Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy
Related Articles: Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy
- 3.1 Genesis and Development: A Storm Takes Shape
- 3.2 Impact: A Widespread Threat
- 3.3 Aftermath: Lessons Learned
- 3.4 Related Searches:
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy
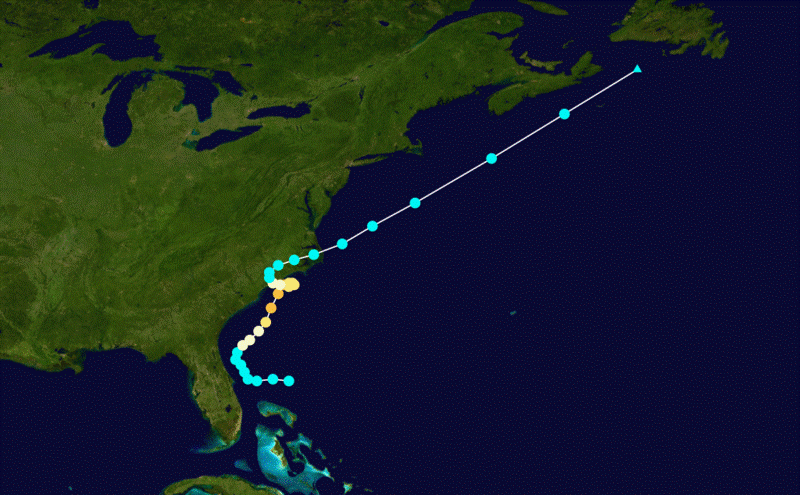
Hurricane Diana of 1984 stands as a testament to the unpredictable nature of tropical cyclones. While it was a formidable storm, its impact extended beyond the immediate destruction, leaving a lasting mark on hurricane preparedness and understanding. This article delves into the genesis, evolution, and aftermath of Hurricane Diana, exploring its significance in the context of hurricane history and forecasting.
Genesis and Development: A Storm Takes Shape
Hurricane Diana originated as a tropical wave that emerged from the African coast on August 20, 1984. It moved westward across the Atlantic, gradually intensifying. On August 24, the wave transformed into a tropical depression, earning the name "Diana." Located in the central Atlantic, the depression rapidly intensified, reaching hurricane strength just a day later.
The storm continued its westward trek, intensifying further. By August 26, Hurricane Diana had achieved Category 3 status on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, boasting maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (195 km/h). The storm’s trajectory then shifted slightly northward, bringing it into the path of the Leeward Islands.
Impact: A Widespread Threat
Hurricane Diana made landfall on the island of Antigua on August 27, 1984, as a Category 2 hurricane. The storm’s powerful winds and heavy rainfall caused significant damage to infrastructure, including power lines and homes. The island nation experienced widespread flooding, disrupting transportation and communication.
As Hurricane Diana continued its northward path, it weakened slightly, but its impact extended far beyond Antigua. The storm’s outer bands brought heavy rains to Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, and the Virgin Islands, leading to localized flooding and landslides.
Aftermath: Lessons Learned
Hurricane Diana‘s passage left a trail of devastation in its wake, prompting a reevaluation of hurricane preparedness in the Caribbean region. The storm highlighted the vulnerability of islands to powerful storms, emphasizing the need for robust infrastructure and effective disaster response mechanisms.
The storm’s path and intensity served as a reminder of the unpredictable nature of hurricanes. Its rapid intensification from a tropical depression to a Category 3 hurricane in a short span highlighted the need for constant monitoring and improved forecasting models.
Related Searches:
1. Hurricane Diana Path:
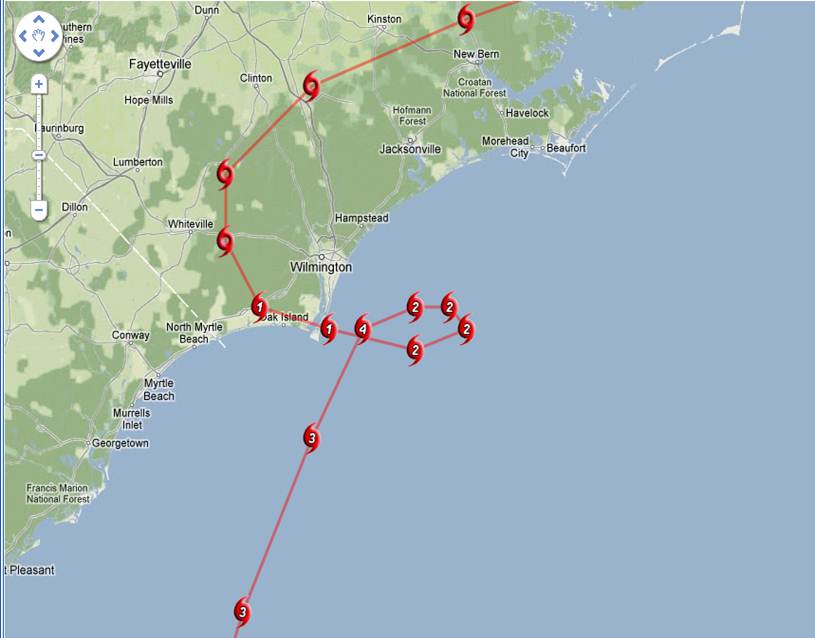
Hurricane Diana followed a relatively typical westward path across the Atlantic, but its northward shift towards the Leeward Islands made it a significant threat to the region. Its path highlights the complex dynamics of hurricane movement, influenced by atmospheric pressure gradients and steering currents.
