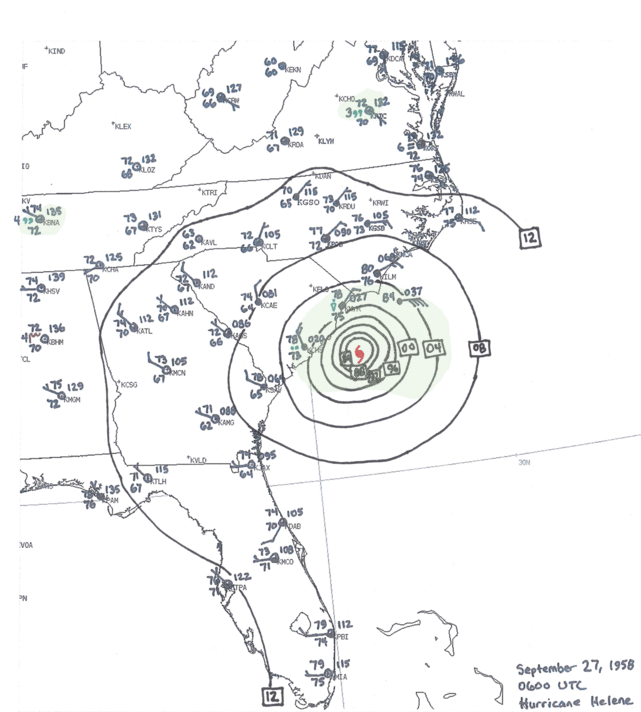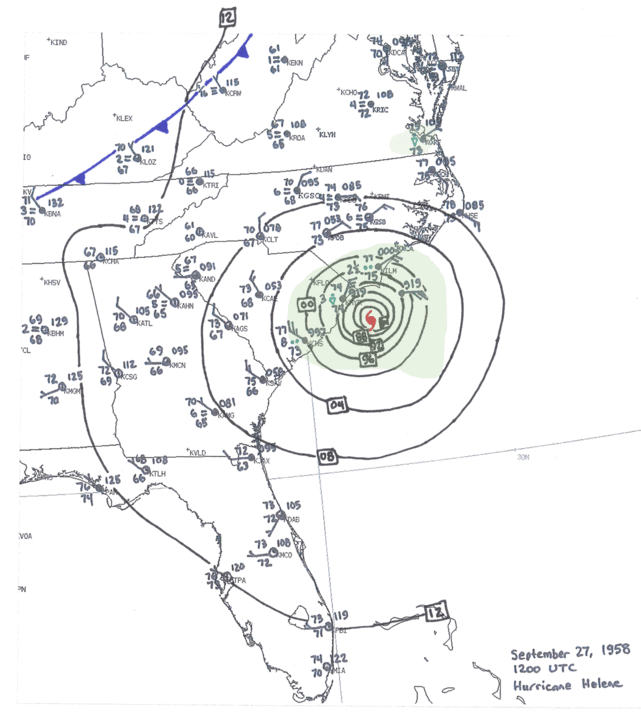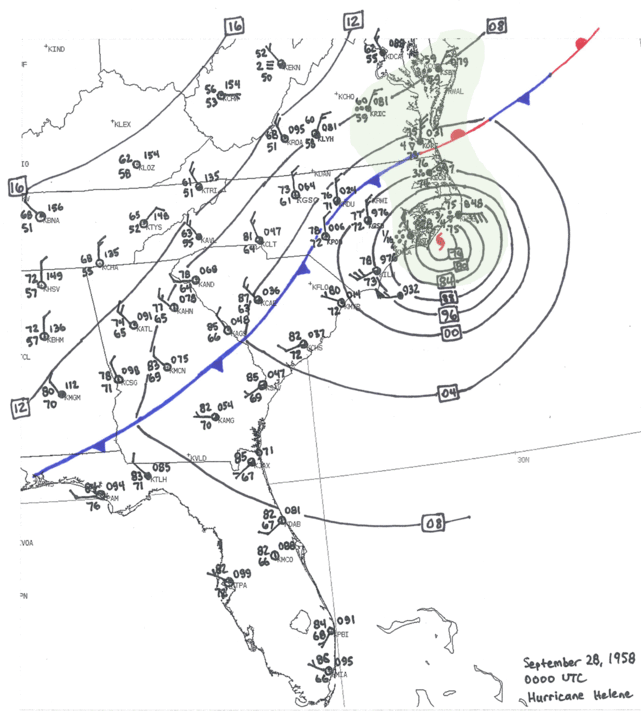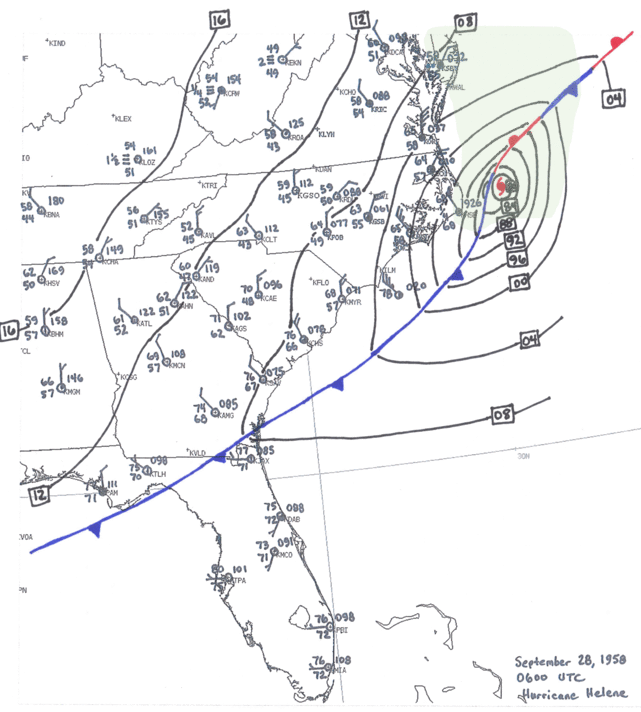

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Helene: A Case Study in Atlantic Hurricane Variability. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!