2. Hurricane Diana Damage:
Hurricane Diana caused substantial damage in Antigua, particularly to infrastructure and homes. The storm’s impact extended to other Caribbean islands, causing flooding and landslides. The damage served as a stark reminder of the destructive power of hurricanes and the importance of preparedness.
3. Hurricane Diana Wind Speed:
Hurricane Diana reached peak wind speeds of 120 mph (195 km/h), making it a Category 3 hurricane. This level of wind intensity is capable of causing significant damage, highlighting the importance of understanding the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale and its implications.
4. Hurricane Diana Rainfall:
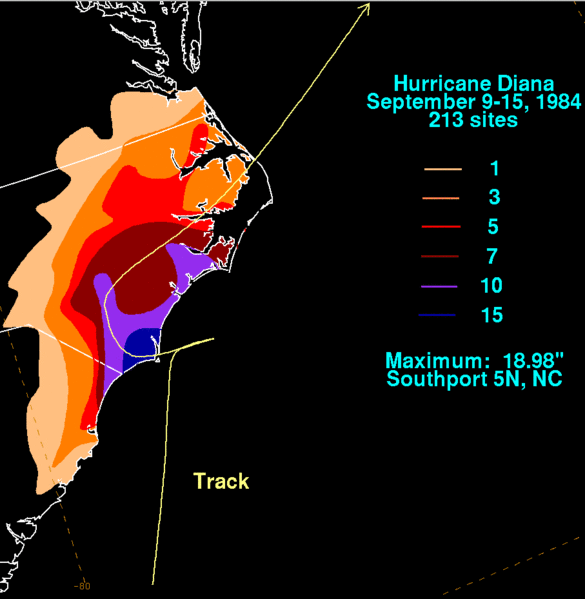
Hurricane Diana produced heavy rainfall across the Caribbean, leading to widespread flooding and landslides. The storm’s rainfall pattern emphasizes the significant impact of hurricanes on water resources and the need for effective drainage systems.
5. Hurricane Diana History:
Hurricane Diana occupies a significant place in the history of hurricanes in the Caribbean. Its impact and the lessons learned from it have contributed to improved hurricane preparedness and forecasting capabilities.
6. Hurricane Diana Statistics:
Hurricane Diana statistics, including its maximum sustained winds, central pressure, and path, provide valuable insights into the storm’s intensity and trajectory. These statistics are crucial for understanding hurricane behavior and predicting future events.
7. Hurricane Diana Forecast:
Hurricane Diana‘s trajectory and intensity were closely monitored by meteorologists using advanced forecasting models. The storm’s rapid intensification underscored the importance of accurate and timely forecasts in mitigating hurricane risks.
8. Hurricane Diana News:
News coverage of Hurricane Diana provided real-time updates on the storm’s progress and its impact on affected areas. This coverage played a crucial role in informing the public and coordinating disaster response efforts.
FAQs:
1. What was the strongest category Hurricane Diana reached?
Hurricane Diana reached Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale, with maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (195 km/h).
2. Where did Hurricane Diana make landfall?
Hurricane Diana made landfall on the island of Antigua in the Leeward Islands on August 27, 1984.
3. What were the main impacts of Hurricane Diana?
The main impacts of Hurricane Diana included significant damage to infrastructure in Antigua, widespread flooding across the Caribbean, and landslides in several island nations.
4. Did Hurricane Diana cause any deaths?
Hurricane Diana resulted in some fatalities, although the exact number is not readily available. The storm’s impact, particularly in Antigua, highlighted the need for effective disaster preparedness measures to minimize casualties.
5. What lessons were learned from Hurricane Diana?
Hurricane Diana highlighted the importance of robust infrastructure, effective disaster response mechanisms, and improved hurricane forecasting models. The storm also emphasized the need for constant monitoring of tropical cyclones and the unpredictable nature of their development.
Tips:
1. Stay Informed:
Stay informed about hurricane forecasts and warnings issued by reliable sources like the National Hurricane Center.
2. Prepare a Hurricane Kit:
Prepare an emergency kit containing essential supplies like food, water, first-aid supplies, and a weather radio.
3. Secure Your Home:
Secure your home by boarding up windows, trimming trees, and securing loose objects.
4. Have an Evacuation Plan:
Develop an evacuation plan and know where to go in case of a hurricane warning.
5. Be Prepared for Power Outages:
Stock up on batteries, flashlights, and other essential items for power outages.
Conclusion:
Hurricane Diana of 1984 serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of hurricanes. The storm’s impact on the Caribbean region underscored the importance of hurricane preparedness, effective disaster response, and continuous advancements in hurricane forecasting. By learning from the lessons of Hurricane Diana, we can better protect ourselves and our communities from the devastating effects of future hurricanes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hurricane Diana 1984: A Powerful Storm’s Legacy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!